(Press-News.org) DURHAM, N.C. - An estimated 9 percent of adults in the U.S. have a history of impulsive, angry behavior and have access to guns, according to a study published this month in Behavioral Sciences and the Law. The study also found that an estimated 1.5 percent of adults report impulsive anger and carry firearms outside their homes.
Angry people with ready access to guns are typically young or middle-aged men, who at times lose their temper, smash and break things, or get into physical fights, according to the study co-authored by scientists at Duke, Harvard, and Columbia universities.
Study participants who owned six or more firearms were also far more likely than people with only one or two firearms to carry guns outside the home and to have a history of impulsive, angry behavior.
"As we try to balance constitutional rights and public safety regarding people with mental illness, the traditional legal approach has been to prohibit firearms from involuntarily-committed psychiatric patients," said Jeffrey Swanson, Ph.D., professor in psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Duke Medicine and lead author of the study.
"But now we have more evidence that current laws don't necessarily keep firearms out of the hands of a lot of potentially dangerous individuals."
The researchers analyzed data from 5,563 face-to-face interviews conducted in the National Comorbidity Study Replication (NCS-R), a nationally representative survey of mental disorders in the U.S. led by Harvard in the early 2000s.
The study found little overlap between participants with serious mental illnesses and those with a history of impulsive, angry behavior and access to guns.
"Gun violence and serious mental illness are two very important but distinct public health issues that intersect only at their edges," Swanson said.
Researchers found that anger-prone people with guns were at elevated risk for a range of fairly common psychiatric conditions such as personality disorders, alcohol abuse, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress, while only a tiny fraction suffered from acute symptoms of major disorders such as schizophrenia and bipolar disorder.
Fewer than one in 10 angry people with access to guns had ever been admitted to a hospital for a psychiatric or substance abuse problem, the study found. As a result, most of these individuals' medical histories wouldn't stop them from being able to legally purchase guns under existing mental-health-related restrictions.
"Very few people in this concerning group suffer from the kinds of disorders that often lead to involuntary commitment and which would legally prohibit them from buying a gun," said Ronald Kessler, Ph.D., professor of health care policy at Harvard and principal investigator of the NCS-R survey.
Kessler, Swanson and co-authors reason that looking at a prospective gun buyer's history of misdemeanor convictions, including violent offenses and multiple convictions for impaired driving, could be more effective at preventing gun violence in the U.S. than screening based on mental health treatment history.
As for those who already own or have access to firearms, the researchers suggest the data could support "dangerous persons" gun removal laws, like those in Connecticut and Indiana, or a "gun violence restraining order" law like California recently enacted. Such laws give family members and law enforcement a legal tool to immediately seize guns and prevent gun or ammunition purchases by people who show warning signs of impending violence.
In 2012, more than 59,000 people were injured by the intentional use of firearms, and another 11,622 were killed in violent gun incidents, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
INFORMATION:
The Duke, Harvard, and Columbia analysis appears in a special issue of the journal Behavioral Sciences and the Law that focuses on mental illness and gun violence. The article presents the first national estimates of the number of people who have access to guns and who also have a history of angry, impulsive behavior, with or without a diagnosable mental illness.
In addition to Swanson and Kessler, study authors include Nancy A. Sampson, Maria V. Petukhova, and Alan M. Zaslavsky of Harvard; Paul S. Appelbaum of Columbia; and Marvin S. Swartz of Duke.
The original survey used in the study, the NCS-R, is supported by the National Institute of Mental Health (U01-MH60220) with supplemental support from the National Institute on Drug Abuse, the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation (044780), the John W. Alden Trust, and the Elizabeth K. Dollard Trust.
Amsterdam, The Netherlands, April 8, 2015 -- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the most common cause of chronic liver disease in the western world. A new study published in the Journal of Hepatology shows that exercise, regardless of frequency or intensity, benefits obese and overweight adults with NAFLD.
NAFLD is considered the hepatic manifestation of metabolic syndrome and is commonly associated with obesity and diabetes. There are no approved drug treatments for NAFLD, but lifestyle interventions such as diet, exercise, and the resulting weight loss have ...
A July, 2014 Call to Action to Prevent Skin Cancer by acting Surgeon General Dr. Boris Lushniak points out that indoor tanning is "strongly associated with increased skin cancer risk," but stops short of reporting that tanning causes cancer. A University of Colorado Cancer Center opinion published today in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine points out that UV tanning meets the same criteria as smoking as a cause of cancer and argues that announcing the causality could save lives.
"In 1964 when the Surgeon General finally reported that smoking causes lung cancer, ...
The secret communication of gibbons has been interpreted for the first time in a study published in the open access journal BMC Evolutionary Biology. The research reveals the likely meaning of a number of distinct gibbon whispers, or 'hoo' calls, responding to particular events and types of predator, and could provide clues on the evolution of human speech.
While lar gibbons (Hylobates lar) are mainly known for their loud and conspicuous songs, they can also produce a number of soft call types known as 'hoo's. These subtle calls have been alluded to in studies dating ...
Life has adapted to all sorts of extreme environments on Earth, among them, animals like the deer mouse, shimmying and shivering about, and having to squeeze enough energy from the cold, thin air to fuel their bodies and survive.
Now, in a new publication in the journal Molecular Biology and Evolution, Scott, Cheviron et al., have examined the underlying muscle physiology from a group of highland and lowland deer mice. Deer mice were chosen because they exhibit the most extreme altitude range of any North American mammal, occurring below sea levels in Death Valley to ...
Cold Spring Harbor, NY - The prefrontal cortex (PFC) plays an important role in cognitive functions such as attention, memory and decision-making. Faulty wiring between PFC and other brain areas is thought to give rise to a variety of cognitive disorders. Disruptions to one particular brain circuit--between the PFC and another part of the brain called the thalamus--have been associated with schizophrenia, but the mechanistic details are unknown. Now, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory scientists have discovered an inhibitory connection between these brain areas in mice that ...
The Burgess Shale Formation, in the Canadian Rockies of British Columbia, is one of the most famous fossil locations in the world. A recent Palaeontology study introduces a 508 million year old (middle Cambrian) arthropod--called Yawunik kootenayi--from exceptionally preserved specimens of the new Marble Canyon locality within the Burgess Shale Formation.
Its frontal appendage--the "megacheiran great appendage"--is remarkably adorned with teeth, emphasizing an advanced predatory function. The appendage also had long hair-like flagella at the end that likely served a sensory ...
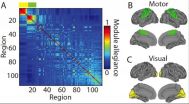
Why do some people learn a new skill right away, while others only gradually improve? Whatever else may be different about their lives, something must be happening in their brains that captures this variation.
Researchers at the University of Pennsylvania, the University of California, Santa Barbara, and Johns Hopkins University have taken a network science approach to this question. In a new study, they measured the connections between different brain regions as participants learned to play a simple game. The differences in neural activity between the quickest and slowest ...
The results appear in the 2015 2nd issue of the journal of Human Genome Variation. To see a video about the partnership between Champions and Insilico, visit: http://tinyurl.com/InsilicoChampions .
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third most commonly diagnosed cancer and the second leading cause of cancer deaths in the United States. More than 50,000 people die of CRC each year due to tumor spreading to other organs and almost half of all newly diagnosed patients are in an advanced stage of cancer (metastatic CRC or mCRC) when they are first diagnosed.
With the development ...
A Northwestern University research team potentially has found a safer way to keep blood vessels healthy during and after surgery.
During open-heart procedures, physicians administer large doses of a blood-thinning drug called heparin to prevent clot formation. When given too much heparin, patients can develop complications from excessive bleeding. A common antidote is the compound protamine sulfate, which binds to heparin to reverse its effects.
"Protamine is a natural compound that has been used in surgeries for many decades," said Guillermo Ameer, professor of biomedical ...
The combination of two well-known drugs will have unprecedented effects on pain management, says new research from Queen's.
Combining morphine, a narcotic pain reliever, and nortriptyline, an antidepressant, has been found to successfully relieve chronic neuropathic pain - or a localized sensation of pain due to abnormal function of the nervous system - in 87 per cent of patients, and significantly better than with either drug alone.
"Chronic pain is an increasingly common problem and can exert disastrous personal, societal, and socio-economic impacts on patients, their ...