Mass extinction led to many new species of bony fish
2014-12-01
(Press-News.org) Today, ray-finned fish, which belong to the bony fish, are by far the most biodiverse fish group in both salt- and freshwater. Their spectacular variety of forms ranges from eels, tuna, flounders and angler fish all the way to seahorses. With around 1,100 species, the second most biodiverse group is the cartilaginous fish, which are almost exclusively marine and include sharks, rays and chimaeras. Exactly why bony fish managed to prevail in different habitats is the subject of debate: Do they have a better body plan, which is suited to more ecological niches than that of the cartilaginous fish? Or are other factors involved in their successful distribution? Paleontologists from the University of Zurich now reveal that climate catastrophes in the past played a crucial role in the dominance of ray-finned fish today.
Cartilaginous fish greatly depleted by extinction events
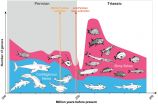
The scientists studied the changes in biodiversity among cartilaginous and bony fish during the Permian and Triassic periods around 300 to 200 million years ago - an interval marked by several serious extinction events. They evaluated the global scientific literature on bony and cartilaginous fish from the last 200 years and collected data on diversity and body size, the latter providing an indication of the fish's position in the food chains in the seas and freshwater.
Based on the data evaluated, the researchers demonstrate that cartilaginous fish, the most biodiverse fish group at the time, especially suffered heavily during an extinction event in the Middle Permian epoch while the Permian ray-finned fish escaped relatively unscathed. After an even bigger mass extinction close to the Permian-Triassic boundary, which wiped out 96 percent of all sea organisms, these bony fish diversified heavily. Of the ray-finned fish, the so-called Neopterygii ("new fins") became particular biodiverse during the Triassic and, with over 30,000 species, today constitute the largest vertebrate group. Triassic Neopterygii primarily developed small species while the majority of the more basal ray-fins produced large predatory fish. Moreover, many bony fish developed morphological specializations in the Triassic, such as in the jaw apparatus, dentition or fins. This enabled new ways of locomotion, including gliding over the surface of the water, much like flying fish do today. Moreover, there is also evidence for viviparity in Triassic bony fish, for the first time ever.
Extinction events correlate with climate changes
Unlike bony fish, cartilaginous fish, which had already been heavily decimated by the end of the Permian, did not really recover. Many groups that were still biodiverse in the Permian disappeared completely or became extremely rare during the extinction events of the Permian and the Triassic. "Our results indicate that repeated extinction events played a key role in the development of today's fish fauna," explains Carlo Romano, a postdoc at the University of Zurich's Paleontological Institute and Museum. Most of these severe crises are linked to massive volcanic activity, global climate changes and sea level lowstands.
INFORMATION:
Literature:
C. Romano, M. B. Koot, I. Kogan, A. Brayard, A. V. Minikh, W. Brinkmann, H. Bucher, J. Kriwet, Permian-Triassic Osteichthyes (bony fishes). Diversity dynamics and body size evolution. Biological Reviews, November 28, 2014. S. 1-44. doi: 10.1111/brv.12161.
Contacts:
Dr. Carlo Romano
Paleontological Institute and Museum
University of Zurich
Tel: +41 44 634 23 47
Email: carlo.romano@pim.uzh.ch
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-12-01
A study from the University of Exeter has found that male flies die earlier than their female counterparts when forced to evolve with the pressures of mate competition and juvenile survival. The results could help researchers understand the mechanisms involved in ageing.
The research, published in the journal Functional Ecology, used populations of the fly Drosophila simulans that had evolved under different selection regimes. The study shows that mate competition (sexual selection), along with survival (natural selection), is tougher on male ageing than it is on females ...
2014-12-01
Washington, DC, December 1, 2014 - Little is known about the often fatal virus known as Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV), but researchers have identified gaps in infection control as a major culprit in all eleven published cases involving healthcare-associated transmission of the virus. The full findings of the review can be found in the December issue of the American Journal of Infection Control, the official publication of the Association for Professionals in Infection Control and Epidemiology (APIC).
Researchers from the Hellenic Center for ...
2014-12-01
Research by the University of Liverpool has identified, for the first time, how global warming is related to the amount of carbon emitted.
A team of researchers from the Universities of Liverpool, Southampton and Bristol have derived the first theoretical equation to demonstrate that global warming is a direct result of the build-up of carbon emissions since the late 1800s when man-made carbon emissions began.
The results are in accord with previous data from climate models.
The theoretical equation revealed the complex relationship between carbon dioxide levels ...
2014-12-01
WASHINGTON, DC - December 1, 2014 -- Microbial succession in a sterilized restroom begins with bacteria from the gut and the vagina, and is followed shortly by microbes from the skin. Restrooms are dominated by a stable community structure of skin and outdoor associated bacteria, with few pathogenic bacteria making them similar to other built environments such as your home. The research is published ahead of print in Applied and Environmental Microbiology.
In the study, the investigators characterized the structure, function, and abundance of the microbial community, ...
2014-12-01
In the wake of recent airline crashes, major news networks have aired concerns about pilots' ability to accurately fly "by hand" when the airplane's cockpit automation systems fail. Although many of these concerns have centered on manual skills such as operating the airplane's controls, new human factors/ergonomics research suggests that pilots' thinking skills, such as navigating, remaining aware of the status of the flight, and diagnosing troublesome situations, are most vulnerable in today's automated cockpits. In a new study published in Human Factors, researchers studied ...
2014-12-01
New research published in the December 2014 issue of the Journal of Leukocyte Biology, shows that a component found in in the plant, Glycyrrhiza uralensis, may inhibit the development of metabolic disorders by stopping the activation of NLRP3, a protein involved in the disease process. Specifically, the researchers identified isoliquiritigenin as having the ability to attenuate high-fat, diet-induced obesity, type 2 diabetes and hepatic steatosis in mice.
"Identification of small compounds that inhibit the NLRP3 inflammasome is required to design effective therapeutics," ...
2014-12-01
Scientists have taken an important step toward a new class of antibiotics aimed at stopping lung infections. They found that a protein found in large airways, called "SPLUNC1," binds to lipids critical to defending against bacterial and viral infections, as well as keeping lung tissue flexible and hydrated. This discovery moves SPLUNC1 closer toward becoming a viable therapy and was reported in the December 2014 issue of The FASEB Journal.
"By shedding light on the mechanisms and interactions between various elements of pulmonary surfactant, our findings represent significant ...
2014-12-01
This news release is available in German. Traumatic events leave their mark. People exposed to a traumatic experience early in life are more likely to be affected by illnesses such as borderline personality disorder or depression. However such experience can also have positive effects in certain circumstances. Thus, moderate stress in childhood may help a person develop strategies to better cope with stress in adulthood.
Further, it has long been recognised by psychologists and psychiatrists that the negative effects of trauma experienced by parents can be seen in ...
2014-12-01
New research involving rats, and published in the December 2014 issue of The FASEB Journal, suggests that if you were born at a low birth weight, supplemental co-enzyme Q (CoQ) may lower your risk for heart disease. This enzyme, which is naturally made in the body, is required to ensure the proper functioning of cell mitochondria and also protects cells from oxidative damage. Feeding low birth weight rat offspring extra CoQ prevented the age-associated damage that causes heart disease. Additionally, the reports shows that CoQ is reduced in white blood cells from low birth ...
2014-12-01
Tropical Storm Hagupit was just a low pressure area on Nov. 30, but warm waters and good atmospheric conditions allowed the storm to develop rapidly. By Dec. 1 the low pressure area strengthened into a tropical storm when NASA's Terra satellite passed overhead.
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Radiometer known as the MODIS instrument that flies aboard NASA's Terra satellite captured a visible image of Tropical Storm Hagupit in the western Pacific Ocean on Dec. 1 at 00:05 UTC (7:05 p.m. EST, Nov. 30). The picture showed a concentration of strong thunderstorms around the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Mass extinction led to many new species of bony fish


