Ocean pipes 'not cool,' would end up warming climate
2015-03-19
(Press-News.org) Washington, D.C.--To combat global climate change caused by greenhouse gases, alternative energy sources and other types of environmental recourse actions are needed. There are a variety of proposals that involve using vertical ocean pipes to move seawater to the surface from the depths in order to reap different potential climate benefits. A new study from a group of Carnegie scientists determines that these types of pipes could actually increase global warming quite drastically. It is published in Environmental Research Letters.
One proposed strategy--called Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion, or OTEC--involves using the temperature difference between deeper and shallower water to power a heat engine and produce clean electricity. A second proposal is to move carbon from the upper ocean down into the deep, where it wouldn't interact with the atmosphere. Another idea, and the focus of this particular study, proposes that ocean pipes could facilitate direct physical cooling of the surface ocean by replacing warm surface ocean waters with colder, deeper waters.
"Our prediction going into the study was that vertical ocean pipes would effectively cool the Earth and remain effective for many centuries," said Ken Caldeira, one of the three co-authors.
The team, which also included lead author Lester Kwiatkowski as well as Katharine Ricke, configured a model to test this idea and what they found surprised them. The model mimicked the ocean-water movement of ocean pipes if they were applied globally reaching to a depth of about a kilometer (just over half a mile). The model simulated the motion created by an idealized version of ocean pipes, not specific pipes. As such the model does not include real spacing of pipes, nor does it calculate how much energy they would require.
Their simulations showed that while global temperatures could be cooled by ocean pipe systems in the short term, warming would actually start to increase just 50 years after the pipes go into use. Their model showed that vertical movement of ocean water resulted in a decrease of clouds over the ocean and a loss of sea-ice.
Colder air is denser than warm air. Because of this, the air over the ocean surface that has been cooled by water from the depths has a higher atmospheric pressure than the air over land. The cool air over the ocean sinks downward reducing cloud formation over the ocean. Since more of the planet is covered with water than land, this would result in less cloud cover overall, which means that more of the Sun's rays are absorbed by Earth, rather than being reflected back into space by clouds.
Water mixing caused by ocean pipes would also bring sea ice into contact with warmer waters, resulting in melting. What's more, this would further decrease the reflection of the Sun's radiation, which bounces off ice as well as clouds.
After 60 years, the pipes would cause an increase in global temperature of up to 1.2 degrees Celsius (2.2degrees Fahrenheit). Over several centuries, the pipes put the Earth on a warming trend towards a temperature increase of 8.5 degrees Celsius (15.3 degrees Fahrenheit).
"I cannot envisage any scenario in which a large scale global implementation of ocean pipes would be advisable," Kwiatkowski said. "In fact, our study shows it could exacerbate long-term warming and is therefore highly inadvisable at global scales."
The authors do say, however, that ocean pipes might be useful on a small scale to help aerate ocean dead zones.
INFORMATION:
A video abstract of the paper is available here: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SenVhmsfze4
The Carnegie Institution for Science is a private, nonprofit organization headquartered in Washington, D.C., with six research departments throughout the U.S. Since its founding in 1902, the Carnegie Institution has been a pioneering force in basic scientific research. Carnegie scientists are leaders in plant biology, developmental biology, astronomy, materials science, global ecology, and Earth and planetary science.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-03-19
What if there were a pill that made you more compassionate and more likely to give spare change to someone less fortunate? UC Berkeley scientists have taken a big step in that direction.
A new study by UC Berkeley and UC San Francisco researchers finds that giving a drug that changes the neurochemical balance in the prefrontal cortex of the brain causes a greater willingness to engage in prosocial behaviors, such as ensuring that resources are divided more equally.
The researchers also say that future research may lead to a better understanding of the interaction between ...
2015-03-19
URBANA, Ill. - Over the last several decades there have been substantial yield improvements in soybean. Because of new varieties and new agronomic practices, the yield potential in soybean is higher now than ever before. But a lack of updated information on the nutritional needs of soybean crops may be limiting the crop's potential.
Researchers from the University of Illinois Crop Physiology Laboratory led by Fred Below have recently provided an updated set of nutrition needs for soybean, identifying exactly which nutrients the plant needs, when those nutrients are accumulated ...
2015-03-19
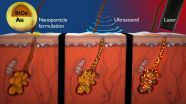
Acne, a scourge of adolescence, may be about to meet its ultra high-tech match. By using a combination of ultrasound, gold-covered particles and lasers, researchers from UC Santa Barbara and the private medical device company Sebacia have developed a targeted therapy that could potentially lessen the frequency and intensity of breakouts, relieving acne sufferers the discomfort and stress of dealing with severe and recurring pimples.
"Through this unique collaboration, we have essentially established the foundation of a novel therapy," said Samir Mitragotri, professor ...
2015-03-19
Our eyes are drawn to several dimensions of an object--such as color, texture, and luminance--even when we need to focus on only one of them, researchers at New York University and the University of Pennsylvania have found. The study, which appears in the journal Current Biology, points to the ability of our visual system to integrate multiple components of an item while underscoring the difficulty we have in focusing on a particular aspect of it.
"Even when we want and need to focus on one dimension of things we come across every day, such as the texture of your cat's ...
2015-03-19
For in vitro fertilization and other assisted reproductive technologies, selecting the healthiest and best swimming sperm from a sample of semen can dramatically increase success. Microfluidics--micro-scale technologies that were originally developed to enable high-throughput gene sequencing and for Point-Of-Care diagnostics--are now being adapted to enhance sperm sorting. These new methods, reviewed by engineers in the journal Trends in Biotechnology, are generating promising results in applications such as single-sperm genomics, in-home male fertility testing, and wildlife ...
2015-03-19
A combination of human stem cell transplantation and antidiabetic drugs proved to be highly effective at improving body weight and glucose metabolism in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes. The findings, published March 19th by Stem Cell Reports, could set the stage for clinical trials to test the first stem cell-based approach for insulin replacement in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Type 2 diabetes, which accounts for 90%-95% of the now approaching 400 million cases of diabetes worldwide, is currently treated by oral medication, insulin injections, or both to control blood ...
2015-03-19
Altered signaling through the vitamin D receptor on certain immune cells may play a role in causing the chronic inflammation that leads to cardiometabolic disease, the combination of type 2 diabetes and heart disease that is the most common cause of illness and death in Western populations. The research appears March 19 in the journal Cell Reports.
"Because low vitamin D levels are associated with diabetes and heart disease, we looked at the connections between vitamin D, immune function, and these disease states," says senior author Carlos Bernal-Mizrachi, of the Washington ...
2015-03-19
Scientists at the University of British Columbia and BetaLogics, part of Janssen Research & Development, LLC have shown for the first time that Type 2 diabetes can be effectively treated with a combination of specially-cultured stem cells and conventional diabetes drugs.
Stem cells - generic cells that haven't yet taken on specialized form and function - have recently been used by scientists at UBC and elsewhere to reverse Type 1 diabetes in mice. In Type 1 diabetes, which usually begins in childhood, the pancreas produces little or no insulin, the hormone that enables ...
2015-03-19
A research team at UC San Francisco has discovered an RNA molecule called Pnky that can be manipulated to increase the production of neurons from neural stem cells.
The research, led by neurosurgeon Daniel A. Lim, MD, PhD, and published on March 19, 2015 in Cell Stem Cell, has possible applications in regenerative medicine, including treatments of such disorders as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease and traumatic brain injury, and in cancer treatment.
Pnky is one of a number of newly discovered long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs), which are stretches of 200 or more ...
2015-03-19
A new study has shown that the dottyback, a small predatory reef fish, can change the colour of its body to imitate a variety of other reef fish species, allowing the dottyback to sneak up undetected and eat their young.
The dottyback also uses its colour-changing abilities to hide from larger predators by colour-matching to the background of its habitat - disappearing into the scenery.
The research, published today in the journal Current Biology, reveals a sophisticated new example of 'mimicry': disguising as a different species to gain evolutionary advantage. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Ocean pipes 'not cool,' would end up warming climate