(Press-News.org) Honeybee populations are clearly under stress--from the parasitic Varroa mite, insecticides, and a host of other factors--but it's been difficult to pinpoint any one of them as the root cause of devastating and unprecedented losses in honeybee hives. Researchers writing in the Cell Press journal Trends in Parasitology on November 24th say that the problem likely stems from a complex and poorly understood interplay of stresses and their impact on bee immunity and health. It's a situation they suspect might be improved through stress management and better honeybee nutrition.
As the bees have grown weaker with stress, they are left susceptible to diseases that the beneficial insects can normally carry without issue. That's especially problematic given that honeybees live together in such close quarters.
Honeybees live in complex societies, characterized by densely packed populations, and have evolved unique mechanisms for interacting with pathogens, explained Francesco Nazzi and Francesco Pennacchio of the Italian universities of Udine and Napoli, respectively. Some pathogens, such as the deformed wing virus, can cause asymptomatic infections that are normally kept under control by the immune system.
"These covert infections are very common all over the world and represent a kind of Damocle's sword for honeybee colonies," Nazzi said. "When bees are exposed to stress agents, which may adversely affect the immune competence, a sudden health decay can occur due to uncontrolled pathogen proliferation."
The first records of mysterious deaths of honeybee colonies were reported in the United States in 2006, followed shortly by similar reports in other countries. Systematic monitoring in Europe and the United States has shown that losses in the range of 20 to 30 percent of hives are common, and, in some places, the situation has been much worse.
The Varroa mite certainly doesn't help matters, as it sucks hemolymph (the equivalent of blood) from the insects' bodies, debilitating the bees and facilitating viral transmission. Neurotoxic insecticides like neonicotinoids, at sublethal doses, may also impair the bees' immune response and contribute to colony decline and eventual losses.
"But," Nazzi and Pennacchio say, "their importance depends on the health conditions of exposed bee populations and cannot be considered the sole factor responsible for colony losses. Looking at bee colony losses from this perspective may allow us to partly explain the multifactorial origin of this multifaceted event."
They call for more basic science to produce sound knowledge of the underlying immune responses and the molecular mechanisms that drive them. Those should be followed by tests under natural, field conditions, along with efforts to select for natural bee populations that are more resistant to those stresses. New schemes of "Integrated Stress Management" are also needed.
Honeybees might be fortified not only by helping to manage their obvious stresses--by keeping parasites in check, for example--but also by paying more attention to their diet, the researchers say.
"Beekeepers should pay extreme attention to parasite control, not only by acting directly on them, but also by enhancing the bee competence to face the challenge of environmental stress that may negatively influence immunity and health conditions," researchers said, drawing special attention to breeding for resistance and supplementary nutrition in the form of sugars, pollen, and other food sources.
INFORMATION:
Trends in Parasitology, Nazzi et al.: "Disentangling multiple interactions in the hive ecosystem"
MINNEAPOLIS, MN - November 24, 2014 - Nearly all individuals in their late 60s and early 70s -- including 100 percent of men -- now qualify for and should consider starting a statin medication to reduce their risk of cardiovascular disease, under the recently released cholesterol guidelines from the American College of Cardiology (ACC) and the American Heart Association (AHA).
That's according to a research letter published today in the 11/20/2014 (JAMA-IM) by Michael D. Miedema, MD, MPH, a research cardiologist at Minneapolis Heart Institute Foundation and cardiologist ...
The immune system is designed to remove things not normally found in the body. Cells undergoing change, e.g. precursors of cancer cells, are therefore normally recognised and removed by the immune system. Unfortunately, the different cancer cells contain mechanisms that block the immune system's ability to recognise them, allowing them to freely continue cancer development.
Certain cancer cells overexpress immunostimulatory molecules in liquid form. Such over-stimulation has a negative impact on the immune system:
"You can say that the stimulating molecules over-activate ...
The degree to which parents sacrifice themselves for their children depends on a variety of factors. On the one hand nest predators pose a threat to the young and the parent birds. But also the time of hatching plays a role. Earlier studies have shown that birds born late in the season are more likely to be protected by their parents, as the adult birds often do not have the chance to produce replacement clutches. Older offspring also tend to be protected more readily than younger ones, as much more parental care and energy have already been invested.
"Studies on the ...
Scientists have argued for half a century about the existence of a form of diamond called lonsdaleite, which is associated with impacts by meteorites and asteroids. A group of scientists based mostly at Arizona State University now show that what has been called lonsdaleite is in fact a structurally disordered form of ordinary diamond.
The scientists' report is published in Nature Communications, Nov. 20, by Péter Németh, a former ASU visiting researcher (now with the Research Centre of Natural Sciences of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences), together with ASU's ...
CORVALLIS, Ore. - If you live in lionfish territory in the Atlantic Ocean, the last thing you want to be is a small fish with a long, skinny body, resting by yourself at night, near the bottom of the seafloor.
If so, your chances of being gobbled up by a lionfish increase by about 200 times.
Findings of a study on lionfish predation behavior, which may also apply to some other fish and animal species, have shed some new light on which types of fish are most likely to face attack by this invasive predator, which has disrupted ecosystems in much of the Caribbean Sea and ...
Philadelphia, PA, November 24, 2014 - Pregnant women with diabetes are at an increased risk for many adverse birth outcomes. Preconception care (PCC) can significantly lower these risks by helping pregnant mothers with diabetes control their glucose levels, resulting in healthier babies and less money spent on complicated deliveries and lifelong medical complications. Effective, universal PCC for diabetic mothers could avert an estimated $5.5 billion in health expenditures and lost employment productivity over affected children's lifetimes, according to a new study published ...
This news release is available in German.
X-ray flashes are a unique scientific tool. They are generated by accelerating electrons to very high energy levels in kilometer-long vacuum tubes, so-called linear accelerators, and then deflecting them with specially arranged magnets. In the process the particles emit X-ray radiation that is amplified until an ultra-short and intensive X-ray flash is released.
Researchers use these X-ray flashes to resolve structures as small as one ten billionth of a meter (0.1 nanometer) in size. That is roughly the diameter of a ...
LA JOLLA, CA--November 24, 2014--A team led by scientists from The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) has found a simple method to convert human skin cells into the specialized neurons that detect pain, itch, touch and other bodily sensations. These neurons are also affected by spinal cord injury and involved in Friedreich's ataxia, a devastating and currently incurable neurodegenerative disease that largely strikes children.
The discovery allows this broad class of human neurons and their sensory mechanisms to be studied relatively easily in the laboratory. The "induced ...
ANN ARBOR--Our bones are smart. Bones know that by adolescence it's time to stop growing longer and stronger, and from that point on bones keep their shape by healing injuries.
This question of why bones grow longer and stronger in children, but stay static in adults--yet retain the ability to heal themselves, has long perplexed scientists in the bone regeneration field. But researchers from the University of Michigan, Kyoto University and Harvard University believe they may have unearthed a big piece of this puzzle.
The team discovered that a certain subset of cartilage-making ...
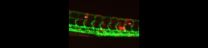
VIDEO:
When zebrafish are infected with bright blue Mycobacterium marinum, bright red immune cells quickly surround the bacteria to form tightly organized nuggets called granulomas (vessels green, bacteria blue, immune cells...
Click here for more information.
DURHAM, N.C. -- The body responds to tuberculosis infection by locking the bacterial offenders into tiny clusters of immune cells called granulomas, which are a hallmark of the disease. This containment strategy succeeds ...