(Press-News.org) MINNEAPOLIS -- Professionals whose jobs require more speaking, developing strategies, conflict resolution and managerial tasks may experience better protection against memory and thinking decline in old age than their co-workers, according to a new study published in the April 29, 2015, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
"Our study is important because it suggests that the type of work you do throughout your career may have even more significance on your brain health than your education does," said study author Francisca S. Then, PhD, with the University of Leipzig in Germany. "Education is a well-known factor that influences dementia risk."
For the study, 1,054 people over the age of 75 were given tests that measured their memory and thinking abilities every one-and-a-half years for eight years.
The researchers also asked the participants about their work history and categorized the tasks they completed into three groups: executive, verbal and fluid. Examples of executive tasks are scheduling work and activities, developing strategies and resolving conflicts. Examples of verbal tasks are evaluating and interpreting information and fluid tasks were considered to be those which included selective attention and analyzing data.
Memory and thinking abilities were examined through a clinical test, the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE). In this clinical test, a small decline in points can indicate a clinically relevant deficit.
The study found that people whose careers included the highest level of all three types of tasks scored highest on the thinking and memory tests by two MMSE points over people with the lowest level.
People with the highest level of all three types of tasks also had the slowest rate of cognitive decline. Over eight years, their rate of decline was half the rate of participants with a low level of mentally demanding work tasks. Among the three types of work tasks, high levels of executive and verbal tasks were distinctively associated with slower rates of memory and thinking decline.
Participants with a high level of executive tasks scored two MMSE points higher on memory and thinking tests at the beginning of the study and five MMSE points higher after eight years in the study compared to participants with a low level of these tasks. Participants with a high level of verbal tasks declined an average two MMSE points less than those with a low level.
"Challenges at work may indeed be a positive element, if they build up a person's mental reserve in the long-term," said Then.
INFORMATION:
The study was supported by the Interdisciplinary Center for Clinical Research of the University of Leipzig and the LIFE Leipzig Research Center for Civilization Diseases at the Leipzig University, Germany, which is funded by means of the European Social Fund and the Free State of Saxony.
To learn more about brain health, please visit http://www.aan.com/patients.
The American Academy of Neurology, an association of more than 28,000 neurologists and neuroscience professionals, is dedicated to promoting the highest quality patient-centered neurologic care. A neurologist is a doctor with specialized training in diagnosing, treating and managing disorders of the brain and nervous system such as Alzheimer's disease, stroke, migraine, multiple sclerosis, brain injury, Parkinson's disease and epilepsy.
For more information about the American Academy of Neurology, visit http://www.aan.com or find us on Facebook, Twitter, Google+ and YouTube.
MISSOULA -- When temperatures rise and less water falls, forests respond. Forest canopies can buffer juvenile trees from drought and heat by providing shade for the younger trees below the leaf and needle cover. Adult trees have deep roots and can handle hot and dry conditions better than juveniles of the same species.
However, current models of how forests will respond to climate change don't account for this difference between adult and juvenile trees. Recent research by Solomon Dobrowski, a University of Montana professor of forest landscape ecology, finds that climatic ...
Children born to mothers experiencing economic hardship, who were also exposed during pregnancy to high levels of PAH (polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons), scored significantly lower on IQ tests at age 5 compared with children born to mothers with greater economic security and less exposure to the pollutants. The findings by researchers at the Columbia Center for Children's Environmental Health (CCCEH) at the Mailman School of Public Health appear in the journal Neurotoxicology and Teratology.
PAH are ubiquitous in the environment from emissions from motor vehicles, oil, ...
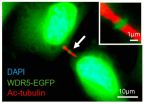
The human body is a cross between a factory and a construction zone -- at least on the cellular level. Certain proteins act as project managers, which direct a wide variety of processes and determine the fate of the cell as a whole.
One group of proteins called the WD-repeat (WDR) family helps a cell choose which of the thousands of possible gene products it should manufacture. These WDR proteins fold into a three-dimensional structure resembling a doughnut -- an unusual shape that allows WDR proteins to act as stable platforms on which large protein complexes can assemble ...
Offering a potential early intervention for Alzheimer's disease (AD), researchers at University of California, San Diego School of Medicine and Cenna Biosciences, Inc. have identified compounds that block the production of beta amyloid peptides in mice. The study is reported April 29 in PLOS ONE.
If the results ultimately translate to human treatment, the most promising compound - a peptide dubbed P8 - could be administered to individuals at high risk of developing the disease, long before the tell-tale signs of dementia occur and perhaps with few side effects, due to ...
Understanding extinct species diets may require a greater understanding of the relationship between skull biomechanics and the animals' ancestry than previously thought, according to a new study published April 29, 2015 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Zhijie Jack Tseng and John Flynn from the American Museum of Natural History.
The diet of long-extinct animals may be inferred by using modern animals with similar skull shapes and tooth patterns as models, but scientists aren't sure if diet is the main factor influencing skull shape and biomechanics. To understand ...
April 24, 2015. Almost since the time of Melville's epic hunt, scientists have been fascinated by the remarkable attributes of the sperm whale and its kin, the smaller pigmy and dwarf whales. Capable of diving to great depths and gifted with an acute sense of echolocation, these animals have remained inseparable from maritime lore.
An international team of scientists, led by the Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County's Curator of Marine Mammals Dr. Jorge Velez-Juarbe, has discovered a new species of an extinct pigmy sperm whale from Panama that clarifies key aspects ...
(Philadelphia, PA) - For more than 100 years, exposing students to basic and clinical research has been an essential component of a medical school education in the United States. However, today, new models of medical education in which research plays a minimal role are likely to create a two-tiered system of education, decrease the physician-scientist pipeline and diminish the application of scientific advances to patient care.
Those are the concerns outlined in "American Medical Education at a Crossroads" - a position paper published April 29 by Science Translational ...
ANN ARBOR, Mich. -- Kaiba was just a newborn when he turned blue because his little lungs weren't getting the oxygen they needed. Garrett spent the first year of his life in hospital beds tethered to a ventilator, being fed through his veins because his body was too sick to absorb food. Baby Ian's heart stopped before he was even six months old.
Three babies all had the same life-threatening condition: a terminal form of tracheobronchomalacia, which causes the windpipe to periodically collapse and prevents normal breathing. There was no cure and life-expectancies were ...
Having to pay for dental health care can put a considerable strain on household finances in many countries, according to an international study led by King's College London.
The new study, published in the journal PLOS ONE, assessed the extent of household 'catastrophic dental health expenditure' (CDHE) in 41 low and middle income countries. Expenditure was defined as catastrophic if it was equal to or higher than 40% of the household's capacity to pay.
Up to 7% of the households surveyed in these countries had incurred catastrophic dental health expenditure in ...
New Haven, Conn.--Improving access to public toilets in South African urban settlements may reduce both the incidence of sexual assaults by nearly 30% and the overall cost to society, a study by researchers at the Yale School of Public Health and Yale School of Management found.
The research was published April 29 in PLOS ONE.
Development and human rights organizations have pointed to inadequate local sanitation facilities as a key factor in a woman's risk for physical or sexual assault. Many women in South Africa must travel out of their homes to public toilets, ...