(Press-News.org) Rather than slowing down, ants speed up in response to a higher density of traffic on their trails, according to new research published in Springer's journal The Science of Nature - Naturwissenschaften. When the researchers increased the supply of food by leaving food next to the trail, ants accelerated their speed by 50 percent. This was despite more than double the density of traffic.
When food increases in supply, more forager ants are sent out to carry it back to the nest. With this increase in ant density, the number of encounters between outbound and incoming individuals increases. Researchers at the University of Halle-Wittenberg in Germany suggest that the encounters provide an opportunity for ants to swap information and to change their behavior according to conditions.
The researchers also identified rules of ant etiquette. For example, workers returning to the colony more often moved to the left than to the right to avoid colliding with an oncoming ant. Rather than segregating strictly into lanes like human traffic, the ants used only a degree of segregation, with inbound ants more frequently using the left side of the trail.
The observations were made in the black-meadow ant, Formica pratensis, a species that lives mainly in open grassland and forages on aphid honeydew as its carbohydrate source. The colonies are situated near favored foraging sites where the ants protect and cultivate aphid populations. Repeated journeys are made more efficient by the use of well-worn trails that can persist for over a decade.
A total of 1,865 individual ants were filmed on a 15 centimeter (ca. 6 inch) section of trail. The video was stopped every 50 frames and the number of ants on each lane was counted. At low and medium densities, ants preferred the central lanes. Of the total number, 496 ants were studied for their speed.
Encounters between ants included touching antennae or exchanging fluids. The number of encounters increased with density but this did not reduce the traffic flow.
"Even under the highest densities we could achieve, we did not observe any traffic jams," says Christiane Hönicke, co-author of the study. "The ants increased their pace and were driven off the central lanes of the trail, resulting in a self-organized optimization of the traffic."
INFORMATION:
Reference:
Hönicke, C. et al (2015). Effect of density on traffic and velocity on trunk trails of Formica pratensis. Science of Nature - Naturwissenschaften DOI 10.1007/s00114-015-1267-6
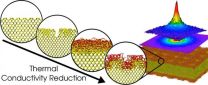
The ability of materials to conduct heat is a concept that we are all familiar with from everyday life. The modern story of thermal transport dates back to 1822 when the brilliant French physicist Jean-Baptiste Joseph Fourier published his book "Théorie analytique de la chaleur" (The Analytic Theory of Heat), which became a corner stone of heat transport. He pointed out that the thermal conductivity, i.e., ratio of the heat flux to the temperature gradient is an intrinsic property of the material itself.
The advent of nanotechnology, where the rules of classical ...
Scientists at The University of Manchester have made an important finding that could help develop an early test for kidney disease.
Dr Rachel Lennon from the Wellcome Trust Centre for Cell-Matrix Research has been studying why some people are more susceptible to kidney disease because of their race and gender.
She explains: "It's well known that impaired kidney function is more common in Afro-Caribbean individuals compared to those from a Caucasian background, and in men compared to women. However, the reasons for the difference in susceptibility are only just being ...
This news release is available in German.
The size of the neonatal skull is large relative to the dimensions of the birth canal in the female pelvis. This is the reason why childbirth is slower and more difficult in humans than in most other primates. Scientists from the Universities of Oslo and Vienna, identified adaptations in the morphology of the human body, which were unknown so far. The results of this new study appeared in the current edition of PNAS.
Upright walking and difficult birth
In hominids, upright walking evolved 4-5 million years ago. The ...
Is it possible to prevent mental health problems in higher education students? The answer is "yes" according to a team of psychologists from Loyola University Chicago who conducted a careful, systematic review of 103 universal interventions involving over 10,000 students enrolled in 2- and 4-year colleges and universities and graduate programs. The findings appear in the May 2015 issue of Prevention Science, published by Springer.
Researchers indicated that universal prevention interventions - that is, programs targeting general students, not just students who are at ...
Researchers from Plymouth University Peninsula Schools of Medicine and Dentistry are part of a team led by the University of Oxford, who have carried out new research that suggests mindfulness-based cognitive therapy (MBCT) could provide an alternative non-drug treatment for people who do not wish to continue long-term antidepressant treatment.
The results are published in "The Lancet".
The results come from the first ever large study to compare MBCT - structured training for the mind and body which aims to change the way people think and feel about their experiences ...
Fragments of asteroids regularly land on Earth as meteorites. If you examine such a find, you can see that it comprises millimetre-sized round stones, known as chondrules. These small particles are believed to be the original building blocks of the solar system. However, the research community has not previously been able to explain how the chondrules formed asteroids. A new study shows that asteroids were formed by capturing chondrules with the help of gravitational force.
"The chondrules are of exactly the right size to be slowed down by the gas that orbited the young ...
Researchers at the Institut Hospital del Mar d'Investigacions Mèdiques (IMIM) have identified a new way of treating colorectal cancer. In the study published in the journal Science Signaling, the team led by LLuís Espinosa, investigator of IMIM's research group into stem cells and cancer, have shown that inhibition of endosomal activity is a potential therapeutic strategy for the treatment of cancers with the BRAF mutated gene. This discovery is an important step in the personalisation of the treatment of colorectal cancer, as the presence of this mutation is ...
Bethesda, MD (April 22, 2015) -- The May issues of AGA's journals -- Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology and Gastroenterology -- highlight important research updates on the most deadly forms of liver disease. Here's what you need to know:
Researchers confirm that NAFLD worsens heart disease.
One specific cardiovascular disease risk factor -- psychological distress -- is linked to death from liver disease in a large, general population sample.
Improvements in cirrhosis care have contributed to a 41 percent decrease in inpatient mortality.
For access to any of ...
Researchers from North Carolina State University have discovered that electron spin brings a previously unknown degree of order to the high entropy alloy nickel iron chromium cobalt (NiFeCrCo) - and may play a role in giving the alloy its desirable properties.
"High entropy alloys have garnered a lot of attention over the past 10 years because they have remarkable properties," says Doug Irving, an associate professor of materials science and engineering at NC State and corresponding author of a paper describing the work. High entropy alloys are materials that consist ...
COLUMBUS, Ohio--An international research team is bringing a new weapon to bear against invasive earthworms.
The ongoing research project at The Ohio State University, the University of Alberta and Simon Fraser University uses statistical analysis to forecast one worm species' spread, in hopes of finding ways to curtail it.
Most recently, they've focused on the boreal forest of northern Alberta. No native worms live in the forest whatsoever; the region had been worm-free since the last ice age 11,000 years ago, until invasive European species began working their way ...