(Press-News.org) People who work around the clock could actually be setting themselves back, according to Virginia Tech biologists.
Researchers found that a protein responsible for regulating the body's sleep cycle, or circadian rhythm, also protects the body from developing sporadic forms of cancers.
"The protein, known as human period 2, has impaired function in the cell when environmental factors, including sleep cycle disruption, are altered," said Carla Finkielstein, an associate professor of biological sciences in the College of Science, Fralin Life Science Institute affiliate, and a Virginia Bioinformatics Institute Fellow.
Supported by a National Science Foundation CAREER award and the Fralin Life Science Institute, the work was published in October in the print edition of the journal Molecular Biology of the Cell, with Tetsuya Gotoh, a research scientist in Finkielstein's lab, as lead author.
Specifically, researchers found that, unaltered, the human period 2 protein directly interacts with tumor suppressor proteins in cells to control cell division.
"When (human period 2 protein) is non-functional because it is either mutated or somehow modified, then, it is unable to do its job and prevent the cells from dividing at certain times of the day," Gotoh said. "This is particularly a problem in cases where tumor suppressor genes are mutated as it happens in more than 80 percent of all cancer cases."
The researchers observed the connection by studying various human and animal tumor cells, where repressing the human period 2 gene led to both abnormal circadian rhythmicity and a malignant transformation.
Researchers are now working closely with patients to identify those at risk of developing cancer due to the malfunctioning of the protein and the gene that produces it.
Results from these studies may help develop new, more effective prevention strategies for populations at risk due to circadian disruption, such as women working night shifts.
"These findings highlight the complexity of the circadian-controlled network and emphasize its physiological relevance for human health and for new therapeutic interventions," Finkielstein said.
"Over the past two decades we've learned a great deal about the inner workings of the circadian clock, the internal timepiece that controls our sleep:wake cycle and a whole host of other daily bodily rhythms," said Ignacio Provencio, a professor of biology at the University of Virginia who was not involved with the study. "The Finkielstein lab discovered that a molecular gear of this clock interacts directly with a well-studied protein whose role is to suppress tumor formation. This remarkable finding is likely to provide insight into how disruption of the internal clock can lead to cancer."
Finkielstein has long studied the connection between circadian rhythms and cancer development, particularly the incidence of breast cancer in women who work night shifts like nurses and flight attendants.
Every October, in partnership with Downtown Blacksburg Inc., Finkielstein helps plan a local outreach event, Pretty in Pink, to raise money for the Virginia Breast Cancer Foundation and educate people in topics that relate to breast cancer prevention and early diagnostics.
INFORMATION:
More resources are available from Virginia Tech News.
The more time you spend getting to and from work, the less likely you are to be satisfied with life, says a new Waterloo study.
Published in World Leisure Journal, the research reveals exactly why commuting is such a contentment killer--and surprisingly, traffic isn't the only reason to blame.
"We found that the longer it takes someone to get to work, the lower their satisfaction with life in general," says Margo Hilbrecht, a professor in Applied Health Sciences and the associate director of research for the Canadian Index of Wellbeing.
While commuting has long been ...
Is your inbox burning you out? Then take heart - research from the University of British Columbia suggests that easing up on email checking can help reduce psychological stress.
Some of the study's 124 adults -- including students, financial analysts medical professionals and others -- were instructed to limit checking email to three times daily for a week. Others were told to check email as often as they could (which turned out to be about the same number of times that they normally checked their email prior to the study).
These instructions were then reversed for ...
RIVERSIDE, Calif. - Geckos, found in places with warm climates, have fascinated people for hundreds of years. Scientists have been especially intrigued by these lizards, and have studied a variety of features such as the adhesive toe pads on the underside of gecko feet with which geckos attach to surfaces with remarkable strength.
One unanswered question that has captivated researchers is: Is the strength of this adhesion determined by the gecko or is it somehow intrinsic to the adhesive system? In other words, is this adhesion a result of the entire animal initiating ...
An efficient method to harvest low-grade waste heat as electricity may be possible using reversible ammonia batteries, according to Penn State engineers.
"The use of waste heat for power production would allow additional electricity generation without any added consumption of fossil fuels," said Bruce E. Logan, Evan Pugh Professor and Kappe Professor of Environmental Engineering. "Thermally regenerative batteries are a carbon-neutral way to store and convert waste heat into electricity with potentially lower cost than solid-state devices."
Low-grade waste heat is an ...
New Rochelle, NY, December 3, 2014--Hereditary angioedema (HAE), a rare genetic disease that causes recurrent swelling under the skin and of the mucosal lining of the gastrointestinal tract and upper airway, usually first appears before 20 years of age. A comprehensive review of the therapies currently available to treat HAE in adults shows that some of these treatments are also safe and effective for use in older children and adolescents. Current and potential future therapies are discussed in a Review article in a special issue of Pediatric Allergy, Immunology, and Pulmonology, ...
Typhoon Hagupit continues to intensify as it continued moving through Micronesia on Dec. 3 triggering warnings. NASA's Aqua satellite passed overhead and captured an image of the strengthening storm while the Rapidscat instrument aboard the International Space Station provided information about the storm's winds.
The International Space Station-RapidScat instrument monitors ocean winds to provide essential measurements used in weather predictions, including hurricanes. "RapidScat measures wind speed and direction over the ocean surface and captured an image of Hagupit ...
This news release is available in French.
Quebec City, December 3, 2014--Researchers at Université Laval's Faculty of Science and Engineering and Centre for Optics, Photonics and Lasers have developed smart textiles able to monitor and transmit wearers' biomedical information via wireless or cellular networks. This technological breakthrough, described in a recent article in the scientific journal Sensors, clears a path for a host of new developments for people suffering from chronic diseases, elderly people living alone, and even firemen and police officers.
A ...
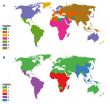
Researchers at North Carolina State University have for the first time mapped human disease-causing pathogens, dividing the world into a number of regions where similar diseases occur.
The findings show that the world can be separated into seven regions for vectored human diseases - diseases that are spread by pests, like mosquito-borne malaria - and five regions for non-vectored diseases, like cholera.
Interestingly, not all of the regions are contiguous. The British Isles and many of its former colonies, such as the United States and Australia, have similar diseases ...
Good news on the panda front: Turns out they're not quite as delicate - and picky - as thought.
Up until now, information gleaned from 30 years worth of scientific literature suggested that pandas were inflexible about habitat. Those conclusions morphed into conventional wisdom and thus have guided policy in China. But a Michigan State University (MSU) research associate has led a deep dive into aggregate data and emerged with evidence that the endangered animal is more resilient and flexible than previously believed.
Vanessa Hull is a postdoctoral research associate ...
Irvine, Calif., Dec. 3, 2014 - High fecal counts frequently detected at so-called "baby beaches" may not be diaper-related. UC Irvine researchers found that during summer months, small drainpipes emptying into enclosed ocean bays have a disproportionate impact on calmer waters. The findings were published Tuesday in the journal Environmental Science & Technology.
Researchers have long known that creeks and tributaries foul coastal waters with major winter storm runoff. But dry seasons like the one that just concluded can spell potential peril, too. Runoff from watering ...