(Press-News.org) LOS ANGELES - November 26, 2014 - Work supported by the Stand Up To Cancer (SU2C) - Cancer Research Institute (CRI) - Immunology Translational Research Dream Team, launched in 2012 to focus on how the patient's own immune system can be harnessed to treat some cancers have pioneered an approach to predict why advanced melanoma patients respond to a new life-saving melanoma drug. This new drug, pembrolizumab (Keytruda), was recently approved by the FDA. These findings are reported in Nature online November 26, 2014, ahead of print in the journal.
Over a two-year study, researchers including Dr. Antoni Ribas of UCLA Jonsson Cancer Center and co-leader of the CRI-SU2C Immunology Dream studied 46 patients with advanced melanoma treated with pembrolizumab. These patients had tumor biopsies before and during treatment. The researchers analyzed those biopsies and classified them according to whether the patient responded or not to pembrolizumab. The study then used the biopsy findings to predict the likelihood whether patients would likely to respond to this treatment
According to the press release issued by UCLA Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center, a protein known as PD-1 puts the immune system's brakes on, preventing T cells from attacking cancer cells. Pembrolizumab removes the brake lines, freeing up the immune system to kill cancer cells. Keytruda was the first PD-1 immunotherapy drug approved by the FDA in September 2014.
"The work of Dr. Ribas, his colleagues and the SU2C-CRI Immunology Dream Team is so important, bringing tangible benefits to patients struggling with advanced melanoma and providing the means to assess why some patients are responsive to this breakthrough drug," said Phillip A. Sharp, Ph.D., chairperson SU2C Scientific Advisory Committee, and MIT Koch Institute for Integrative Cancer Research, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge. "Not only has this research validated a pathway to determine which patients may be responsive to pembrolizumab, we anticipate it will significantly inform development of better drug combinations that are more effective, less costly and with fewer side effects for even more patients with melanoma and other cancers."
INFORMATION:
In addition to support from Stand Up to Cancer, this research was supported by the National Institute of Health and the UCLA Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center through philanthropy and other sources.
Media Contacts
SU2C
Jane Rubinstein
646-386-7969
jrubinstein@eifoundation.org
About Stand Up To Cancer
Stand Up To Cancer (SU2C) raises funds to accelerate the pace of research to get new therapies to patients quickly and save lives now. SU2C, a program of the Entertainment Industry Foundation (EIF), a 501(c)(3) charitable organization, was established in 2008 by film and media leaders who utilize the industry's resources to engage the public in supporting a new, collaborative model of cancer research, and to increase awareness about progress being made in the fight against the disease. As SU2C's scientific partner, the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) and a Scientific Advisory Committee led by Nobel Laureate Phillip A. Sharp, PhD, conduct rigorous, competitive review processes to identify the best research proposals to recommend for funding, oversee grants administration, and provide expert review of research progress.
Current members of the SU2C Council of Founders and Advisors (CFA) include Katie Couric, Sherry Lansing, Kathleen Lobb, Lisa Paulsen, Rusty Robertson, Sue Schwartz, Pamela Oas Williams, and Ellen Ziffren. All current members of the CFA were co-producers of the 2012 and 2014 televised specials. The late co-founder Laura Ziskin executive produced both the Sept. 5, 2008, and Sept. 10, 2010, broadcasts. SU2C was formally launched on May 27, 2008. Sung Poblete, PhD, RN, has served as SU2C's president and CEO since 2011.
For more information on Stand Up To Cancer visit http://www.standup2cancer.org.
High above Earth's atmosphere, electrons whiz past at close to the speed of light. Such ultrarelativistic electrons, which make up the outer band of the Van Allen radiation belt, can streak around the planet in a mere five minutes, bombarding anything in their path. Exposure to such high-energy radiation can wreak havoc on satellite electronics, and pose serious health risks to astronauts.
Now researchers at MIT, the University of Colorado, and elsewhere have found there's a hard limit to how close ultrarelativistic electrons can get to the Earth. The team found that ...
CORVALLIS, Ore. - The use of renewable energy in the United States could take a significant leap forward with improved storage technologies or more efforts to "match" different forms of alternative energy systems that provide an overall more steady flow of electricity, researchers say in a new report.
Historically, a major drawback to the use and cost-effectiveness of alternative energy systems has been that they are too variable - if the wind doesn't blow or the sun doesn't shine, a completely different energy system has to be available to pick up the slack. This lack ...
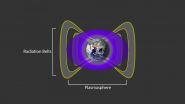
Two donuts of seething radiation that surround Earth, called the Van Allen radiation belts, have been found to contain a nearly impenetrable barrier that prevents the fastest, most energetic electrons from reaching Earth.
The Van Allen belts are a collection of charged particles, gathered in place by Earth's magnetic field. They can wax and wane in response to incoming energy from the sun, sometimes swelling up enough to expose satellites in low-Earth orbit to damaging radiation. The discovery of the drain that acts as a barrier within the belts was made using NASA's ...
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] -- A new study led by Brown University reports that older learners retained the mental flexibility needed to learn a visual perception task but were not as good as younger people at filtering out irrelevant information.
The findings undermine the conventional wisdom that the brains of older people lack flexibility, or "plasticity," but highlight a different reason why learning may become more difficult as people age: They learn more than they need to. Researchers call this the "plasticity and stability dilemma." The new study suggests ...
VIDEO:
When people hear another person talking to them, they respond not only to what is being said -- those consonants and vowels strung together into words and sentences --but also...
Click here for more information.
When people hear another person talking to them, they respond not only to what is being said--those consonants and vowels strung together into words and sentences--but also to other features of that speech--the emotional tone and the speaker's gender, for instance. ...
Older people can actually take in and learn from visual information more readily than younger people do, according to new evidence reported in the Cell Press journal Current Biology on November 26. This surprising discovery is explained by an apparent decline with age in the ability to filter out irrelevant information.
"It is quite counterintuitive that there is a case in which older individuals learn more than younger individuals," says Takeo Watanabe of Brown University.
Older individuals take in more at the same time as the stability of their visual perceptual ...
Enzymes inside cells that normally repair damaged DNA sometimes wreck it instead, researchers at the Stanford University School of Medicine have found. The insight could lead to a better understanding of the causes of some types of cancer and neurodegenerative disease.
In a paper to be published online Nov. 27 in Molecular Cell, the researchers explain how the recently discovered mechanism of DNA damage occurs when genetic transcripts, composed of RNA, stick to the DNA instead of detaching from it.
Certain enzymes, called endonucleases, are attracted to DNA/RNA hybrids ...
Researchers at the Center for iPS Cell Research and Application (CiRA), Kyoto University, show that induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells can be used to correct genetic mutations that cause Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD). The research, published in Stem Cell Reports, demonstrates how engineered nucleases, such as TALEN and CRISPR, can be used to edit the genome of iPS cells generated from the skin cells of a DMD patient. The cells were then differentiated into skeletal muscles, in which the mutation responsible for DMD had disappeared.
DMD is a severe muscular degenerative ...
Mutations in the KRAS gene have long been known to cause cancer, and about one third of solid tumors have KRAS mutations or mutations in the KRAS pathway. KRAS promotes cancer formation not only by driving cell growth and division, but also by turning off protective tumor suppressor genes, which normally limit uncontrolled cell growth and cause damaged cells to self-destruct.
A new University of Iowa study provided a deeper understanding of how KRAS turns off tumor suppressor genes and identifies a key enzyme in the process. The findings, published online Nov. 26 in the ...
SALT LAKE CITY--Researchers from Huntsman Cancer Institute (HCI) at the University of Utah (U of U) discovered the unusual role of lactate in the metabolism of alveolar soft part sarcoma (ASPS), a rare, aggressive cancer that primarily affects adolescents and young adults. The study also confirmed that a fusion gene is the cancer-causing agent in this disease. The research results were published online in the journal Cancer Cell Nov. 26, 2014.
ASPS tumor cells contain a chromosomal translocation--strands of DNA from two chromosomes trade places. The two strands fuse ...