NASA analyzes rainfall in Tropical Cyclone Joalane
2015-04-08
(Press-News.org) NASA and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's GPM satellite provided scientists with a look "under the hood" of Tropical Cyclone Joalane's clouds at the rate in which rain was falling throughout the storm.
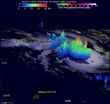
The Global Precipitation Measurement or GPM core observatory satellite flew over intensifying cyclone Joalane in the South Indian Ocean on April 6, 2015 at 0406 UTC (12:06 a.m. EDT). GPM's Microwave Imager (GMI) found that intense convective thunderstorms within Joalane were dropping rain at a rate of over 63 mm (2.5 inches) per hour.
Cyclone Joalane was located northeast of Mauritius at the time of that GPM pass. At NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland a 3-D view of Joalane's vertical precipitation structure was constructed using GPM's Radar (Ku Band) data. This cross section showed that several towering thunderstorms near Joalane's center were reaching heights of over 15 km (9.3 miles). A few storm tops in a strong rain band south of Joalane's center were found reaching even higher to altitudes of 17.4 km (10.8 miles).
Two days later, on April 8 at 09:35 UTC (5:35 a.m. EDT) the MODIS instrument that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured a visible light image of Tropical Cyclone Joalane that showed the storm maintained an eye that it developed the previous day. Bands of thunderstorms wrapped into the center of circulation. The largest, thickest band of thunderstorms appeared on the eastern side of the center.
At 1500 UTC (11 a.m. EDT) on April 8, 2015, Tropical Cyclone Joalane's maximum sustained winds were near 90 knots (103.5 mph/166.7 kph). It was centered near 15.6 south and 64.9 east, about 624 nautical miles (718.1 miles/1,156 km) east-northeast of St. Denis. Joalane is moving to the southeast at 9 knots (10.3 mph/16.6 kph). At that time, there were no tropical cyclone warnings in effect for Rodrigues Island.
Tropical Cyclone Joalane has intensified and the Joint Typhoon Warning Center forecast a southeastern track through the Southern Indian Ocean. Joalane is expected to weaken to a tropical storm by April 13.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-04-08
Scientists who have spent much of their careers peering out of deep-sea submersibles to learn about deep-sea coral and sponges recently turned their attention to the Web, watching each other share their experiences and expertise through an innovative series of online seminars.
The seminars, sponsored by NOAA Fisheries, are now publicly available online. They cover the latest research into the fragile corals and sponges that bring color, habitat, and three-dimensional beauty to the deep ocean floor, far beyond the reach of snorkelers or scuba divers.
The web-based seminars ...
2015-04-08
In a study that included more than 32,000 cases of melanoma among Medicare patients, approximately 1 in 5 experienced a delay of surgery that was longer than 1.5 months, and about 8 percent of patients waited longer than 3 months for surgery, according to an article published online by JAMA Dermatology.
Melanoma is a leading cause of new cancer diagnoses in the United States, accounting for most skin cancer¬related deaths. Surgical excision is the primary therapy for melanoma. Surgical delay may result in the potential for increased illness and death from other malignant ...
2015-04-08
African-American women who live in rural areas have lower rates of major depressive disorder (MDD) and mood disorder compared with their urban counterparts, while rural non-Hispanic white women have higher rates for both than their urban counterparts, according to an article published online by JAMA Psychiatry.
MDD is a common and debilitating mental illness and the prevalence of depression among both African Americans and rural residents is understudied, according to background in the study.
Addie Weaver, Ph.D., of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and coauthors ...
2015-04-08
A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)-based screening program for individuals at high risk of pancreatic cancer identified pancreatic lesions in 16 of 40 (40 percent) of patients, of whom 5 five underwent surgery, according to a report published online by JAMA Surgery.
Pancreatic cancer is a leading cause of cancer death and can be considered a global lethal disease because incidence and mortality rates are nearly identical. Although treatment has improved, the surgery rate in patients with ductal adenocarcinoma is around 30 percent and the five-year survival rate is less ...
2015-04-08
New Haven, Conn. -- One in five Medicare patients with melanoma experience delays in getting surgery, a Yale study found.
The research was published April 8 in JAMA Dermatology.
Melanoma, a type of skin cancer, is a leading cause of new cancer diagnoses in the United States. A delay between diagnosis and surgery to remove melanomas may cause patients psychological harm and affect health-care quality. Using the national Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Result-Medicare database, the Yale team conducted the first population-based analysis of delay of surgery among Medicare ...
2015-04-08
DENVER - The Women's Health Initiative Studies, a large prospective study of lung cancer, found no strong associations between lung cancer risk and a wide range of reproductive history variables and only revealed weak support for a role of hormone use in the incidence of lung cancer.
In the United States 40% of the 160,000 deaths from lung cancer are women. In men 90% of lung cancer deaths are associated with tobacco usage; however in women this number is around 75-80%. Female never-smokers are more likely to develop lung cancer than male never-smokers and the histological ...
2015-04-08
The discovery of antibiotics produced by soil fungi and bacteria gave the world life-saving medicine. But new antimicrobials from this resource have become scarce as the threat of drug resistance grows. Now, scientists have started mining lakes and rivers for potential pathogen-fighters, and they've found one from Lake Michigan that is effective against drug-resistant tuberculosis. Their report on the new compound appears in the journal ACS Infectious Diseases.
Brian T. Murphy and colleagues point out that the emergence of drug-resistant strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis ...
2015-04-08
COLLEGE PARK, Md. - Companies work fairly hard to place one woman -- but only one -- in a top management position, according to research by Cristian Desz?, an associate professor at the Robert H. Smith School of Business, and two co-authors. The article found evidence of a "quota" effect: Once a company had appointed one woman to a top-tier job, the chances of a second woman landing an elite position at the same firm drop substantially -- by about 50 percent, in fact.
The study's design did not allow a conclusion about whether the quota was the result of conscious discrimination ...
2015-04-08
Now that most consumers download and stream their movies and music, more and more CDs and DVDs will end up in landfills or be recycled. But soon these discarded discs could take on a different role: curbing the release of greenhouse gases. In the journal ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, scientists report a way to turn the discs into a material that can capture carbon dioxide, a key greenhouse gas, and other compounds.
Mietek Jaroniec and colleagues from Poland and the U.S. note that manufacturers typically use natural sources, such as coal and wood, to make activated ...
2015-04-08
Figuring out why the French have low cardiovascular disease rates despite a diet high in saturated fats has spurred research and many theories to account for this phenomenon known as the "French paradox." Most explanations focus on wine and lifestyle, but a key role could belong to another French staple: cheese. The evidence, say scientists in ACS' Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, is in cheese metabolism.
Hanne Bertram and colleagues note that recent research on some dairy products' positive effects on health has cast doubt on the once-firm rule that saturated ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] NASA analyzes rainfall in Tropical Cyclone Joalane