The ryanodine receptor: Calcium channel in muscle cells
Scientists decode the 3-D structure of the calcium channel with unprecedented accuracy
2014-12-02
(Press-News.org) This news release is available in German.
VIDEO:
Scientists decode the three-dimensional structure of the calcium channel with unprecedented accuracy.
Click here for more information.
Whenever muscles contract, so-called ryanodine receptors come into play. Calcium ions, which are ultimately responsible for the contraction of muscle cells, are released from storage organs and flow through these ion channels. Defective ryanodine receptors can lead, for example, to cardiac arrhythmias or sudden heart failure. Researchers at the Max Planck Institute of Molecular Physiology in Dortmund have now analysed the three-dimensional structure of the ryanodine receptor. The researchers inserted the receptors into tiny nano-membranes in order to study the proteins in a milieu similar to their natural environment in cells. With the help of electron cryo-microscopy and a new technique for detecting electrons, they were able to elucidate the structure of the receptor with high accuracy. The animation shows how the protein changes its structure when calcium ions bind to it. Armed with this knowledge, scientists may be able to develop new materials in future to repair malfunctioning ryanodine receptors.
The ryanodine receptor forms a channel that is permeable for calcium ions. The animation illustrates how the protein changes its structure upon the binding of calcium. Four helical domains in the center form an ion gate, which allows solely calcium to pass. The so-called EF-hand is the sensor that recognizes the ions. The domain is also known from other calcium-sensing proteins. It consists of charged amino acids and opens the gate region when calcium is bound.
INFORMATION:
Original Publication
Julian von der Ecken, Mirco Müller, William Lehman, Dietmar J. Manstein, Pawel A. Penczek & Stefan Raunser
Structure of the F-actin-tropomyosin complex
Nature, 1 December 2014, published online
[Attachments] See images for this press release:


ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-12-02
Researchers working at the Advanced Light Source (ALS) of the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE)'s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) have combined key features of two highly acclaimed X-ray spectroscopy techniques into a new technique that offers sub-nanometer resolution of every chemical element to be found at heterogeneous interfaces, such as those in batteries and fuel cells. This new technique is called SWAPPS for Standing Wave Ambient Pressure Photoelectron Spectroscopy, and it combines standing-wave photoelectron spectroscopy (SWPS) with high ambient ...
2014-12-02
When wild birds are a big part of your diet, opening a freshly shot bird to find worms squirming around under the skin is a disconcerting sight. That was exactly what Victoria Kotongan saw in October, 2012, when she set to cleaning two of four spruce grouse (Falcipennis canadensis) she had taken near her home in Unalakleet, on the northwest coast of Alaska. The next day, she shot four grouse and all four harbored the long, white worms. In two birds, the worms appeared to be emerging from the meat.
Kotongan, worried about the health of the grouse and the potential risk ...
2014-12-02
NASA's Aqua satellite captured a visible picture of Tropical Storm Hagupit in the western North Pacific Ocean on December 2, when several warnings were in effect for islands in Micronesia.
Micronesia warnings include a Typhoon Warning for Woleai, Yap and Ngulu in Yap state, a Typhoon Watch posted for Faraulep, Fais and Ulithi in Yap state, and a Tropical Storm Warning for Faraulep in Yap state.
When NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Hagupit on Dec. 2 at 03:45 UTC (Dec. 1 at 10:45 p.m. EST) the MODIS instrument took a visible picture of the storm that showed it had become ...
2014-12-02
Over the past thirty years, physical activity among children has declined markedly. The public health implications of this decline include a growing prevalence of obesity and chronic diseases such as diabetes and hypertension. A new issue of Monographs of the Society for Research in Child Development expands the focus to ask whether physical activity is also related to children's brain and cognitive development and achievement in school. Scholarly articles published by over 20 researchers in Monographs, titled "The Relation of Childhood Physical Activity to Brain Health, ...
2014-12-02
CORVALLIS, Ore. - Chemists and engineers at Oregon State University have discovered a fascinating new way to take some of the atmospheric carbon dioxide that's causing the greenhouse effect and use it to make an advanced, high-value material for use in energy storage products.
This innovation in nanotechnology won't soak up enough carbon to solve global warming, researchers say. However, it will provide an environmentally friendly, low-cost way to make nanoporous graphene for use in "supercapacitors" - devices that can store energy and release it rapidly.
Such devices ...
2014-12-02
New research in mice suggests that restricting access to food to 8-12 hours rather than allowing constant access to food may help prevent and even reverse obesity and type 2 diabetes. The results of two studies publishing online December 2 in the Cell Press journal Cell Metabolism suggest that this time-restricted eating affects the balance of bacteria found in the gut. Researchers also found the occasional "cheat days" on weekends did not undo the benefits of time-restricted eating in mice.
Previously, investigators led by Dr. Satchidananda Panda of the Salk Institute ...
2014-12-02
VIDEO:
This video gives another case against the midnight snack.
Click here for more information.
LA JOLLA-These days, with the abundance of artificial light, TV, tablets and smartphones, adults and children alike are burning the midnight oil. What they are not burning is calories: with later bedtimes comes the tendency to eat.
A new study by researchers at the Salk Institute cautions against an extended period of snacking, suggesting instead that confining caloric consumption ...
2014-12-02
Researchers from Weill Cornell Medical College and the Gladstone Institutes have found a way to prevent noise-induced hearing loss in a mouse using a simple chemical compound that is a precursor to vitamin B3. This discovery has important implications not only for preventing hearing loss, but also potentially for treating some aging-related conditions that are linked to the same protein.
Published today in Cell Metabolism, the researchers used the chemical nicotinamide riboside (NR) to protect the nerves that innervate the cochlea. The cochlea transmits sound information ...
2014-12-02
The aging process affects everything from cardiovascular function to memory to sexuality. Most worrisome for many, however, is the potential loss of eyesight due to retinal degeneration.
New progress towards a prosthetic retina could help alleviate conditions that result from problems with this vital part of the eye. An encouraging new study published in Nano Letters describes a revolutionary novel device, tested on animal-derived retinal models, that has the potential to treat a number of eye diseases. The proof-of-concept artificial retina was developed by an international ...
2014-12-02
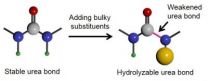
Researchers at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign have figured out how to reverse the characteristics of a key bonding material--polyurea--providing an inexpensive alternative for a broad number of applications, such as drug delivery, tissue engineering, and packaging.
"Polymers with transient stability in aqueous solution, also known as hydrolysable polymers, have been applied in many biomedical applications, such as in the design of drug delivery systems, scaffolds for tissue regeneration, surgical sutures, and transient medical devices and implants," ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] The ryanodine receptor: Calcium channel in muscle cells
Scientists decode the 3-D structure of the calcium channel with unprecedented accuracy