(Press-News.org) Australian average incomes are falling with the country's population growth "masking underlying economic weakness", according to a QUT economist.
Dr Mark McGovern, a senior lecturer in QUT's Business School, said while it was regularly proclaimed Australia had experienced positive economic growth for more than 20 years, there had been periodic per capita declines, indicating the economy was not as healthy as assumed.
"Looking at national income figures in recent years shows our economy is under stress," Dr McGovern, whose research was recently published in the Economic Analysis and Policy journal, said.
"For example, according to Australian Bureau of Statistics figures, Gross Domestic Product (GDP) per capita peaked in the June 2008 quarter, fell for three periods then took six further quarters to revisit the 2008 high in the September 2010 quarter.
"But if you look at Real net National Disposable Incomes per capita, which is how much money people are receiving, the 2011 December quarter income peak was at $13,406 with $13,156 estimated for June 2014. This is a per capita income drop of $250, or two per cent over ten quarters.
"The overall GDP has continued to increase slightly, but that is the result of population growth, which is masking underlying economic weakness."
Dr McGovern said GDP was growing while national incomes were falling because investment earnings were flowing out of the country to overseas investors.
"Australian GDP does not fully accrue to Australians due to this net outflow of money," he said.
"If these funds continue to leave the country, we could suffer the same financial fate as Ireland and others, where incomes fell despite GDP increasing.
"The Celtic Tiger prided itself on attracting foreign investors who inflated asset values, paid little tax and then left insolvent banks and depressed incomes across the nation."
More immediately, Dr McGovern said the drop in disposable income per capita helped explain why the Federal Government's budget had been badly received by many in the population.
"People rejected the budget and the calls for belt-tightening and there is a general financial ill-ease evident within Australians," he said.
"While the Federal Government is preoccupied with servicing the modest government debt, households are receiving falling incomes to service their own greater debts. All are struggling to make ends meet, and the income drain to overseas only makes things more difficult.
"All will be much worse off if this depressive synchronisation is allowed to continue. Actions need to be taken to rebalance household and government balance sheets, as well as those of some businesses. Interest rates are increasingly unserviceable so they must be further reduced.
"Recognition of problems allows them to be addressed sensibly so we need to refresh public and commercial policies so that the preoccupations of some do not undermine the interests of all.
"There are good ways forward and we need to understand and adopt them."
INFORMATION:
Few agribusinesses or governments regulate the types of plants that farmers use in their pastures to feed their livestock, according to an international team of researchers that includes one plant scientist from Virginia Tech.
The problem is most of these so-called pasture plants are invasive weeds.
In a Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences study this month, the scientists recommended tighter regulations, including a fee for damage to surrounding areas, evaluation of weed risk to the environment, a list of prohibited species based on this risk, and closer ...
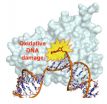
Using a new imaging technique, National Institutes of Health researchers have found that the biological machinery that builds DNA can insert molecules into the DNA strand that are damaged as a result of environmental exposures. These damaged molecules trigger cell death that produces some human diseases, according to the researchers. The work, appearing online Nov. 17 in the journal Nature, provides a possible explanation for how one type of DNA damage may lead to cancer, diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular and lung disease, and Alzheimer's disease.
Time-lapse crystallography ...
PHILADELPHIA (Nov. 25, 2014) - As the linked epidemics of obesity and diabetes continue to escalate, a staggering one in five U.S. adults is projected to have diabetes by 2050.
Ground zero for identifying ways to slow and stop that rise is Philadelphia, which has the highest diabetes rate among the nation's largest cities. For public health researchers at Drexel University, it is also a prime location to learn how neighborhood and community-level factors -- not just individual factors like diet, exercise and education-- influence people's risk.
A new Drexel study published ...
PITTSBURGH, Nov. 24, 2014 -Barriers to the sharing of public health data hamper decision-making efforts on local, national and global levels, and stymie attempts to contain emerging global health threats, an international team led by the University of Pittsburgh Graduate School of Public Health announced today.
The analysis, published in the journal BMC Public Health and funded by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation and the National Institutes of Health (NIH), classifies and examines the barriers in order to open a focused international dialogue on solutions.
"Data on ...
The proper regulation of body size is of fundamental importance, but the mechanisms that stop growth are still unclear. In a study now published in the scientific journal eLife*, a research group from Instituto Gulbenkian de Ciência (IGC), led by Christen Mirth, shed new light on how animals regulate body size. The researchers uncovered important clues about the molecular mechanisms triggered by environmental conditions that ultimately affect final body size. They show that the timing of synthesis of a steroid hormone called ecdysone is sensitive to nutrition in the ...
People's views on income inequality and wealth distribution may have little to do with how much money they have in the bank and a lot to do with how wealthy they feel in comparison to their friends and neighbors, according to new findings published in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science.
"Our research shows that subjective feelings of wealth or poverty motivate people's attitudes toward redistribution, quite independently of objective self-interest," says psychological scientist and study co-author Keith Payne of the University ...
WASHINGTON, Nov. 25, 2014 -- Your beer may attract annoying fruit flies, but listen up before you give them a swat. Researchers found the yeast cells in beer are producing odor compounds -- acetate esters -- that lure flies and that could lead to the best beer you haven't even tasted yet. This week's Speaking of Chemistry explains why. Check it out at http://youtu.be/HQNlGuZvCvA.
Speaking of Chemistry is a production of Chemical & Engineering News, a weekly magazine of the American Chemical Society. The program features fascinating, weird and otherwise interesting chemistry ...
Bitcoin is the new money: minted and exchanged on the Internet. Faster and cheaper than a bank, the service is attracting attention from all over the world. But a big question remains: are the transactions really anonymous? Several research groups worldwide have shown that it is possible to find out which transactions belong together, even if the client uses different pseudonyms. However it was not clear if it is also possible to reveal the IP address behind each transaction. This has changed: researchers at the University of Luxembourg have now demonstrated how this is ...
The study at Sahlgrenska Academy, University of Gothenburg, was based on the Swedish National Epilepsy Surgery Register, which includes all cases since 1990. The researchers reviewed data for the 865 patients who were operated on at Sweden's six epilepsy surgery clinics from 1996 to 2010.
The purpose of surgery is to enable a person with severe epilepsy to be free of seizures or to reduce their frequency to the point that (s)he can enjoy better quality of life.
Downward trend
Only 3% (25) of the patients suffered lasting complications. A comparison with a previous ...
Researchers at KU Leuven's Centre for Surface Chemistry and Catalysis have successfully converted sawdust into building blocks for gasoline. Using a new chemical process, they were able to convert the cellulose in sawdust into hydrocarbon chains. These hydrocarbons can be used as an additive in gasoline, or as a component in plastics. The researchers reported their findings in the journal Energy & Environmental Science.
Cellulose is the main substance in plant matter and is present in all non-edible plant parts of wood, straw, grass, cotton and old paper. "At the molecular ...