(Press-News.org) TEMPE, Ariz. - As the search continues for Earth-size planets orbiting at just the right distance from their star, a region termed the habitable zone, the number of potentially life-supporting planets grows. In two decades we have progressed from having no extrasolar planets to having too many to search. Narrowing the list of hopefuls requires looking at extrasolar planets in a new way. Applying a nuanced approach that couples astronomy and geophysics, Arizona State University researchers report that from that long list we can cross off cosmic neighbor Tau Ceti.
The Tau Ceti system, popularized in several fictional works, including Star Trek, has long been used in science fiction, and even popular news, as a very likely place to have life due to its proximity to Earth and the star's sun-like characteristics. Since December 2012 Tau Ceti has become even more appealing, thanks to evidence of possibly five planets orbiting it, with two of these - Tau Ceti e and f - potentially residing in the habitable zone.
Using the chemical composition of Tau Ceti, the ASU team modeled the star's evolution and calculated its habitable zone. Although their data confirms that two planets (e and f) may be in the habitable zone it doesn't mean life flourishes or even exists there.
"Planet e is in the habitable zone only if we make very generous assumptions. Planet f initially looks more promising, but modeling the evolution of the star makes it seem probable that it has only moved into the habitable zone recently as Tau Ceti has gotten more luminous over the course of its life," explains astrophysicist Michael Pagano, ASU postdoctoral researcher and lead author of the paper appearing in the Astrophysical Journal. The collaboration also included ASU astrophysicists Patrick Young and Amanda Truitt and mineral physicist Sang-Heon (Dan) Shim.
Based upon the team's models, planet f has likely been in the habitable zone much less than 1 billion years. This sounds like a long time, but it took Earth's biosphere about 2 billion years to produce potentially detectable changes in its atmosphere. A planet that entered the habitable zone only a few hundred million years ago may well be habitable and even inhabited, but not have detectable biosignatures.
According to Pagano, he and his collaborators didn't pick Tau Ceti "hoping, wanting, or thinking" it would be a good candidate to look for life, but for the idea that these might be truly alien new worlds.
Tau Ceti has a highly unusual composition with respect to its ratio of magnesium and silicon, which are two of the most important rock forming minerals on Earth. The ratio of magnesium to silicon in Tau Ceti is 1.78, which is about 70% more than our sun.
The astrophysicists looked at the data and asked, "What does this mean for the planets?"
Building on the strengths of ASU's School of Earth and Space Exploration, which unites earth and space scientists in an effort to tackle research questions through a holistic approach, Shim was brought on board for his mineral expertise to provide insights into the possible nature of the planets themselves.
"With such a high magnesium and silicon ratio it is possible that the mineralogical make-up of planets around Tau Ceti could be significantly different from that of Earth. Tau Ceti's planets could very well be dominated by the mineral olivine at shallow parts of the mantle and have lower mantles dominated by ferropericlase," explains Shim.
Considering that ferropericlase is much less viscous, or resistant to flowing, hot, yet solid, mantle rock would flow more easily, possibly having profound effects on volcanism and tectonics at the planetary surface, processes which have a significant impact on the habitability of Earth.
"This is a reminder that geological processes are fundamental in understanding the habitability of planets," Shim adds.
"Tau Ceti has been a popular destination for science fiction writers and everyone's imagination as somewhere there could possibly be life, but even though life around Tau Ceti may be unlikely, it should not be seen as a letdown, but should invigorate our minds to consider what exotic planets likely orbit the star, and the new and unusual planets that may exist in this vast universe," says Pagano.
INFORMATION:
This work was supported by funding from the NASA Astrobiology Institute and NASA Nexus for Exoplanet System Science.
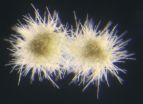
Image 1 caption: How would an alien world like this look? That's the question that undergraduate art major Joshua Gonzalez attempted to answer. He worked with Professor Patrick Young's group to learn how to analyze stellar spectra to find chemical abundances, and inspired by the scientific results, he created two digital paintings of possible unusual extrasolar planets, one being Tau Ceti for his Barrett Honors Thesis. Credit: Joshua Gonzalez
Image 2 caption: An artist's impression of the Tau Ceti system. Credit: J. Pinfield for the RoPACS network at the University of Hertfordshire, 2012
SOURCE:
Mike Pagano, mpagano@asu.edu
MEDIA CONTACT:
Nikki Cassis, ncassis@asu.edu
(602) 710-7169
Arizona State University
School of Earth and Space Exploration
College of Liberal Arts and Sciences
Tempe, Arizona USA
http://www.sese.asu.edu
Scientists have found something they can't quite explain in one of the most barren environments on Earth: a bacterium whose DNA sequence contains elements usually only found in a much higher organism.
Trichodesmium is a type of bacteria known as an oligotroph, meaning that it can survive in incredibly nutrient-poor regions of the ocean. In fact, it thrives there -- to the point that great blooms of the microorganism can be seen both with the naked eye and from satellites in space, earning it the name "sea sawdust" from ancient mariners.
This is because Trichodesmium ...
A new type of graphene aerogel will make for better energy storage, sensors, nanoelectronics, catalysis and separations.
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory researchers have made graphene aerogel microlattices with an engineered architecture via a 3D printing technique known as direct ink writing. The research appears in the April 22 edition of the journal, Nature Communications.
The 3D printed graphene aerogels have high surface area, excellent electrical conductivity, are lightweight, have mechanical stiffness and exhibit supercompressibility (up to 90 percent ...
Montréal, April 22, 2015 - Researchers at the IRCM led by Artur Kania, PhD, uncovered the critical role in pain processing of a gene associated with a rare disease. Their breakthrough, published in The Journal of Neuroscience, paves the way for a better understanding of chronic pain conditions.
Dr. Kania's team studies the way neural circuits transform harmful stimuli (such as cold, heat, and pinch) into the perception of pain. More precisely, they examined the gene Lmx1b and its involvement in pain processing. Mutations in this gene also cause a rare human disease ...
PHILADELPHIA - In the first major study to examine the use of a computer-assisted, photo-driven differential diagnosis generator for skin conditions, researchers at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania found physicians routinely used the tool, without an increase in calling for inpatient dermatology consultations. The software diagnostic tool, VisualDx, aids in diagnosing dermatologic conditions by allowing physicians to enter information such as the type and location of a rash, and associated symptoms such as pain or itching, and then generating ...
SAN FRANCISCO--It may seem unlikely that a large earthquake would take place hundreds of kilometers away from a tectonic plate boundary, in areas with low levels of strain on the crust from tectonic motion. But major earthquakes such as the Mw 7.9 2008 Chengdu quake in China and New Zealand's 2011 Mw 6.3 quake have shown that large earthquakes do occur and can cause significant infrastructure damage and loss of life. So what should seismologists look for if they want to identify where an earthquake might happen despite the absence of historical seismic activity?
Roger ...
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Researchers have uncovered the first evidence of a genetic link between prodigy and autism.
The scientists found that child prodigies in their sample share some of the same genetic variations with people who have autism.
These shared genetic markers occur on chromosome 1, according to the researchers from The Ohio State University and Nationwide Children's Hospital in Columbus.
The findings confirm a hypothesis made by Joanne Ruthsatz, co-author of the study and assistant professor of psychology at Ohio State's Mansfield campus.
In a previous study, ...
WASHINGTON - Vehicle cost, current battery technology, and inadequate consumer knowledge are some of the barriers preventing widespread adoption of plug-in electric vehicles, says a new congressionally mandated report from the National Research Council. Developing less expensive, better performing batteries is essential to reducing overall vehicle cost, and a market strategy is needed to create awareness and overcome customer uncertainty. The report recommends a range of incentives that the federal government can offer to address these and other barriers.
The report ...
The brain is a privileged organ in the body. So vital to life, the brain is protected from alterations elsewhere in the body by a highly regulated gateway known as the blood-brain barrier, which allows only selected molecules to pass through.
In certain diseases, however, such as multiple sclerosis, the barrier can be improperly breached. These "leaks" can allow immune cells and inflammatory molecules to pass through, causing inflammation that leads to neuronal damage.
In a new study, researchers have made insights into how the blood-brain barrier, or BBB, is maintained, ...
The widespread use of cloth masks by healthcare workers may actually put them at increased risk of respiratory illness and viral infections and their global use should be discouraged, according to a UNSW study.
The results of the first randomised clinical trial (RCT) to study the efficacy of cloth masks were published today in the journal BMJ Open.
The trial saw 1607 hospital healthcare workers across 14 hospitals in the Vietnamese capital, Hanoi, split into three groups: those wearing medical masks, those wearing cloth masks and a control group based on usual practice, ...
(Boston)-- Individuals with mild Traumatic Brain Injury (mTBI), particularly those who have had loss of consciousness (LOC), show structural brain abnormalities in their white matter as measured by Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI).
These findings, which appear in the journal NeuroImage: Clinical, is the only study to date to demonstrate that mTBI with LOC is associated with brain abnormalities that lead to decreased performance in verbal memory.
Blast-related TBI has been a common injury among returning troops due to the widespread use of improvised explosive devices ...