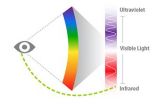
But an international team of researchers co-led by scientists at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis has found that under certain conditions, the retina can sense infrared light after all.
Using cells from the retinas of mice and people, and powerful lasers that emit pulses of infrared light, the researchers found that when laser light pulses rapidly, light-sensing cells in the retina sometimes get a double hit of infrared energy. When that happens, the eye is able to detect light that falls outside the visible spectrum.
"We're using what we learned in these experiments to try to develop a new tool that would allow physicians to not only examine the eye but also to stimulate specific parts of the retina to determine whether it's functioning properly," said senior investigator Vladimir J. Kefalov, PhD, associate professor of ophthalmology and visual sciences at Washington University. "We hope that ultimately this discovery will have some very practical applications."
The findings are published Dec. 1 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) Online Early Edition. Collaborators include scientists in Cleveland, Poland, Switzerland and Norway,
The research was initiated after scientists on the research team reported seeing occasional flashes of green light while working with an infrared laser. Unlike the laser pointers used in lecture halls or as toys, the powerful infrared laser the scientists worked with emits light waves thought to be invisible to the human eye.
"They were able to see the laser light, which was outside of the normal visible range, and we really wanted to figure out how they were able to sense light that was supposed to be invisible," said Frans Vinberg, PhD, one of the study's lead authors and a postdoctoral research associate in the Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences at Washington University.
Vinberg, Kefalov and their colleagues examined the scientific literature and revisited reports of people seeing infrared light. They repeated previous experiments in which infrared light had been seen, and they analyzed such light from several lasers to see what they could learn about how and why it sometimes is visible.
"We experimented with laser pulses of different durations that delivered the same total number of photons, and we found that the shorter the pulse, the more likely it was a person could see it," Vinberg explained. "Although the length of time between pulses was so short that it couldn't be noticed by the naked eye, the existence of those pulses was very important in allowing people to see this invisible light."
Normally, a particle of light, called a photon, is absorbed by the retina, which then creates a molecule called a photopigment, which begins the process of converting light into vision. In standard vision, each of a large number of photopigments absorbs a single photon.
But packing a lot of photons in a short pulse of the rapidly pulsing laser light makes it possible for two photons to be absorbed at one time by a single photopigment, and the combined energy of the two light particles is enough to activate the pigment and allow the eye to see what normally is invisible.
"The visible spectrum includes waves of light that are 400-720 nanometers long," explained Kefalov, an associate professor of ophthalmology and visual sciences. "But if a pigment molecule in the retina is hit in rapid succession by a pair of photons that are 1,000 nanometers long, those light particles will deliver the same amount of energy as a single hit from a 500-nanometer photon, which is well within the visible spectrum. That's how we are able to see it."
Although the researchers are the first to report that the eye can sense light through this mechanism, the idea of using less powerful laser light to make things visible isn't new. The two-photon microscope, for example, uses lasers to detect fluorescent molecules deep in tissues. And the researchers said they already are working on ways to use the two-photon approach in a new type of ophthalmoscope, which is a tool that allows physicians to examine the inside of the eye.
AUDIO: Our eyes aren't supposed to be able to see infrared light because infrared light waves are longer than the waves in the visual spectrum, but new work from vision researchers...
Click here for more information.
The idea is that by shining a pulsing, infrared laser into the eye, doctors might be able to stimulate parts of the retina to learn more about its structure and function in healthy eyes and in people with retinal diseases such as macular degeneration.
INFORMATION:
The research was made possible, in part, by the Kefalov team's development of a tool that allowed the scientists to obtain light responses from retinal cells and photopigment molecules. That device already is commercially available and being used at several vision research centers around the world.
Funded by the National Eye Institute (NEI) and the National Institute on Aging (NIA) of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), Research to Prevent Blindness, the Norwegian Research Council, the TEAM project financed by the European Union and the Foundation for Polish Science. NIH grant numbers: R24EY021126, R01EY009339, R01EY019312, P30EY002686, P30EY011373 and R44AG043645.
Palczewska G, Vinberg F, Stremplewski P, Bircher MP, Salom D, Komar K, Zhang J, Cascell M, Wojtkowski M, Kefalov VJ, Palczewski K. PNAS Online Early Edition, Dec. 1, 2014 http:http://www.pnas.org/cgi/doi/10.1073/pnas.1410162111
Washington University School of Medicine's 2,100 employed and volunteer faculty physicians also are the medical staff of Barnes-Jewish and St. Louis Children's hospitals. The School of Medicine is one of the leading medical research, teaching and patient-care institutions in the nation, currently ranked sixth in the nation by U.S. News & World Report. Through its affiliations with Barnes-Jewish and St. Louis Children's hospitals, the School of Medicine is linked to BJC HealthCare.