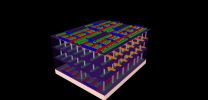
Live images from inside materials
2014-12-15
(Press-News.org) In medicine, X-rays provide high-resolution images of our insides to help doctors make a definitive diagnosis. Industry uses X-rays, too - as a reliable, non-destructive way of seeing what's hidden on inside materials and components and to check for cracks or irregularities. However industry additionally draws upon different technologies that are not used in the medical field. Whereas medical X-ray machines have been specifically designed for human test subjects, industrial X-ray machines are used to analyze objects that vary much more in their size and material composition. This calls for X-ray equipment that is correspondingly more flexible.
Researchers at the Development Center for X-Ray Technology EZRT, a division of the Fraunhofer Institute for Integrated Circuits IIS, have developed MULIX - an X-ray detector for industrial computed tomography (CT) based on the design of medical X-ray devices. "Our challenge was to combine high image quality with a high degree of flexibility," explains Frank Nachtrab from the EZRT. MULIX harnesses two concepts already in use, making it a kind of hybrid solution that incorporates elements of line and flat-panel detectors commonly used in industry. The researchers already know what they plan to achieve with their work: "We've had very promising results with our demonstrator and have shown that MULIX works. We're now looking for industrial partners to help develop a MULIX prototype," says Nachtrab.
Combining the benefits of two different methods
Single-line detectors use a fan-shaped beam to X-ray a certain section of the test object, whereas flat-panel detectors are working with a cone-shaped beam that encompasses the entire object. There are pros and cons to both solutions. A flat-panel detector will quickly give you a 2D image of the entire object. However, it causes scattered radiation - in other words, rays deflected by the test object - which greatly impairs image quality. A single-line detector is less sensitive for scatter and will therefore deliver extremely sharp images. But since it captures only a small portion of the test object, this scanning method is much more time-consuming. "We have combined the benefits of the two solutions," says Nachtrab. The new equipment is based on a detector with multiple lines, a design that until now has been used only in the medical field. Multiple-line detectors work according to the same principle as their single-line counterparts, but can also cover larger areas and thus radically reduce the scanning time. MULIX uses a total of 256 lines, allowing it to scan larger objects such as car body parts very quickly. What's really remarkable is that the new detector delivers images so fast, it becomes possible to use CT techniques to make a 3D-scan of the object almost in real time.
MULIX opens up new application opportunities in materials research and quality assurance, which would allow the automotive industry, aerospace and research institutions to observe processes going on within the materials they use. "When testing mechanical properties such as tensile strength, we can use the images we get to see just how a compromising fault comes about," says Nachtrab. The researchers also came up with an innovative solution for the detector's mechanics: "This enhances the quality of the images further," says Nachtrab. Unlike commercially available detectors, it is possible to adjust MULIX's curvature. This ensures the flexibility that industrial CT needs to adapt the system to the various sizes and material properties of test objects.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-12-15
MANHASSET, NY -- Molecular Medicine, a peer-reviewed biomedical journal published by the Feinstein Institute Press, published the results of a new study reporting clinically significant pain reduction in type 2 diabetic patients. In an exploratory study conducted by Araim Pharmaceuticals, a biotech company developing novel treatments for chronic diseases, investigators also observed improvements in metabolic control in patients administered ARA 290. ARA 290 is a peptide engineered to activate the innate repair receptor, a receptor discovered by Araim scientists, which is ...
2014-12-15
Scientists at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) in Germany have discovered a new signal pathway in the brain that plays an important role in learning and the processing of sensory input. It was already known that distinct glial cells receive information from neurons. However, it was unknown that these same glial cells also transmit information to neurons. The glia release a specific protein fragment that influences neuronal cross-talk, most likely by binding to the synaptic contacts that neurons use for communication. Disruption of this information flow from the ...
2014-12-15
New research led by the University of Exeter has found that people who have a stronger sense of place at the global than the national level are more likely to accept that climate change is caused by human activities. This is the first time that acceptance of human causes of climate change has been shown to be linked to people's sense of place at the global level. The findings have significant implications both for climate change communications and for our understanding of place and identities.
The study 'My country or my planet? Exploring the influence of multiple place ...
2014-12-15
BLOOMINGTON, Ind. -- Scientists at Indiana University and colleagues at Stanford and the University of Texas have demonstrated a technique for "editing" the genome in sperm-producing adult stem cells, a result with powerful potential for basic research and for gene therapy.
The researchers completed a "proof of concept" experiment in which they created a break in the DNA strands of a mutant gene in mouse cells, then repaired the DNA through a process called homologous recombination, replacing flawed segments with correct ones.
The study involved spermatogonial stem ...
2014-12-15
Patients with Parkinson's, medics and carers have identified the top ten priorities for research into the management of the condition in a study by the University of East Anglia and Parkinson's UK.
Commissioned by Parkinson's UK, people with direct and indirect personal experience of the condition worked together to identify crucial gaps in the existing evidence to address everyday practicalities in the management of the complexities of Parkinson's. Patients stated that the overarching research aspiration was an effective cure for Parkinson's but whilst waiting for this ...
2014-12-15
DALLAS - Dec. 15, 2014 - UT Southwestern Medical Center neurology researchers have identified an important cell signaling mechanism that plays an important role in brain cancer and may provide a new therapeutic target.
Researchers found that this mechanism -- a type of signaling termed constitutive or non-canonical epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling -- is highly active in glioblastomas, the most common type of adult brain cancer and a devastating disease with a poor prognosis.
When activated in cancer cells, it protects the tumor cells, making them more ...
2014-12-15
In the same way as we now connect computers in networks through optical signals, it could also be possible to connect future quantum computers in a 'quantum internet'. The optical signals would then consist of individual light particles or photons. One prerequisite for a working quantum internet is control of the shape of these photons. Researchers at Eindhoven University of Technology (TU/e) and the FOM foundation have now succeeded for the first time in getting this control within the required short time. These findings are published today in Nature Communications.
Quantum ...
2014-12-15
For decades, the mantra of electronics has been smaller, faster, cheaper.
Today, Stanford engineers add a fourth word - taller.
At a conference in San Francisco, a Stanford team will reveal how to build high-rise chips that could leapfrog the performance of the single-story logic and memory chips on today's circuit cards.
Those circuit cards are like busy cities in which logic chips compute and memory chips store data. But when the computer gets busy, the wires connecting logic and memory can get jammed.
The Stanford approach would end these jams by building layers ...
2014-12-15
PEOPLE who have problems with numbers may be more likely to feel negative about bowel cancer screening, including fearing an abnormal result, while some think the test is disgusting or embarrassing, according to a Cancer Research UK supported study* published today (Monday) in the Journal of Health Psychology.
The researchers** sent information about bowel cancer screening to patients aged from 45 to 59 along with a questionnaire which assessed their numerical skills and attitudes to the screening test, which looks for blood in stool samples.
Almost 965 people - registered ...
2014-12-15
E-cigarette use among teenagers is growing in the U.S., and Hawaii teens take up e-cigarette use at higher rates than their mainland counterparts, a new study by University of Hawaii Cancer Center researchers has found.
The findings come as e-cigarettes grow in popularity and the Food and Drug Administration is considering how to regulate their sale. Some public health officials are concerned that e-cigarettes may be recruiting a new generation of young cigarette smokers who otherwise might not take up smoking at all, and the study's results bolster this position.
Data ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Live images from inside materials