Study offers future hope for tackling signs of ageing
Team identifies 'markers' to spot old cells in the body -- offering hope in the fight against cancer and ageing
2014-12-08
(Press-News.org) A new advance in biomedical research at the University of Leicester could have potential in the future to assist with tackling diseases and conditions associated with ageing - as well as in treating cancer.
The research, which has shown promise in clinical samples, has been published in the prestigious scientific journal, Cell Death and Disease.
The group of scientists coordinated by Dr Salvador Macip from the Mechanisms of Cancer and Ageing Lab and the Department of Biochemistry of the University of Leicester carried out the study to find new ways of identifying old cells in the body.
This is important because the accumulation of old cells (called "senescent") in human tissue can contribute to symptoms of ageing. But old cells can also appear as a result of the activation of the internal anti-cancer mechanisms of the human body.
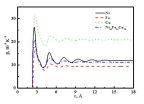
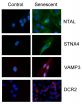
Dr Macip said: "What we have found is a series of novel markers - a way to detect senescent cells. What is more, we have shown that they can be used to predict increased survival in certain types of cancer.
"Until now, good protocols to help spot these cells have been sadly lacking. Our research has described new markers located on the surface of the old cells. This makes these markers particularly useful to quickly identify these cells in laboratory and human samples using a range of techniques."
As a first clinical application of these markers, the researchers observed that they were present in high numbers in samples from different types of cancer and that this correlated with a better prognosis of the disease. This was particularly evident in breast cancer.
Dr Macip said: "These markers could be useful tools not only to study senescent cells in the lab but also they could be developed into diagnostics to help predict survival in cancer patients.
"Moreover, they could also be used in the future to define strategies to selectively eliminate the old cells from the tissues and thus reduce their effects on promoting ageing in healthy subjects."
INFORMATION:
The work was funded by the MRC, the University of Leicester, the Saudi Arabian Government and the RSCF and involved scientists from the Departments of Biochemistry and Cancer Studies of the University of Leicester, the Umm AL-Qura University and the Russian Academy of Sciences.
Link to the paper: http://www.nature.com/cddis/journal/v5/n11/full/cddis2014489a.html
Lab webpage: http://lab.macip.org
Note to newsdesk:
For more information, please contact: Salvador Macip, sm460@le.ac.uk
The Medical Research Council has been at the forefront of scientific discovery to improve human health. Founded in 1913 to tackle tuberculosis, the MRC now invests taxpayers' money in some of the best medical research in the world across every area of health. Twenty-nine MRC-funded researchers have won Nobel prizes in a wide range of disciplines, and MRC scientists have been behind such diverse discoveries as vitamins, the structure of DNA and the link between smoking and cancer, as well as achievements such as pioneering the use of randomised controlled trials, the invention of MRI scanning, and the development of a group of antibodies used in the making of some of the most successful drugs ever developed. Today, MRC-funded scientists tackle some of the greatest health problems facing humanity in the 21st century, from the rising tide of chronic diseases associated with ageing to the threats posed by rapidly mutating micro-organisms. http://www.mrc.ac.uk
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-12-08
Insects are full of marvels - and this is certainly the case with a beetle from the Tenebrionind family, found in the extreme conditions of the Namib desert. Now, a team of scientists has demonstrated that such insects can collect dew on their backs - and not just fog as previously thought. This is made possible by the wax nanostructure on the surface of the beetle's elytra. These findings by José Guadarrama-Cetina, then working at ESPCI ParisTech, France - on leave from the University of Navarra, in Spain - and colleagues were recently published in EPJ E. They bring ...
2014-12-08
MOUNT VERNON, WA - Cider - or "hard cider" as it is typically known in the United States - is experiencing a real revival. The fermented apple juice with 0.5% to 7% alcohol-by-volume is the fastest growing alcohol market segment in the US, boasting a 54% increase in production annually from 2007 to 2012. Naturally, increasing consumer demand for cider translates to a need for more apples to make quality cider products.
Carol A. Miles and Jaqueline King from Washington State University's Department of Horticulture published a study in HortTechnology that can provide apple ...
2014-12-08
An article published in the Health Affairs December issue is the first ever comprehensive analysis to investigate the Affordable Care Act's (ACA) Essential Health Benefit (EHB) as it relates to children. The study found that the EHB has resulted in a state-by-state patchwork of coverage for children and adolescents that has significant exclusions, particularly for children with developmental disabilities and other special health care needs.
Previous studies have compared the EHB standard more broadly to the Children's Health Insurance Program (CHIP), but this analysis ...
2014-12-08
WEST LAFAYETTE, IN/ITHACA, NY - Energy costs account for one of the largest expenses in commercial greenhouse production of annual bedding plants. Naturally, bedding plant producers are searching for more energy-efficient production methods that can reduce fuel usage and increase profits. Christopher Currey, Roberto Lopez, and Neil Mattson published a study in HortTechnology that gives growers in northern latitudes valuable information on finishing practices for annual bedding plants. The researchers compared traditional heated greenhouses with unheated high tunnels for ...
2014-12-08
(SAN FRANCISCO, December 6, 2014) - New treatment combinations and targeted therapies for lymphoma and multiple myeloma are improving outcomes for vulnerable patient populations with hard-to-treat disease, according to studies presented today at the 56th American Society of Hematology (ASH) Annual Meeting and Exposition.
Despite advances in lymphoma treatments, improving the prognosis for patients with relapsed and treatment-resistant disease remains a challenge. The early success of several precision therapies associated with fewer side effects than conventional approaches ...
2014-12-08
(SAN FRANCISCO, December 7, 2014) - Studies presented at the 56th American Society of Hematology (ASH) Annual Meeting and Exposition compare new and standard-of-care treatments for blood clots and further illuminate clot risks in vulnerable populations, such as cancer patients.
Although significant advances have been made in the treatment and prevention of blood clots through new and improved therapies for clotting disorders, challenges remain in balancing the benefits and risks of these therapies. Specifically, while these treatments can reduce patients' risk of suffering ...
2014-12-08
It is estimated that about 35 million people worldwide currently suffer from dementia and it is expected that the number will increase to 135 million by the year 2050. The disease is already one of the most common health problems in the elderly, which is why experts predict that the numbers of people affected will increase over time. Researchers at the Department of Psychiatry and Psychotherapy of the University Medical Center of Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) have recently gained new insights into how it may in future be possible to treat patients with the currently ...
2014-12-08
The ability to predict macroscopic physical and chemical properties from information derived at the micro-scale or atomic scale for various kinds of materials has yet to be perfected in the field of materials physics and chemistry. Although macro-scopic properties are determined by the micro or atomic structure of materials, it is still difficult to obtain such properties as hardness, intensity, surface tension, density, thermal expansion, thermal diffusion, viscosity and specific heat from a cell with just several atoms because of multi-scale effects.
For solids, particularly ...
2014-12-08
Gallium nitride (GaN) based devices are attractive for harsh environment electronics because of their high chemical and the mechanical stability of GaN itself that has a higher atomic displacement energy than other semiconductor materials.
However, degradation mechanisms of GaN device under radiation environments is not clear mainly because devices consist of many different types of semiconductors, such as p-type and n-type layers in light emitting diode (LED), and each layer has different hardness to radiation.
Now, researchers at the Electronics-Inspired Interdisciplinary ...
2014-12-08
Macrophages are best known for their Pac Man-like ability to gobble up cellular debris and pathogens in order to thwart infection. A new study in The Journal of Cell Biology describes how these immune cells also help resolve inflammation by inducing white blood cells called neutrophils to leave wounded tissue.
Neutrophils are "first responders" that are attracted to wounds by signaling molecules called reactive oxygen species (ROS) that activate a protein kinase. When neutrophils finish their work, inflammation is partly resolved through apoptosis, or cell suicide, and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Study offers future hope for tackling signs of ageing
Team identifies 'markers' to spot old cells in the body -- offering hope in the fight against cancer and ageing