INFORMATION:
The Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute, headquartered in Panama City, Panama, is a unit of the Smithsonian Institution. The institute furthers the understanding of tropical nature and its importance to human welfare, trains students to conduct research in the tropics and promotes conservation by increasing public awareness of the beauty and importance of tropical ecosystems. Website: http://www.stri.si.edu
C. Montes, A. Cardona, C. Jaramillo, A. Pardo, J.C. Silva, V. Valencia, C. Ayala, L.C. Pérez-Angel, L.A. Rodriguez-Parra, V. Ramirez, H. Niño. 2015. Middle Miocene closure of the Central American Seaway. Science. April 10.
Smithsonian's Panama debate fueled by zircon dating
2015-04-10
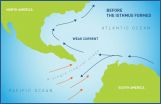
(Press-News.org) New evidence published in Science by Smithsonian geologists dates the closure of an ancient seaway at 13 to 15 million years ago and challenges accepted theories about the rise of the Isthmus of Panama and its impact on world climate and animal migrations.
A team analyzed zircon grains from rocks representing an ancient sea and riverbeds in northwestern South America. The team was led by Camilo Montes, former director of the Panama Geology Project at the Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute. He is now at the Universidad de los Andes.
The team's new date for closure of the Central American Seaway, from 13 to 15 million years ago, conflicts with the widely accepted 3 million year date for the severing of all connections between the Atlantic and the Pacific, the result of work done by the Panama Paleontology Project, directed by emeritus scientists Jeremy B.C. Jackson and Anthony Coates, also at the Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute.
If a land connection was complete by this earlier date, the rise of the Isthmus of Panama from the sea by tectonic and volcanic action predates the movement of animals between continents known as the Great American Biotic Interchange. The rise of the Isthmus is implicated in major shifts in ocean currents, including the creation of the Gulf Stream that led to warmer temperatures in northern Europe and the formation of a great ice sheet across North America.
"Beds younger than about 13 to 15 million years contain abundant zircon grains with a typically Panamanian age," said Montes. "Older beds do not. We think these zircons were deposited by rivers flowing from the Isthmus of Panama when it docked to South America, nearly 10 million years earlier than the date of 3 million years that is usually given for the connection."
The new model sends scientists like the University of Colorado at Boulder's Peter Molnar off to look for other explanations for climate change. Molnar wrote in the journal Paleoceanography, "...let me state that the closing of the Central America Seaway seems to be no more than a bit player in global climate change. Quite likely it is a red herring."
"What is left now is to rethink what else could have caused such dramatic global processes nearly 3 million years ago," said Carlos Jaramillo, Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute scientist and member of the research team.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Dynamic dead zones alter fish catches in Lake Erie
2015-04-09
New research shows that Lake Erie's dead zones are actually quite active, greatly affecting fish distributions, catch rates and the effectiveness of fishing gear.
Scientists with the U.S. Geological Survey, the Illinois-Indiana Sea Grant and partners recently found that dead zones caused by hypoxia, the depletion of oxygen in water, are unexpectedly variable in Lake Erie, sometimes disappearing and reemerging elsewhere in the matter of hours. They also found that fish like yellow perch cluster at the edges of these areas. The discovery of erratic dead zones can help ...
Carnegie Mellon scientists question representation of women in international journal
2015-04-09
PITTSBURGH-- Three leading cognitive scientists from Carnegie Mellon University are questioning the gender representation of invited contributors in the special February 2015 issue, "The Changing Face of Cognition," published by the international journal Cognition.
Cognition, a highly regarded scientific journal, publishes theoretical and experimental papers on the study of the mind - a topic that has been a research strength of CMU for decades and that is receiving intense focus through the federal government's BRAIN Initiative.
In an opinion piece to appear in Cognition, ...
Early physical therapy for low back pain reduces costs, resources
2015-04-09
A study in the scientific journal BMC Health Services Research shows that early and guideline adherent physical therapy following an initial episode of acute, nonspecific low back pain (LBP) resulted in substantially lower costs and reduced use of health care resources over a 2-year period.
Physical therapist researchers John D. Childs, PT, PhD, et al analyzed 122,723 patients who went to a primary care physician following an initial LBP episode and received physical therapy within 90 days. Of these, 24% (17,175) received early physical therapy (within 14 days) that adhered ...
Who's a CEO? Google image results can shift gender biases
2015-04-09
Getty Images last year created a new online image catalog of women in the workplace - one that countered visual stereotypes on the Internet of moms as frazzled caregivers rather than powerful CEOs.
A new University of Washington study adds to those efforts by assessing how accurately gender representations in online image search results for 45 different occupations match reality.
In a few jobs -- including CEO -- women were significantly underrepresented in Google image search results, the study found, and that can change searchers' worldviews. Across all the professions, ...
TGen finds likely genetic source of muscle weakness in 6 previously undiagnosed children
2015-04-09
PHOENIX, Ariz. -- April 9, 2015 -- Scientists at the Translational Genomics Research Institute (TGen), using state-of-the-art genetic technology, have discovered the likely cause of a child's rare type of severe muscle weakness.
The child was one of six cases in which TGen sequenced -- or decoded -- the genes of patients with Neuromuscular Disease (NMD) and was then able to identify the genetic source, or likely genetic source, of each child's symptoms, according to a study published April 8 in the journal Molecular Genetics & Genomic Medicine.
"In all six cases of ...
Golgi trafficking controlled by G-proteins
2015-04-09
A family of proteins called G proteins are a recognized component of the communication system the human body uses to sense hormones and other chemicals in the bloodstream and to send messages to cells. In work that further illuminates how cells work, researchers at University of California, San Diego School of Medicine have discovered a new role for G proteins that may have relevance to halting solid tumor cancer metastasis.
The study is reported online April 9 in Developmental Cell.
"Our work provides the first direct evidence that G proteins are signaling on membranes ...
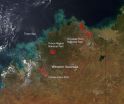
Fires in Western Australia April 2015
2015-04-09
Bushfires are inevitable in the fire-prone landscapes of Western Australia. Long dry summers, vegetation and undergrowth, and ignition from lightning or human causes mean that bushfires can and do occur every summer.
A bushfire is an unplanned fire (in the U.S. this is referred to as a wildfire). Each year Australia's Department of Parks and Wildlife responds to more than 600 bushfires that occur on or near land managed by the department. Bushfires have many causes, some natural such as lightning and some as a result of human activity such as camp fires, escapes from ...
Mental practice and physical therapy effective treatment for stroke, research shows
2015-04-09
ATLANTA--A combination of mental practice and physical therapy is an effective treatment for people recovering from a stroke, according to researchers at Georgia State University.
The findings, published on March 30 in the journal Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, examine how the brains of stroke patients change after treatment.
Mental practice and physical therapy are interventions used to improve impaired motor movement, coordination and balance following stroke. Mental practice, also known as motor imagery, is the mental rehearsal of a motor action without an overt ...
Scientists tackle our addiction to salt and fat by altering foods' pore size, number
2015-04-09
URBANA, Ill. - Two University of Illinois food scientists have learned that understanding and manipulating porosity during food manufacturing can affect a food's health benefits.
Youngsoo Lee reports that controlling the number and size of pores in processed foods allows manufacturers to use less salt while satisfying consumers' taste buds. Pawan Takhar has found that meticulously managing pore pressure in foods during frying reduces oil uptake, which results in lower-fat snacks without sacrificing our predilection for fried foods' texture and taste.
Both scientists ...
Choice of protein & carbohydrate-rich foods may have big effects on long-term weight gain
2015-04-09
BOSTON (April 9, 2015)- Making small, consistent changes to the types of protein- and carbohydrate-rich foods we eat may have a big impact on long-term weight gain, according to a new study led by researchers at the Friedman School of Nutrition Science & Policy at Tufts University. The results were published on-line this week in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition.
Based on more than 16 years of follow-up among 120,000 men and women from three long-term studies of U.S. health professionals, the authors first found that diets with a high glycemic load (GL) from ...