(Press-News.org) According to the World Health Organization, breast cancer is the most common cancer in women both in the developed and less developed world, and in the long term the scientists hope that the new method will lead to better prevention and early treatment of the disease.
"The method is better than mammography, which can only be used when the disease has already occurred. It is not perfect, but it is truly amazing that we can predict breast cancer years into the future," said Rasmus Bro, a professor of chemometrics in the Department of Food Science at University of Copenhagen. He stressed the method has been tested and validated only for a single population (cohort) and needs to be validated more widely before it can be used practically.
A new way of detecting diseases
Nevertheless, the method could create a paradigm shift in early diagnosis of breast cancer as well as other diseases.
"The potential is that we can detect a disease like breast cancer much earlier than today. This is important as it is easier to treat if you discover it early. In the long term, it will probably also be possible to use similar models to predict other diseases," said Lars Ove Dragsted, a professor of biomedicine in the Department of Nutrition, Exercise and Sports.
The method has been developed in cooperation with the Danish Cancer Society and the study was recently published in Metabolomics.
Food science showed the way
The researchers' approach to developing the method was adopted from food science, where it is used for control of complex industrial processes. Basically, it involves handling and analysing huge amounts of biological data in a holistic and explorative way. The researchers analysed all compounds a blood sample contains instead of - as is often done in health and medical science - examining what a single biomarker means in relation to a specific disease.
"When a huge amount of relevant measurements from many individuals is used to assess health risks - here breast cancer - it creates very high quality information. The more measurements our analyses contain, the better the model handles complex problems," continued Professor Rasmus Bro.
The model does not reveal anything about the importance of the single biomarkers in relation to breast cancer, but it does reveal the importance of a set of biomarkers and their interactions.
"No single part of the pattern is actually necessary nor sufficient. It is the whole pattern that predicts the cancer," said Professor Dragsted.
A metabolic blood profile describes the amounts of all compounds (metabolites) in our blood. The scientists measured metabolic blood profiles for this project. When you are in a pre-cancer state, the pattern for how certain metabolites are processed apparently changes.
While a mammography can detect newly developed breast cancer with a sensitivity of 75 per cent, the new metabolic blood profile is able to predict the likelihood of a woman developing breast cancer within the next two to five years with a sensitivity of 80 per cent.
Based on population study
The research is based on a population study of 57,000 people followed by the Danish Cancer Society over 20 years. The participants were first examined in 1994-96, during which time their weight and other measurements were recorded and they answered a questionnaire. They also provided a blood sample that was stored in liquid nitrogen.
The scientists used the 20-year-old blood samples and other available data from 400 women who were healthy when they were first examined but who were diagnosed with breast cancer two to seven years after providing the first sample, and from 400 women who did not develop breast cancer.
The method was also used to test a different dataset of women examined in 1997. Predictions based on the new set of data matched the first dataset, which indicates the validity of the model.
INFORMATION:
Today it is not possible to predict spreading from malignant melanomas. Melanoma metastases are furthermore extremely difficult to eliminate as traditional treatment such as chemotherapy and radiotherapy is mostly ineffective. Only ten per cent of the patients survive once they reach an advanced stage with distant metastases.
New research now demonstrates that the presence of the protein megalin in a malignant melanoma is an indicator of cancer cells that are particularly aggressive. The protein improves the ability of the cancer cells to divide and to survive. Accordingly, ...
COLLEGE STATION, TX - The bedding plants sold in retail outlets are typically grown in greenhouse production environments where professionals can monitor irrigation, light, and temperature. When the greenhouse-grown plants reach the retail market, however, they are often subjected to a range of less-than-ideal light levels, temperatures, and irrigation schedules that can be detrimental to plant quality and vigor. Researchers are looking for ways to increase bedding plants' shelf life to offset the negative impacts of postharvest handling.
A new research study of the popular ...
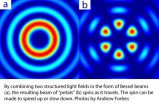
Light must travel in a straight line and at a constant speed, or so the laws of nature suggest. Now, researchers at the University of the Witwatersrand in Johannesburg have demonstrated that laser light traveling along a helical path through space, can accelerate and decelerate as it spins into the distance.
This is the first time that angular acceleration has been observed with light, and is therefore likely to lead to new applications using these structured light fields.
The results are contained in a research paper by Professor Andrew Forbes from the Wits School of ...
E-cigarettes are not without health risks for people who vape or for bystanders. This is one of the conclusions from a new risk assessment report from the Norwegian Institute of Public Health (NIPH).
The report has only considered e-cigarettes with nicotine since there has been very little research about e-cigarettes without nicotine.
In summary
Since e-cigarettes supply nicotine in the same quantities as cigarette smoking, the same harmful effects from nicotine can be expected.
The vapour from e-cigarettes contains so much nicotine that bystanders can ingest ...
Health surveys may underestimate the number of poisonings in the United States by 60 percent to 90 percent, according to a report in the journal Clinical Toxicology by University of Illinois at Chicago researchers.
As of 2009, poisonings became the leading cause of fatal injury in the U.S., surpassing transportation-related deaths and gun-related deaths.
The researchers analyzed hospital billing records, patient demographics, exposure information, and outcomes for Illinois hospital visits related to poisonings in 2010. They also looked at poisoning incidence data from ...
AMES, Iowa - It was a discovery that changed what researchers knew about the hunting techniques of chimpanzees. In 2007, Jill Pruetz first reported savanna chimps at her research site in Fongoli, Senegal, were using tools to hunt prey. That alone was significant, but what also stood out to Pruetz was the fact that female chimps were the ones predominantly hunting with tools.
It was a point some dismissed or criticized because of the small sample size, but the finding motivated the Iowa State University anthropology professor to learn more. In the years following, Pruetz ...
COLUMBUS, Ohio--The unassuming piece of stainless steel mesh in a lab at The Ohio State University doesn't look like a very big deal, but it could make a big difference for future environmental cleanups.
Water passes through the mesh but oil doesn't, thanks to a nearly invisible oil-repelling coating on its surface.
In tests, researchers mixed water with oil and poured the mixture onto the mesh. The water filtered through the mesh to land in a beaker below. The oil collected on top of the mesh, and rolled off easily into a separate beaker when the mesh was tilted.
The ...
The sound, light and temperature levels in paediatric hospital wards often vary, highlighting the lack of consistent environmental standards, according to a new study.
The research is being presented today at the 2015 Sleep and Breathing Conference (16 April, 2015).
Children and parents often suffer sleep deprivation when the environment on a ward is disruptive, which can affect disease recovery and quality of life in hospitalised children. There are no general consistent recommendations covering sound, light and temperature levels to help guide hospitals across ...
Sleep disordered breathing can hamper memory processes in children, according to a new study.
The research, which will be presented today at the Sleep and Breathing Conference (16 April 2015), found that disrupted sleep had an impact on different memory processes and how children learn.
Eszter Csabi led a team of researchers from the University of Szeged and Eötvös Loránd University in Hungary. They analysed 17 children with sleep disordered breathing aged between 6 and 12 years. They looked at different memory processes compared to a control group ...
Imagine having your MRI results sent directly to your phone, with no concern over the security of your private health data. Or knowing your financial information was safe on a server halfway around the world. Or sending highly sensitive business correspondence, without worrying that it would fall into the wrong hands.
Thanks to new research from engineers at the University of Toronto, these types of perfectly secure information exchanges are one step closer to reality. Published this week in Nature Communications, researchers have designed the first all-photonic quantum ...