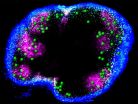
In Alzheimer's mice, memory restored with cancer drug
2015-03-31
(Press-News.org) Memory and as well as connections between brain cells were restored in mice with a model of Alzheimer's given an experimental cancer drug, Yale School of Medicine researchers reported in the journal Annals of Neurology.
The drug, AZD05030, developed by Astra Zeneca proved disappointing in treating solid tumors but appears to block damage triggered during the formation of amyloid-beta plaques, a hallmark of Alzheimer's disease. The new study, funded by an innovative National Institutes of Health (NIH) program to test failed drugs on different diseases, has led to the launch of human trials to test the efficacy of AZD05030 in Alzheimer's patients.
"With this treatment, cells under bombardment by beta amyloid plaques show restored synaptic connections and reduced inflammation, and the animal's memory, which was lost during the course of the disease, comes back," said Stephen M. Strittmatter, the Vincent Coates Professor of Neurology and senior author of the study.
In the last five years, scientists have developed a more complete understanding of the complex chain of events that leads to Alzheimer's disease. The new drug blocks one of those molecular steps, activation of the enzyme FYN, which leads to the loss of synaptic connections between brain cells. Several other steps in the disease process have the potential to be targets for new drugs, Strittmatter said.
"The speed with which this compound moved to human trials validates our New Therapeutic Uses program model and serves our mission to deliver more treatments to more patients more quickly," said Christopher P. Austin, M.D., director of NIH's National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS), which funded the work.
INFORMATION:
Yale's Christopher H. van Dyck, a co-author of the paper, and Strittmatter have initiated a multi-site clinical trial to determine whether the drug can also benefit Alzheimer's patients. For more information, visit https://clinicaltrials.gov/ (NCT02167256 and NCT01864655).
The study was funded by the NCATS and the NIH Common Fund, through the Office of Strategic Coordination/Office of the NIH Director
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-03-31
Study the label of almost any food product and you're likely to see the rather vague warning "May contain peanuts" somewhere on there, unless of course it's a product that definitely does contain peanuts. As now revealed in a paper in the latest issue of JNIRS--Journal of Near Infrared Spectroscopy, these warnings of peanut contamination could soon lose much of their uncertainty, thanks to a novel form of near infrared (NIR) spectroscopy known as NIR hyperspectral imaging (HSI).
Any food product may contain traces of peanut if it is made with powdered foodstuffs like ...
2015-03-31
March 31, 2015 - For chronically ill patients with major depression, an approach to cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) that incorporates patients' religious beliefs is at least as effective as conventional CBT, suggests a study in the April issue of The Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease. The journal is published by Wolters Kluwer.
"Integrating religious clients' beliefs into CBT does not appear to significantly reduce its effectiveness, especially in religious clients," write Dr Harold Koenig of Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C., and colleagues. They ...
2015-03-31
Research by Johns Hopkins scientists suggests that having a short series of phone conversations with trained counselors can substantially boost recovery and reduce pain in patients after spinal surgery.
The phone calls, designed to enrich standard pre- and post-operative care by reinforcing the value of sticking with physical therapy and back-strengthening exercise regimens, are a relatively inexpensive and simple intervention that can maximize surgical outcomes for the hundreds of thousands of Americans who undergo spinal surgeries every year, the investigators say.
A ...
2015-03-31
Lung diseases like emphysema and pulmonary fibrosis are common among people with malfunctioning telomeres, the "caps" or ends of chromosomes. Now, researchers from Johns Hopkins say they have discovered what goes wrong and why.
Mary Armanios, M.D., an associate professor of oncology at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine., and her colleagues report that some stem cells vital to lung cell oxygenation undergo premature aging -- and stop dividing and proliferating -- when their telomeres are defective. The stem cells are those in the alveoli, the tiny air exchange ...
2015-03-31
Increasing state alcohol taxes could prevent thousands of deaths a year from car crashes, say University of Florida Health researchers, who found alcohol-related motor vehicle crashes decreased after taxes on beer, wine and spirits went up in Illinois.
A team of UF Health researchers discovered that fatal alcohol-related car crashes in Illinois declined 26 percent after a 2009 increase in alcohol tax. The decrease was even more marked for young people, at 37 percent.
The reduction was similar for crashes involving alcohol-impaired drivers and extremely drunken drivers, ...
2015-03-31
Soil organic matter, long thought to be a semi-permanent storehouse for ancient carbon, may be much more vulnerable to climate change than previously thought.
Plants direct between 40 percent and 60 percent of photosynthetically fixed carbon to their roots and much of this carbon is secreted and then taken up by root-associated soil microorganisms. Elevated carbon dioxide (CO2) concentrations in the atmosphere are projected to increase the quantity and alter the composition of root secretions released into the soil.
In new research in the March 30 edition of the journal, ...
2015-03-31
CAMBRIDGE, Mass--Sitting in traffic during rush hour is not just frustrating for drivers; it also adds unnecessary greenhouse gas emissions to the atmosphere.
Now a study by researchers at MIT could lead to better ways of programming a city's stoplights to reduce delays, improve efficiency, and reduce emissions.
The new findings are reported in a pair of papers by assistant professor of civil and environmental engineering Carolina Osorio and alumna Kanchana Nanduri SM '13, published in the journals Transportation Science and Transportation Research: Part B. In these ...
2015-03-31
Australian scientists have discovered a new population of 'memory' immune cells, throwing light on what the body does when it sees a microbe for the second time. This insight, and others like it, will enable the development of more targeted and effective vaccines.
Two of the key players in our immune systems are white blood cells known as 'T cells' and 'B cells'. B cells make antibodies, and T cells either help B cells make antibodies, or else kill invading microbes. B cells and killer T cells are known to leave behind 'memory' cells to patrol the body, after they have ...
2015-03-31
At some point, probably 50,000 to 100,000 years ago, humans began talking to one another in a uniquely complex form. It is easy to imagine this epochal change as cavemen grunting, or hunter-gatherers mumbling and pointing. But in a new paper, an MIT linguist contends that human language likely developed quite rapidly into a sophisticated system: Instead of mumbles and grunts, people deployed syntax and structures resembling the ones we use today.
"The hierarchical complexity found in present-day language is likely to have been present in human language since its emergence," ...
2015-03-31
Alcoholism takes a toll on every aspect of a person's life, including skin problems. Now, a new research report appearing in the April 2015 issue of the Journal of Leukocyte Biology, helps explain why this happens and what might be done to address it. In the report, researchers used mice show how chronic alcohol intake compromises the skin's protective immune response. They also were able to show how certain interventions may improve the skin's immune response. Ultimately, the hope is that this research could aid in the development of immune-based therapies to combat skin ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] In Alzheimer's mice, memory restored with cancer drug