(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, Dec. 15, 2014--Credit card fraud and identify theft are serious problems for consumers and industries. Though corporations and individuals work to improve safeguards, it has become increasingly difficult to protect financial data and personal information from criminal activity. Fortunately, new insights into quantum physics may soon offer a solution.
As reported in The Optical Society's (OSA) new high-impact journal Optica, a team of researchers from the Netherlands has harnessed the power of quantum mechanics to create a fraud-proof method for authenticating a physical "key" that is virtually impossible to thwart.
This innovative security measure, known as Quantum-Secure Authentication, can confirm the identity of any person or object, including debit and credit cards, even if essential information (like the complete structure of the card) has been stolen. It uses the unique quantum properties of light to create a secure question-and-answer (Q&A) exchange that cannot be "spoofed" or copied.
The "Question-and-Answer" Security Game
Traditional magnetic-stripe-only cards are relatively simple to use but also simple to copy. Recently, banks have begun issuing so-called "smart cards" that include a microprocessor chip to authenticate, identify and enhance security. But regardless of how complex the code or how many layers of security, the problem remains that an attacker who obtains the information stored inside the card can copy or emulate it.
The new approach outlined in this paper avoids this risk entirely by using the peculiar quantum properties of photons that allow them to be in multiple locations at the same time to convey the authentication questions and answers. Though difficult to reconcile with our everyday experiences, this strange property of light can create a fraud-proof Q&A exchange, like those used to authorize credit card transactions.
"Single photons of light have very special properties that seem to defy normal behavior," said Pepijn Pinkse, a researcher from the University of Twente and lead author on the paper. "When properly harnessed, they can encode information in such a way that prevents attackers from determining what the information is."
The process works by transmitting a small, specific number of photons onto a specially prepared surface on a credit card and then observing the tell-tale pattern they make. Since -- in the quantum world -- a single photon can exist in multiple locations, it becomes possible to create a complex pattern with a few photons, or even just one.
Due to the quantum properties of light, any attempt by a hacker to observe the Q&A exchange would, as physicists say, collapse the quantum nature of the light and destroy the information being transmitted. This makes Quantum-Secure Authentication unbreakable regardless of any future developments in technology.
Making Cards Quantum Secure
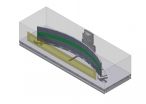
To provide security in the real world, a credit card -- for example -- would be equipped with a paper-thin section of white paint containing millions of nanoparticles. Using a laser, individual photons of light are projected into the paint where they bounce around the nanoparticles like metal balls in a pinball machine until they escape back to the surface, creating the pattern used to authenticate the card.
If "normal" light is projected onto the area, an attacker could measure the entering pattern and return the correct response pattern. A bank would therefore not be able to see a difference between the real card and the counterfeit signal projected by the attacker.
However, if a bank sends a pattern of single "quantum" photons into the paint, the reflected pattern would appear to have more information - or points of light - than the number of photons projected. An attacker attempting to intercept the "question" would destroy the quantum properties of the light and capture only a fraction of the information needed to authenticate the transaction.
"It would be like dropping 10 bowling balls onto the ground and creating 200 separate impacts," said Pinkse. "It's impossible to know precisely what information was sent (what pattern was created on the floor) just by collecting the 10 bowling balls. If you tried to observe them falling, it would disrupt the entire system."
Quantum, But Not Difficult
According to Pinkse, this unique way of providing security is suitable for protecting government buildings, bank cards, credit cards, identification cards, and even cars. "The best thing about our method is that secrets aren't necessary. So they can't be filched either," he said.
Quantum-Secure Authentication could be employed in numerous situations relatively easily, since it uses simple and cheap technology -- such as lasers and projectors -- that is already available.
INFORMATION:
Paper: S. A. Goorden, M. Horstmann, A. P. Mosk, B. Škorić and P. W. H. Pinkse, "Quantum-Secure Authentication of a Physical Unclonable Key," Optica, 1, 6, 421-424 (2014)
doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1364/OPTICA.1.000421
About Optica
Optica is an open-access, online-only journal dedicated to the rapid dissemination of high-impact peer-reviewed research across the entire spectrum of optics and photonics. Published monthly by The Optical Society (OSA), Optica provides a forum for pioneering research to be swiftly accessed by the international community, whether that research is theoretical or experimental, fundamental or applied. Optica maintains a distinguished editorial board of more than 20 associate editors from around the world and is overseen by Editor-in-Chief Alex Gaeta of Cornell University. For more information, visit http://optica.osa.org.
About OSA
Founded in 1916, The Optical Society (OSA) is the leading professional organization for scientists, engineers, students and entrepreneurs who fuel discoveries, shape real-life applications and accelerate achievements in the science of light. Through world-renowned publications, meetings and membership initiatives, OSA provides quality research, inspired interactions and dedicated resources for its extensive global network of optics and photonics experts. OSA is a founding partner of the National Photonics Initiative and the 2015 International Year of Light. For more information, visit http://www.osa.org.
A survey of more than 300 college students reveals that college students who use "fake weed" or synthetic THC are most likely to have tried the drug because they were curious. Rebecca Vidourek, a University of Cincinnati assistant professor of health promotion and assistant director of the Center for Prevention Science; Keith King, a UC professor of health promotion and director of the Center for Prevention Science; and Michelle Burbage, a graduate student and graduate assistant for UC's Health Promotion and Education Program, published their findings in the current issue ...
This news release is available in French. "Media reports about behavioural genetics unintentionally induce unfounded beliefs, therefore going against the educational purpose of scientific reporting," writes the University of Montreal's Alexandre Morin-Chassé, following his study of 1,500 Americans. "Among other things, we wanted to know if the public understood (or misunderstood) popular science articles about a new research field, genopolitics, and whether this popularization indeed helped people have an informed opinion on human genetics," Morin-Chassé explained.
The ...
This news release is available in German. The ways animals play with inedible objects may be precursors of functional behaviors such as tool use and goal directed object manipulation. For these reasons, species of high technical intelligence are also expected to play intensely with inanimate objects when no obvious goal is pursued. Within object play, combinatory actions are considered a particularly informative trait in animals as well as human infants: Children start bashing two objects together when they are about 8 months old, at 10 months, they combine toys with ...
A study conducted by University of Granada scientists (from the Physiology, Obstetrics and Gynaecology Departments) and from the San Cecilio Clinical Hospital (Granada) has demonstrated that delaying the cutting of the umbilical cord in newborns by two minutes leads to a better development of the baby during the first days of life.
This multidisciplinary work, published in the prestigious journal Pediatrics reveals that the time in cutting the umbilical cord (also called umbilical cord clampling) influences the resistance to oxidative stress in newborns.
For this research, ...
In medicine, X-rays provide high-resolution images of our insides to help doctors make a definitive diagnosis. Industry uses X-rays, too - as a reliable, non-destructive way of seeing what's hidden on inside materials and components and to check for cracks or irregularities. However industry additionally draws upon different technologies that are not used in the medical field. Whereas medical X-ray machines have been specifically designed for human test subjects, industrial X-ray machines are used to analyze objects that vary much more in their size and material composition. ...
MANHASSET, NY -- Molecular Medicine, a peer-reviewed biomedical journal published by the Feinstein Institute Press, published the results of a new study reporting clinically significant pain reduction in type 2 diabetic patients. In an exploratory study conducted by Araim Pharmaceuticals, a biotech company developing novel treatments for chronic diseases, investigators also observed improvements in metabolic control in patients administered ARA 290. ARA 290 is a peptide engineered to activate the innate repair receptor, a receptor discovered by Araim scientists, which is ...
Scientists at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) in Germany have discovered a new signal pathway in the brain that plays an important role in learning and the processing of sensory input. It was already known that distinct glial cells receive information from neurons. However, it was unknown that these same glial cells also transmit information to neurons. The glia release a specific protein fragment that influences neuronal cross-talk, most likely by binding to the synaptic contacts that neurons use for communication. Disruption of this information flow from the ...
New research led by the University of Exeter has found that people who have a stronger sense of place at the global than the national level are more likely to accept that climate change is caused by human activities. This is the first time that acceptance of human causes of climate change has been shown to be linked to people's sense of place at the global level. The findings have significant implications both for climate change communications and for our understanding of place and identities.
The study 'My country or my planet? Exploring the influence of multiple place ...
BLOOMINGTON, Ind. -- Scientists at Indiana University and colleagues at Stanford and the University of Texas have demonstrated a technique for "editing" the genome in sperm-producing adult stem cells, a result with powerful potential for basic research and for gene therapy.
The researchers completed a "proof of concept" experiment in which they created a break in the DNA strands of a mutant gene in mouse cells, then repaired the DNA through a process called homologous recombination, replacing flawed segments with correct ones.
The study involved spermatogonial stem ...
Patients with Parkinson's, medics and carers have identified the top ten priorities for research into the management of the condition in a study by the University of East Anglia and Parkinson's UK.
Commissioned by Parkinson's UK, people with direct and indirect personal experience of the condition worked together to identify crucial gaps in the existing evidence to address everyday practicalities in the management of the complexities of Parkinson's. Patients stated that the overarching research aspiration was an effective cure for Parkinson's but whilst waiting for this ...