(Press-News.org) A species of bone-eating worm that was believed to have evolved in conjunction with whales has been dated back to prehistoric times when it fed on the carcasses of giant marine reptiles.
Scientists at Plymouth University found that Osedax - popularised as the 'zombie worm' - originated at least 100 million years ago, and subsisted on the bones of prehistoric reptiles such as plesiosaurs and sea turtles.
Reporting in the Royal Society journal Biology Letters this month, the research team at Plymouth reveal how they found tell-tale traces of Osedax on plesiosaur fossils held in the Sedgwick Museum at the University of Cambridge.
Dr Nicholas Higgs, a Research Fellow in the Marine Institute, said the discovery was important for both understanding the genesis of the species and its implications for fossil records. "The exploration of the deep sea in the past decades has led to the discovery of hundreds of new species with unique adaptations to survive in extreme environments, giving rise to important questions on their origin and evolution through geological time." said Nicholas. "The unusual adaptations and striking beauty of Osedax worms encapsulate the alien nature of deep-sea life in public imagination.
"And our discovery shows that these bone-eating worms did not co-evolve with whales, but that they also devoured the skeletons of large marine reptiles that dominated oceans in the age of the dinosaurs. Osedax, therefore, prevented many skeletons from becoming fossilised, which might hamper our knowledge of these extinct leviathans."
The finger-length Osedax is found in oceans across the globe at depths of up to 4,000m, and it belongs to the Siboglinidae family of worms, which, as adults, lack a mouth and digestive system. Instead, they penetrate bone using root-like tendrils through which they absorb bone collagen and lipids that are then converted into energy by bacteria inside the worm.
Typically they consume whale bones, prompting many scientists to believe that they co-evolved 45 million years ago, branching out from their cousins that used chemosysnthesis to obtain food.
But Nicholas, and research lead Dr Silvia Danise, of Plymouth's School of Geography, Earth and Environmental Sciences, studied fossil fragments taken from a plesiosaur unearthed in Cambridge, and a sea turtle found in Burham, Kent.
Using a computed tomography scanner at the Natural History Museum - essentially a three-dimensional X-ray - they were able to create a computer model of the bones, and found tell-tale bore holes and cavities consistent with the burrowing technique of Osedax.
Dr Danise said: "The increasing evidence for Osedax throughout the oceans past and present, combined with their propensity to rapidly consume a wide range of vertebrate skeletons, suggests that Osedax may have had a significant negative effect on the preservation of marine vertebrate skeletons in the fossil record.
"By destroying vertebrate skeletons before they could be buried, Osedax may be responsible for the loss of data on marine vertebrate anatomy and carcass-fall communities on a global scale. The true extent of this 'Osedax effect', previously hypothesized only for the Cenozoic, now needs to be assessed for Cretaceous marine vertebrates."
INFORMATION:
The paper, Mesozoic origin for the bone-eating Osedax worms, is available in the Royal Society journal Biology Letters.
UCLA researchers have found that 77 percent of California primary care and specialty physicians understand the basics of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act and 59 percent support it. The survey, conducted by doctors from the UCLA department of family medicine, was published in the peer-reviewed journal Family Medicine.
Researchers also found that a majority of the 525 doctors surveyed believe ACA will steer the country's health care in the right direction.
The doctors' stance on the law appeared to be closely correlated with their political affiliations ...
New research from New Zealand's University of Otago is providing the most comprehensive picture of the evolutionary history of baleen whales, which are not only the largest animals ever to live on earth, but also among the most unusual.
Most other mammals feed on plants or grab a single prey animal at a time, but baleen whales are famous for their gigantic mouths and their ability to gulp and filter an enormous volume of water and food.
In a paper appearing in the UK journal Royal Society Open Science, Otago Geology PhD graduate Dr Felix Marx and Professor Ewan Fordyce ...
New York, NY--April 15, 2015--A research team led by Shree K. Nayar, T.C. Chang Professor of Computer Science at Columbia Engineering, has invented a prototype video camera that is the first to be fully self-powered--it can produce an image each second, indefinitely, of a well-lit indoor scene. They designed a pixel that can not only measure incident light but also convert the incident light into electric power. The team is presenting its work at the International Conference on Computational Photography at Rice University in Houston, April 24 to 26.
"We are in the middle ...
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, BERKELEY'S HAAS SCHOOL OF BUSINESS -CEOs make a lot of money from incentive pay tied to stock performance. Although such schemes help align executives' interests with shareholders, they are not necessarily the best schemes as compared to schemes that rely on trust between board and executives.
"Ironically, the necessary trust is easier to establish when the alternative of using stock-based pay is less powerful. Our research found that government-imposed limits on contingent compensation make stock-based pay a worse alternative, facilitating superior ...
Thermoluminescence is used extensively in archaeology and the earth sciences to date artefacts and rocks. When exposed to radiation quartz, a material found in nature, emits light proportional to the energy it absorbs. Replicating the very low dose of background radiation from natural sources present in quartz is a key precondition for precise and accurate dating results. Italian scientists have now developed a method to control the accuracy of the dose calibrations delivered to the samples during laboratory irradiation with heavy particles, replicating natural radiation ...
According to the World Health Organization, breast cancer is the most common cancer in women both in the developed and less developed world, and in the long term the scientists hope that the new method will lead to better prevention and early treatment of the disease.
"The method is better than mammography, which can only be used when the disease has already occurred. It is not perfect, but it is truly amazing that we can predict breast cancer years into the future," said Rasmus Bro, a professor of chemometrics in the Department of Food Science at University of Copenhagen. ...
Today it is not possible to predict spreading from malignant melanomas. Melanoma metastases are furthermore extremely difficult to eliminate as traditional treatment such as chemotherapy and radiotherapy is mostly ineffective. Only ten per cent of the patients survive once they reach an advanced stage with distant metastases.
New research now demonstrates that the presence of the protein megalin in a malignant melanoma is an indicator of cancer cells that are particularly aggressive. The protein improves the ability of the cancer cells to divide and to survive. Accordingly, ...
COLLEGE STATION, TX - The bedding plants sold in retail outlets are typically grown in greenhouse production environments where professionals can monitor irrigation, light, and temperature. When the greenhouse-grown plants reach the retail market, however, they are often subjected to a range of less-than-ideal light levels, temperatures, and irrigation schedules that can be detrimental to plant quality and vigor. Researchers are looking for ways to increase bedding plants' shelf life to offset the negative impacts of postharvest handling.
A new research study of the popular ...
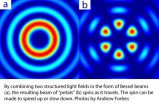
Light must travel in a straight line and at a constant speed, or so the laws of nature suggest. Now, researchers at the University of the Witwatersrand in Johannesburg have demonstrated that laser light traveling along a helical path through space, can accelerate and decelerate as it spins into the distance.
This is the first time that angular acceleration has been observed with light, and is therefore likely to lead to new applications using these structured light fields.
The results are contained in a research paper by Professor Andrew Forbes from the Wits School of ...
E-cigarettes are not without health risks for people who vape or for bystanders. This is one of the conclusions from a new risk assessment report from the Norwegian Institute of Public Health (NIPH).
The report has only considered e-cigarettes with nicotine since there has been very little research about e-cigarettes without nicotine.
In summary
Since e-cigarettes supply nicotine in the same quantities as cigarette smoking, the same harmful effects from nicotine can be expected.
The vapour from e-cigarettes contains so much nicotine that bystanders can ingest ...