Genes and environment: Complex interactions at the heart of personalized medicine
2014-12-01
(Press-News.org) Personalized medicine uses methods of molecular analysis, especially genetic sequencing and transcription, in order to simultaneously identify genetic mutations to evaluate each individual's risk of contracting a given disease. It seems that there is more than a single mechanism at hand, as proven by the work of a team of geneticists at the University of Geneva's (UNIGE) Faculty of Medicine, and the Swiss Institute for Bioinformatics (SIB). They have sequenced the RNA of 400 pairs of twins; with this information, they can quantify the roles of both genetic and environmental context on the expression of genes. They concluded that establishing the list of mutations present in a person's genome is not sufficient to predict that person's future health. The study can be found in the latest online edition of Nature Genetics.
What influence does the environment have on genes activity? How do certain types of mutations interact with one another in a single individual? These are the complex interactions that Emmanouil Dermitzakis, Louis-Jeantet Professor in the Department of Genetic Medicine and Development at the UNIGE's Faculty of Medicine, and his team have sought to understand, working together with scientists from Kings College London and the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute.
Although we know that carriers of the same mutation do not necessarily both develop the same disease, how much of this discrepancy is due to genetics and how much is environmental remains unclear. Understanding how a mutation behaves when confronted with another mutation, on the one hand, and assessing the person's environmental context, on the other, forms the basis of the complex challenge of true personalized medicine.
Twins that are similar, but not identical
In Geneva, the scientists sequenced the RNA of 400 pairs of monozygotic and dizygotic twins and combined this information with genetic variations that had already been identified in these subjects. In this large sample, they identified a significant series of mutations that controlled gene expression. The researchers discovered that the influence that purely genetic (between genes) and environmental interactions (between a gene and the environment) had on gene expression were both substantial. They conclude that genetic or environmental context contributes significantly to the way in which a person's genetic composition is expressed, as well as to their risk of developing certain diseases.
The researchers used the differences between monozygotic twins, whose genomes are identical, to identify mutations that interact with the environment. Dizygotic twins, who only share half of their genome, but who were raised in the same environment, allowed researchers to separate purely genetic effects from effects caused by the similar environmental context in which the twins were raised.
«We have discovered that the genetic and environmental contexts of a mutation have a much greater influence on its expression in a given individual than we previously thought,» emphasized Dr Alfonso Buil, lead author of this study. «Understanding the architecture of genetic expression constitutes an essential step in understanding the genetic bases of complex diseases,» he adds.
Focusing Personalized Medicine on Context
Establishing the list of mutations present in a person's genome is therefore not enough to be able to predict that person's future health. In fact, in many cases, it is impossible to measure the effects of genetic mutations in an isolated way, without taking into account the context, meaning the rest of the genome as well as the environment, both of which modify the effect this mutation has on the person's health, and therefore the risk of developing a given disease.
«We can make the following analogy: until now, the approach has been like trying to understand a book by reading each sentence in a random order» explained Prof. Emmanouil Dermitzakis senior author of the study. «If personalized medicine really wants to be effective, we absolutely need more studies in order to understand these mechanisms much more precisely. The methodology we propose clearly shows that not only are these elements crucial for understanding individual gene expression, but it also shows that analysis at the level of the individual is possible,» he concludes.
INFORMATION:
This project was funded by the European Commission Framework Programme 7 under the project «EuroBATS».
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-12-01
HOUSTON -- (Dec. 1, 2014) - Most genes are inherited as two working copies, one from the mother and one from the father. However, in a few instances, a gene is imprinted, which means that one copy is silenced. This is called genomic imprinting. If the active copy is mutated, then disease results, even though the silenced gene copy may be normal.
Angelman syndrome, which causes learning difficulties, speech problems, seizures, jerky movements and an unusually happy disposition, results when a gene inherited from the mother in a particular area of chromosome 15 is mutated ...
2014-12-01
PHILADELPHIA-- Chronic kidney disease (CKD) affects at least one in four Americans who are older than 60 and can significantly shorten lifespan. Yet the few available drugs for CKD can only modestly delay the disease's progress towards kidney failure. Now, however, a team led by researchers at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, has found an aspect of CKD's development that points to a promising new therapeutic strategy.
"We found that a defect in energy production in affected kidney cells plays a key role in CKD development," says Katalin ...
2014-12-01
"I can't get the memories out of my mind!... I am right back in Vietnam, in the middle of the monsoon season at my guard post. My hands are freezing, yet sweat pours from my entire body...I smell a damp sulfur smell. Suddenly I see what's left of my buddy Troy, his head on a bamboo platter, sent back to our camp by the Viet Cong."i
This veteran of the US army, who served in Vietnam, has intense flashbacks of his decapitated friend whenever he hears a clap of thunder, touches a bamboo mat, or sees an Oriental woman. Although the traumatic incident happened decades ago in ...
2014-12-01
A new study* that challenges the prevailing view of how bowel cancer develops in the large intestine is published today in Nature Medicine.
Cancer Research UK scientists have discovered that bowel cancer may not be restricted to starting its journey in the stem cells in the lining of the intestines as previously thought.
The researchers, based at the Wellcome Trust Centre for Human Genetics, studied a hereditary faulty gene which can cause bowel cancer in middle age. The faulty gene causes normal cells to behave like immortal stem cells and develop tumours of their ...
2014-12-01
Many of the complex computer models which are used to predict climate change could be missing an important ozone 'feedback' factor in their calculations of future global warming, according to new research led by the University of Cambridge and published today (1 December) in the journal Nature Climate Change.
Computer models play a crucial role in informing climate policy. They are used to assess the effect that carbon emissions have had on the Earth's climate to date, and to predict possible pathways for the future of our climate.
Increasing computing power combined ...
2014-12-01
This news release is available in French. Micronutrient malnutrition affects more than 2 billion people. Researchers working at the Crop Development Centre at the University of Saskatchewan are seeking long term solutions to help to alleviate the increasing micronutrient malnutrition problem by enriching food grains with essential micronutrients through breeding and appropriate management practices, collectively known as biofortification.
Chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) is considered an excellent whole food as source of dietary proteins, carbohydrates, micronutrients ...
2014-12-01
DARIEN, IL - A new study shows that obstructive sleep apnea is associated with impaired exercise capacity, which is an indicator of increased cardiovascular risk.
Results show that the predicted peak oxygen uptake, a measure of aerobic physical fitness, was significantly lower in people with moderate to severe obstructive sleep apnea than in controls. Further analysis found that sleep apnea severity alone explained 16.1 percent of this variability.
"We found a significant association indicating that there is likely a very strong independent relationship between obstructive ...
2014-12-01
Obese patients who have undergone bariatric surgery to shed weight should take the supplements prescribed to them to protect their eyes. Taking in too little Vitamin A, in particular, could in some cases actually cause night blindness, dry eyes, corneal ulcers, and in extreme cases total blindness. This advice comes from Rui Azevedo Guerreiro and Rui Ribeiro of the Centro Hospitalar de Lisboa Central in Portugal, who reviewed what little research there currently is on the occurrence of eye conditions following bariatric surgery. The review is published in Springer's journal ...
2014-12-01
The latest research from the University of Adelaide challenges current thinking on whether many people with tooth loss really need dentures.
The findings have major implications for public dental health resources and costs for patients.
Studies conducted by the University's Australian Research Center for Population Oral Health in the School of Dentistry have found that people with tooth loss do not have their quality of life interfered with provided they still have a certain number and type of teeth left.
In dentistry terms, these patients are considered to have "shortened ...
2014-12-01
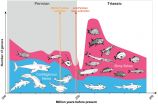
Today, ray-finned fish, which belong to the bony fish, are by far the most biodiverse fish group in both salt- and freshwater. Their spectacular variety of forms ranges from eels, tuna, flounders and angler fish all the way to seahorses. With around 1,100 species, the second most biodiverse group is the cartilaginous fish, which are almost exclusively marine and include sharks, rays and chimaeras. Exactly why bony fish managed to prevail in different habitats is the subject of debate: Do they have a better body plan, which is suited to more ecological niches than that of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Genes and environment: Complex interactions at the heart of personalized medicine