Fires in Western Australia April 2015
2015-04-09
(Press-News.org) Bushfires are inevitable in the fire-prone landscapes of Western Australia. Long dry summers, vegetation and undergrowth, and ignition from lightning or human causes mean that bushfires can and do occur every summer.
A bushfire is an unplanned fire (in the U.S. this is referred to as a wildfire). Each year Australia's Department of Parks and Wildlife responds to more than 600 bushfires that occur on or near land managed by the department. Bushfires have many causes, some natural such as lightning and some as a result of human activity such as camp fires, escapes from prescribed burning operations, industrial activity such as timber harvesting, mining, farming and power transmission, and some from deliberate arson.
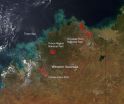
The fires which are indicated by red spots on this satellite image may be bushfires. These are areas where the thermal detectors on the MODIS instrument recognized temperatures higher than background. When accompanied by plumes of smoke, as in this image, such hot spots are diagnostic for fire.The Sentinel hotspot locator on Geoscience Australia show that the fires on this image are up to 24 hours old.
This natural-color satellite image was collected by the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) aboard the Aqua satellite on April 09, 2015. Actively burning areas, detected by MODIS's thermal bands, are outlined in red.
INFORMATION:
NASA image courtesy Jeff Schmaltz, MODIS Rapid Response Team. Caption: NASA/Goddard, Lynn Jenner END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-04-09
ATLANTA--A combination of mental practice and physical therapy is an effective treatment for people recovering from a stroke, according to researchers at Georgia State University.
The findings, published on March 30 in the journal Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, examine how the brains of stroke patients change after treatment.
Mental practice and physical therapy are interventions used to improve impaired motor movement, coordination and balance following stroke. Mental practice, also known as motor imagery, is the mental rehearsal of a motor action without an overt ...
2015-04-09
URBANA, Ill. - Two University of Illinois food scientists have learned that understanding and manipulating porosity during food manufacturing can affect a food's health benefits.
Youngsoo Lee reports that controlling the number and size of pores in processed foods allows manufacturers to use less salt while satisfying consumers' taste buds. Pawan Takhar has found that meticulously managing pore pressure in foods during frying reduces oil uptake, which results in lower-fat snacks without sacrificing our predilection for fried foods' texture and taste.
Both scientists ...
2015-04-09
BOSTON (April 9, 2015)- Making small, consistent changes to the types of protein- and carbohydrate-rich foods we eat may have a big impact on long-term weight gain, according to a new study led by researchers at the Friedman School of Nutrition Science & Policy at Tufts University. The results were published on-line this week in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition.
Based on more than 16 years of follow-up among 120,000 men and women from three long-term studies of U.S. health professionals, the authors first found that diets with a high glycemic load (GL) from ...
2015-04-09
The one common element in recent weather has been oddness. The West Coast has been warm and parched; the East Coast has been cold and snowed under. Fish are swimming into new waters, and hungry seals are washing up on California beaches.
A long-lived patch of warm water off the West Coast, about 1 to 4 degrees Celsius (2 to 7 degrees Fahrenheit) above normal, is part of what's wreaking much of this mayhem, according to two University of Washington papers to appear in Geophysical Research Letters, a journal of the American Geophysical Union.
"In the fall of 2013 and ...
2015-04-09
April 9, 2015 - A new University of Utah study is the first to provide clear insight into contributors to suicide risk among military personnel and veterans who have deployed.
The study, published today in the journal Suicide and Life-Threatening Behavior, found that exposure to killing and death while deployed is connected to suicide risk. Previous studies that looked solely at the relationship between deployment and suicide risk without assessing for exposure to killing and death have shown inconsistent results.
"Many people assume that deployment equals exposure ...
2015-04-09
When black holes tango, one massive partner spins head over heels (or in this case heels over head) until the merger is complete, said researchers at Rochester Institute of Technology in a paper published in Physical Review Letters.
This spin dynamic may affect the growth of black holes surrounded by accretion disks and alter galactic and supermassive binary black holes, leading to observational effects, according to RIT scientists Carlos Lousto and James Healy.
The authors of the study will present their findings at the American Physical Society meeting in Baltimore ...
2015-04-09
The RapidScat instrument that flies aboard the International Space Station (ISS) provided data about Tropical Cyclone Joalane's surface winds that showed how the strongest sustained winds consolidated as the tropical cyclone intensified and developed an eye. As of April 9, warnings were in effect at Rodrigues Island in the Southern Indian Ocean as Joalane approached.
RapidScat measured the surface winds within Tropical Cyclone Joalane late on April 7 and on April 8, revealing that the strongest winds consolidated over a 24 hour period. RapidScat measured Joalane's winds ...
2015-04-09
Outbreaks of leukemia that have devastated some populations of soft-shell clams along the east coast of North America for decades can be explained by the spread of cancerous tumor cells from one clam to another. Researchers call the discovery, reported in the Cell Press journal Cell on April 9, 2015, "beyond surprising."
"The evidence indicates that the tumor cells themselves are contagious--that the cells can spread from one animal to another in the ocean," said Stephen Goff of the Howard Hughes Medical Institute and Columbia University. "We know this must be true because ...
2015-04-09
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) can produce strikingly different clinical outcomes in young children, with some having strong conversation abilities and others not talking at all. A study published by Cell Press April 9th in Neuron reveals the reason: At the very first signs of possible autism in infants and toddlers, neural activity in language-sensitive brain regions is already similar to normal in those ASD toddlers who eventually go on to develop good language ability but nearly absent in those who later have a poor language outcome.
"Why some toddlers with ASD get ...
2015-04-09
Using induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), a team led by Mount Sinai researchers has gained new insight into genetic changes that may turn a well known anti-cancer signaling gene into a driver of risk for bone cancers, where the survival rate has not improved in 40 years despite treatment advances.
The study results, published today in the journal Cell, revolve around iPSCs, which since their 2006 discovery have enabled researchers to coax mature (fully differentiated) bodily cells (e.g. skin cells) to become like embryonic stem cells. Such cells are pluripotent, able ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Fires in Western Australia April 2015


