INFORMATION:
Thoughts drive dieting plans but feelings drive dieting behavior, study finds
2015-05-05
(Press-News.org) BUFFALO, N.Y. - A majority of American adults say they've tried dieting to lose weight at some point in their lives, and at any given time, about one-third of the adult population say they're currently dieting.
Yet 60 percent of American adults are clinically overweight or obese and more than 16 percent of deaths nationwide are related to diet and physical activity.
"There is clearly a disconnect if we have a majority of the population that has tried to lose weight and a majority of the population that is overweight," says Marc Kiviniemi, a public health researcher at the University at Buffalo. "People are planning to diet and trying to diet, but that's not translating into a successful weight loss effort."
Many issues, from biological to environmental, determine effective weight control, but how people manage their own behavior is a big piece of that puzzle.
Dieting is a process that involves a plan to change eating behavior and behaving according to that plan. But the factors that guide diet planning differ from those that guide actual diet behavior, according to the results of Kiviniemi's new study with Carolyn Brown-Kramer of the University of Nebraska-Lincoln published this month in the Journal of Health Psychology.
"The crux of the disconnect is the divide between thoughts and feelings. Planning is important, but feelings matter, and focusing on feelings and understanding their role can be a great benefit," says Kiviniemi, associate professor of community health and health behavior in the UB School of Public Health and Health Professions.
Plans to change behavior are a function of thoughts, the belief that weight loss is possible by making better food choices. But when it comes to making a food choice and decidingto execute the plan, feelings guide behavior.
"If you're sitting back conceiving a plan you may think rationally about the benefits of eating healthier foods, but when you're in the moment, making a decision, engaging in a behavior, it's the feelings associated with that behavior that may lead you to make different decisions from those you planned to make."
The findings highlight the shortcomings of deprivation diets or diets based on food choices that ignore people's preferences.
"First of all, the deprivation experience is miserable. If you didn't associate negative feelings with it to start, you will after a few days," says Kiviniemi. "The other thing that's important is the distinction between things that require effort and things that are automatic.
"Planning is an effort that demands mental energy, but feelings happen automatically. Deprivation or anything that demands a high degree of self-control is a cognitive process. If you put yourself in a position to use that energy every time you make a food choice that energy is only going to last so long."
Kiviniemi says dieters should seriously consider enjoyment when framing and shaping a behavior change.
"In the dietary domain, eating more fruits and vegetables is fabulous advice. But if you have negative feelings about those food choices, they might not represent elements of a good plan," says Kiviniemi. "It's not just about eating healthy foods. It's about eating the healthy foods you like the most."
It's not easy, and a lot of work is required to move intention to action, which is why Kiviniemi says planning should be broadly based on both thoughts and feelings.
"Think seriously about how you're going to implement the plans you make to change your behavior, and that includes not only the feeling component, but how you plan to overcome a negative reaction that might surface during a diet."
It's not just the knowledge of what we're eating, but consideration of how we'll feel having decided to eat those foods, he says.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Who benefits from a catheter -- and who doesn't? New guide aims to protect patients
2015-05-05
ANN ARBOR, Mich. -- What's the only thing worse than having a urinary catheter when you're in the hospital? Having one and getting a urinary tract infection (UTI) - or worse - as a result.
Now, a new detailed guide gives doctors and nurses information to help decide which hospital patients may benefit from a urinary catheter - and which ones don't.
And that should help spare patients the pain, embarrassment, and potentially serious side effects that can come with having a catheter placed -- which may bring more risk than benefit to the patient.
Called the Ann ...
ASTRO issues guideline on definitive and adjuvant RT for locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer
2015-05-05
Fairfax, Va., May 5, 2015--The American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO) is issuing a new guideline, "Definitive and adjuvant radiotherapy in locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer: An American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO) evidence-based clinical practice guideline." The guideline's executive summary is published in the May-June issue of Practical Radiation Oncology (PRO), ASTRO's clinical practice journal. The complete guideline, which cites 35 years of data to help guide current treatment and future research, is available online as an open-access ...
Just like humans, dolphins have social networks
2015-05-05
They may not be on Facebook or Twitter, but dolphins do, in fact, form highly complex and dynamic networks of friends, according to a recent study by scientists at Harbor Branch Oceanographic Institute (HBOI) at Florida Atlantic University. Dolphins are known for being highly social animals, and a team of researchers at HBOI took a closer look at the interactions between bottlenose dolphins in the Indian River Lagoon (IRL) and discovered how they mingle and with whom they spend their time.
Through intensive photo-ID surveys conducted along the IRL, which were carried ...
U of T astrophysicists offer proof that famous image shows forming planets
2015-05-05
A recent and famous image from deep space marks the first time we've seen a forming planetary system, according to a study by U of T astrophysicists.
The team, led by Daniel Tamayo from the Centre for Planetary Science at U of T Scarborough and the Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics, found that circular gaps in a disk of dust and gas swirling around the young star HL Tau are in fact made by forming planets.
"HL Tau likely represents the first image taken of the initial locations of planets during their formation," says Tamayo. "This could be an enormous ...
Childhood maltreatment linked to sleep problems among adult Canadians
2015-05-05
TORONTO, ON - Adults who experienced multiple incidents of childhood maltreatment were more than two times as likely to have trouble sleeping than their counterparts who were not maltreated during childhood, according to a new study from researchers at the University of Toronto, University of Ottawa, and Western University. The study appears online in the journal Sleep Medicine.
"We found a significant association between childhood maltreatment and difficulty sleeping later in life," says lead author Philip Baiden, a PhD Student at the University of Toronto's Factor-Inwentash ...
Redesigned systems may increase access to MRI for patients with implanted medical devices
2015-05-05
New technology developed at the Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) may extend the benefits of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to many patients whose access to MRI is currently limited. A redesign of the wire at the core of the leads that carry signals between implanted medical devices and their target structures significantly reduces the generation of heat that occurs when standard wires are exposed to the radiofrequency (RF) energy used in MRI. The novel system is described in a paper published in the online Nature journal Scientific ...
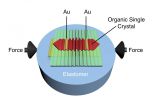
Improving organic transistors that drive flexible and conformable electronics
2015-05-05
AMHERST, Mass. -- A revolution is coming in flexible electronic technologies as cheaper, more flexible, organic transistors come on the scene to replace expensive, rigid, silicone-based semiconductors, but not enough is known about how bending in these new thin-film electronic devices will affect their performance, say materials scientists at the University of Massachusetts Amherst.
Writing in the current issue of Nature Communications, polymer scientists Alejandro Briseño and Alfred Crosby at UMass Amherst, with their doctoral student Marcos Reyes-Martinez, now ...
Study finds positive effects of job corps participation
2015-05-05
ALEXANDRIA, VA, MAY 5, 2015 -- A statistical analysis of Job Corps data strongly suggests positive average effects on wages for individuals who participated in the federal job-training program.
Results of the analysis recently were included in an article in the Journal of Business & Economic Statistics (http://www.tandfonline.com/toc/ubes20/current), a professional journal published by the American Statistical Association . The study was conducted by Xuan Chen of Renmin University of China and Carlos A. Flores of California Polytechnic State University.
Job Corps is ...
Interferon-free therapy clears hepatitis C in 93 percent of patients in trial
2015-05-05
DURHAM, N.C. -- A 12-week dose of an investigational three-drug hepatitis C combination cleared the virus in 93 percent of patients with liver cirrhosis who hadn't previously been treated, according to a study in the May 5, 2015, issue of The Journal of the American Medical Association.
Bristol-Myers Squibb funded the trial of the combination of three drugs -- daclatasvir, asunaprevir, and beclabuvir. None of the three drugs are FDA-approved, but daclatasvir is currently under review by the FDA. Duke Medicine researchers collaborated on the design and analysis of the ...
Studies show effectiveness of combo treatment for HCV patients with, without cirrhosis
2015-05-05
In two studies appearing in the May 5 issue of JAMA, patients with chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) genotype 1 infection and with or without cirrhosis achieved high rates of sustained virologic response after 12 weeks of treatment with a combination of the direct-acting-antiviral drugs daclatasvir, asunaprevir, and beclabuvir.
Current estimates indicate that 130 million to 150 million people worldwide are chronically infected with HCV, resulting in up to 350,000 deaths per year. Of the 7 HCV genotypes identified, genotype 1 is the most prevalent worldwide, accounting for ...