(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON - In certain circumstances, women may be more effective than men when negotiating money matters, contrary to conventional wisdom that men drive a harder bargain in financial affairs, according to a new meta-analysis published by the American Psychological Association.
"One reason men earn higher salaries than women could be women's apparent disadvantage vis-à-vis men in some types of negotiations," said lead author Jens Mazei, a doctoral candidate at Germany's University of Münster. "But we discovered that this disadvantage is not inevitable; rather, it very much depends on the context of the negotiation."
Researchers examined 51 studies from several countries, including the U.S., The Netherlands, Germany, India and China, with a total of 10,888 participants, of whom 4,656 were women and 6,232 were men. The samples included business people as well as graduate and undergraduate students. The researchers found that negotiation results depended on the situation and the person involved. When women negotiated on behalf of another person, when they knew about the bargaining range in the negotiations and when they had experience in negotiating, they were better at negotiating than men, according to the study, which was published in APA's Psychological Bulletin.
Society's beliefs about gender roles may be at the root of men's advantage in some negotiations, the authors wrote. Previous research has found that gender roles reflect certain expectations of men's and women's behavior. Male gender role characteristics include behaving in competitive, assertive or profit-oriented ways, whereas the traditional female gender role has communal characteristics, such as being relationship-oriented, accommodating and concerned with the welfare of others.
"Women in negotiations might feel social pressure to adhere to the female role and display gender-consistent behavior such as accommodation or cooperation," the study said. When women behave in a manner not consistent with society's expectations, they have historically risked backlash and disapproval, the authors noted.
"Our analysis suggests ways to lessen or even reverse gender differences in negotiations favoring men," said co-lead author Joachim Hüffmeier, PhD, of the Federal Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, Dortmund, Germany. "It looks as though gender roles no longer give men a bargaining advantage if women are trained in negotiation, have information about the bargaining range and if they are negotiating for other individuals."
The analysis looked exclusively at research that had compared and reported final economic negotiation outcomes achieved by women and men in actual negotiations. Examples included negotiating for an increase in one's own salary and negotiating a financial interest on behalf of a client, friend or on behalf of an organization or company. While women performed better when negotiating on behalf of another individual, such was not the case when they negotiated on behalf of themselves or on behalf of a large organization, according to the study. "It remains to be seen if this effect would hold when negotiating for smaller social entities, such as a team, workgroup or family," the authors wrote.
INFORMATION:
Article: "A Meta-Analysis on Gender Differences in Negotiation Outcomes and Their Moderators," Jens Mazei, Dipl-Psych, University of Münster, Germany; Joachim Hüffmeier, PhD, Federal Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, Dortmund, Germany; Philipp Alexander Freund, PhD, Leuphana University at Lüneburg, Germany; Alice F. Stuhlmacher, PhD, DePaul University; Lena Bilke; Dipl-Psych, University of Münster, Germany; Guido Hertel, PhD, University of Münster, Germany; online Nov. 24; Psychological Bulletin.
Full text of the article is available from the APA Public Affairs Office and at
http://www.apa.org/pubs/journals/releases/bul-a0038184.pdf.
Contact: Jens Mazei at jens.mazei@wwu.de, +492518339445 or Joachim Hüffmeier at hueffmeier@uni-muenster.de, +492517480670.
The American Psychological Association, in Washington, D.C., is the largest scientific and professional organization representing psychology in the United States. APA's membership includes nearly 130,000 researchers, educators, clinicians, consultants and students. Through its divisions in 54 subfields of psychology and affiliations with 60 state, territorial and Canadian provincial associations, APA works to advance the creation, communication and application of psychological knowledge to benefit society and improve people's lives.
http://www.apa.org
EAST LANSING, Mich. --- Scientists have presented the most comprehensive evidence to date that climate extremes such as droughts and record temperatures are failing to change people's minds about global warming.
Instead, political orientation is the most influential factor in shaping perceptions about climate change, both in the short-term and long-term, said Sandra Marquart-Pyatt, a Michigan State University sociologist and lead investigator on the study.
"The idea that shifting climate patterns are influencing perceptions in the United States - we didn't find that," ...
It is said to represent a "cosmic constant" found in the curvature of elephant tusks, the shape of a kudu's horn, the destructive beauty of Hurricane Katrina, and in the astronomical grandeur of how planets, moons, asteroids and rings are distributed in the solar system, to name but a few.
Now, researchers from the Universities of the Witwatersrand and Pretoria are also suggesting that the "Golden Ratio" - designated by the Greek symbol ∅ (letter Phi) with a mathematical value of about 1.618 - also relates to the topology of space-time, and to a biological species ...
Thanks to the more than 11,200 sightings of cetaceans over the course of ten years, Spanish and Portuguese researchers have been able to identify, in detail, the presence of orcas in the Gulf of Cadiz, the Strait of Gibraltar and the Alboran Sea. According to the models that have been generated, the occurrence of these cetaceans is linked to the distribution of their main prey (red tuna) and their presence in Spanish, Portuguese and Moroccan waters is thus more limited than previously thought.
In 2011, the Spanish Ministry of the Environment considered the small population ...
The report was presented in Brussels today at an event held under the auspices of the Italian EU Presidency, gathering over sixty experts in the fields of nuclear physics and medical research.
This document provides an updated overview of how fundamental nuclear physics research has had and will continue to have an impact on developments in medicine.
While most nuclear physics phenomena are far beyond our daily experience there is a great variety of related techniques and applications such as those in medicine which have considerable impact on society. The development ...
The negative impact of contractions during in vitro fertilisation is a well-known fact. What was unknown until now was the effect it had on artificial insemination. A new study has discovered that it is the contrary to that seen in embryo transfer: there is an improved chance of getting pregnant.
Researchers from the Valencian Infertility Institute (IVI) have demonstrated that the number of contractions of the uterus per minute is a parameter associated with success in artificial insemination procedures.
The study, recently published in the journal 'Fertility & Sterility', ...
BERKELEY -- Greater income inequality is linked to more deaths among African Americans, but the effect is reversed among white Americans, who experienced fewer deaths, according to a new study by researchers at the University of California, Berkeley.
The study, published in the fall 2014 issue of the International Journal of Health Services, highlights stark racial differences in the effects of the widening gap between the rich and poor. The United States has one of the largest gaps between rich and poor among developed nations. According to a report from the nonpartisan ...
In a new register study in the scientific journal BMJ, researchers at Karolinska Institutet are able to dismiss previous claims that there is a link between the increased use of antibiotics in society and a coinciding rise in childhood asthma. The study includes half a million children and shows that exposure to antibiotics during pregnancy or early in life does not appear to increase the risk of asthma.
Several previous studies have shown that if the mother is given antibiotics during pregnancy or if a small child is given antibiotics in early life, the child has an ...
CHICAGO - Researchers are using computed tomography (CT) and 3-D printing technology to recreate life-size models of patients' heads to assist in face transplantation surgery, according to a study presented today at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Physicians at Brigham and Women's Hospital in Boston performed the country's first full-face transplantation in 2011 and have subsequently completed four additional face transplants. The procedure is performed on patients who have lost some or all of their face as a result of injury or ...
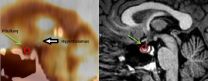
CHICAGO - Hybrid imaging with positron emission tomography and computed tomography (PET/CT) in the pituitary region of the brain is a promising tool for differentiating military veterans with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) from those with mild traumatic brain injury (MTBI), according to a new study presented at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
The findings also lend support to the theory that many veterans diagnosed with PTSD may actually have hormonal irregularities due to pituitary gland damage from blast injury.
MTBI ...
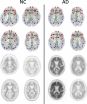
CHICAGO - Changes in brain connections visible on MRI could represent an imaging biomarker of Alzheimer's disease, according to a new study presented today at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Alzheimer's disease is the most common form of dementia. As many as 5 million Americans are affected, a number expected to grow to 14 million by 2050, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Preventive treatments may be most effective before Alzheimer's disease is diagnosed, such as when a person is suffering from mild ...