New study explains the role of oceans in global 'warming hiatus'
2014-12-03
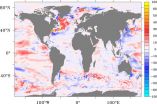
(Press-News.org) New research shows that ocean heat uptake across three oceans is the likely cause of the 'warming hiatus' - the current decade-long slowdown in global surface warming.
Using data from a range of state-of-the-art ocean and atmosphere models, the research shows that the increased oceanic heat drawdown in the equatorial Pacific, North Atlantic and Southern Ocean basins has played a significant role in the hiatus.
The new analysis has been published in Geophysical Research Letters by Professor Sybren Drijfhout from the University of Southampton and collaborators from the National Oceanography Centre (NOC) Dr Adam Blaker, Professor Simon Josey, Dr George Nurser and Dr Bablu Sinha, together with Dr Magdalena Balmaseda from the European Centre for Medium Range Weather Forecasting (ECMWF).
Professor Drijfhout said: "This study attributes the increased oceanic heat drawdown in the equatorial Pacific, North Atlantic and Southern Ocean to specific, different mechanisms in each region. This is important as current climate models have been unable to simulate the hiatus. Our study gives clues to where the heat is drawn down and by which processes. This can serve as a benchmark for climate models on how to improve their projections of future global mean temperature."
Previously, the drawdown of heat by the Equatorial Pacific Ocean over the hiatus period, due to cool sea-surface temperatures associated with a succession of cool-surface La Nina episodes, was thought to be sufficient to explain the hiatus.
However, this new analysis reveals that the northern North Atlantic, the Southern Ocean and Equatorial Pacific Ocean are all important regions of ocean heat uptake. Each basin contributes a roughly equal amount to explaining the hiatus, but the mechanisms of heat drawdown are different and specific in each basin.
In the North Atlantic, more heat has been retained at deep levels as a result of changes to both the ocean and atmospheric circulations, which have led to the winter atmosphere extracting less heat from the ocean.
In the Southern Ocean, the extra drawdown of heat had gone unnoticed and is increasing on a much longer timescale (multi-decadal) than the other two regions (decadal). Here, gradual changes in the prevailing westerly winds have modified the ocean-atmosphere heat exchange, particularly in the Southern Indian Ocean.
The team calculated the change in the amount of heat entering the ocean using a state-of-the-art high resolution ocean model developed and run by NOC scientists that is driven by surface observations. This estimate was compared with results from an ocean model-data synthesis from ECMWF and a leading atmospheric model-data synthesis produced in the US. Professor Josey said: "It is the synthesis of information from models and observational data that provides a major strength of our study."
Dr Sinha concluded: "The deeper understanding gained in this study of the processes and regions responsible for variations in oceanic heat drawdown and retention will improve the accuracy of future climate projections."
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-12-03
This news release is available in German.
The new study establishes that the best combination for incentives and punishment that promotes cooperation are in the form of "First carrot, then stick". The mathematical proof shows how the combined sequential use of reward ("carrot") and punishment ("stick") promotes cooperation in collaborative endeavors, such as protecting social commons and maintaining mutual aid.
Rewards and punishments are the most tried and true approaches when trying to promote cooperation in collaborative endeavors. New research, in terms of ...
2014-12-03
Analysis of data from the MATROSHKA experiment, the first comprehensive measurements of long-term exposure of astronauts to cosmic radiation, has now been completed. This experiment, carried out on board and outside of the International Space Station, showed that the cosmos may be less hostile to space travellers than expected.
Among the many life-threatening hazards to the space traveller, cosmic radiation is a major one, considerably limiting the time astronauts may spend in space without incurring excessive risk to their health from too high a dose of this ionizing ...
2014-12-03
An Australian National University (ANU) mathematician has developed a new way to uncover simple patterns that might underlie apparently complex systems, such as clouds, cracks in materials or the movement of the stockmarket.
The method, named fractal Fourier analysis, is based on new branch of mathematics called fractal geometry.
The method could help scientists better understand the complicated signals that the body gives out, such as nerve impulses or brain waves.
"It opens up a whole new way of analysing signals," said Professor Michael Barnsley, who presented ...
2014-12-03
INDIANAPOLIS, December 2, 2014 -- Today, Eli Lilly and Company announced results from new analyses of two Phase 3 trials evaluating the relationship between cognitive and functional treatment effects in patients with mild Alzheimer's disease. Based on post-hoc analyses of the Phase 3 trials, the findings suggested that cognitive deficits were more apparent than functional deficits in mild Alzheimer's disease when measured with the Alzheimer's disease Assessment Scale-Cognitive (ADAS-Cog) and the Alzheimer's disease Cooperative Study-Activities of Daily Living (ADCS-ADL) ...
2014-12-03
Amsterdam, The Netherlands, December 2, 2014 - Detection, prevention, and preclinical treatment are three key areas that may make a difference in the battle to reduce the rapid rise of new Alzheimer's disease (AD) cases every year. These three topics are the focus of an important new supplement to the Journal of Alzheimer's Disease.
Organized by Guest Editor Jack de la Torre, MD, PhD, Professor of Neuropsychology at The University of Texas at Austin, the supplement is a novel guide to how Alzheimer dementia may be approached and managed right now, not years from now. ...
2014-12-03
Scientists have released details of a raft of new chemicals with potent anti-malarial properties which could open the way to new drugs to fight the disease.
A new paper in PNAS is the third published by the group at the Australian National University (ANU), which has collaborated with groups from around the globe to uncover potential ammunition in the fight against malaria.
Over 200 million people contract malaria each year, and the parasite that causes the disease has become resistant to most of the drugs currently available.
"The papers show the malaria parasite ...
2014-12-03
A glimmer of hope for corals as baby reef builders cope with acidifying oceans
While the threat of coral bleaching as a result of climate change poses a serious risk to the future of coral reefs worldwide, new research has found that some baby corals may be able to cope with the negative effects of ocean acidification.
Ocean acidification, which is a direct consequence of increased atmospheric carbon dioxide levels, is expected to have a deleterious effect on many marine species over the next century.
An international team examining the impact of ocean acidification ...
2014-12-03
Coral reefs provide a range of benefits, such as food, opportunities for income and education, but not everyone has the same access to them, according to a new study conducted by the ARC Centre of Excellence for Coral Reef Studies (Coral CoE) at James Cook University.
The researchers examined how people from 28 fishing communities in Madagascar, Kenya, Tanzania and Seychelles benefit from the marine environment.
For many years conservation in developing countries has been based on the assumption that improvements in ecosystem conditions, such as increasing coral reef ...
2014-12-03
December 3, 2014 -- Individuals conceived in the severe Dutch Famine, also called the Hunger Winter, may have adjusted to this horrendous period of World War II by making adaptations to how active their DNA is. Genes involved in growth and development were differentially regulated, according to researchers at the Leiden University Medical Center, Harvard University, and Columbia University's Mailman School of Public Health. Findings are published in the journal Nature Communications.
During the winter of 1944-1945 the Western part of The Netherlands was struck by a severe ...
2014-12-03
CHAPEL HILL, NC - UNC School of Medicine researchers have found for the first time a biochemical mechanism that could be a cause of "chemo brain" - the neurological side effects such as memory loss, confusion, difficulty thinking, and trouble concentrating that many cancer patients experience while on chemotherapy to treat tumors in other parts of the body.
The research, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, shows how the common chemotherapy drug topotecan can drastically suppress the expression of Topoisomerase-1, a gene that triggers the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New study explains the role of oceans in global 'warming hiatus'