(Press-News.org) (MEMPHIS, Tenn. -- May 8, 2015) St. Jude Children's Research Hospital scientists have gained ground toward developing more targeted therapies for the most common childhood brain tumor. The findings appear today in the Journal of Molecular Biology.
The findings involve the DDX3X gene. In 2012, the St. Jude Children's Research Hospital -- Washington University Pediatric Cancer Genome Project highlighted DDX3X as a promising focus for efforts to develop targeted therapies against medulloblastoma. Such treatments target the genetic mistakes that give rise to the brain tumor's four subtypes.
The Pediatric Cancer Genome Project found that DDX3X was mutated in a high percentage of patients with the wingless (WNT) subtype of medulloblastoma. Researchers identified eight DDX3X mutations associated with the WNT subtype, which is named for the pathway that is disrupted in the tumors.
Now scientists have determined the DDX3X mutations lead to different molecular defects.
"Our research indicates that mutations of DDX3X do not all lead to a common defect in cells," said Eric Enemark, Ph.D., an associate member of the St. Jude Department of Structural Biology. He and Janet Partridge, Ph.D., associate member of the St. Jude Department of Pathology, are the study's co-corresponding authors. "As a result, therapies that target DDX3X mutations will need to be tailored to account for the specific molecular defects caused by the different disease-associated mutations," Enemark said.
Medulloblastoma is diagnosed in about 400 children and adolescents annually in the U.S., making it the nation's most common pediatric brain tumor. Historically, medulloblastoma has been treated as a single disease even though researchers at St. Jude and elsewhere showed that patient outcomes vary widely based on their tumor subtype. About 11 percent of medulloblastoma patients have the WNT subtype. Nearly all survive with the current treatments that involve surgery, radiation and chemotherapy, but have serious treatment-related side effects.
In this study, scientists used a variety of biochemical, genetic and structural techniques to identify the molecular defects associated with two of the DDX3X mutations associated with medulloblastoma. Investigators demonstrated the mutations interfere with the ability of the DDX3X protein to bind to RNA. Cells use RNA to translate instructions carried by DNA to make the proteins that do the work of cells.
To function properly, DDX3X must bind RNA and also release the chemical energy stored in ATP molecules. In this study, researchers discovered the process depends on a short, flexible loop in DDX3X they call the ATP-binding loop. Without the loop, researchers found that DDX3X and related enzymes could not access energy stored in ATP.
Researchers showed that two DDX3X mutant proteins were unable to tap ATP energy. In contrast, the other DDX3X mutations associated with medulloblastoma exhibited little or no decrease in ATP consumption activity.
Researchers used a yeast model to better understand the consequences of the mutations. If either of the same two mutant DDX3X proteins were substituted for the most similar protein in fission yeast, the yeast died. The yeast survived, however, when the substitution involved the normal human DDX3X protein or DDX3X proteins with other medulloblastoma-associated mutations.
"Putting the mutant proteins into the yeast model identified which defects were harmful and provided insight into the DDX3X protein function," Partridge said. "We know from previous studies that the fission yeast version of DDX3X is thought to play a role in translation of key regulatory proteins, possibly by helping untangle parts of the RNA molecule." Those proteins include cyclins that regulate cell division, a process often disrupted in cancer.
Enemark added: "We have identified a set of defects for one set of DDX3X mutants that provides a foundation for efforts to develop more individualized treatments for patients with those defects. We still need to determine the molecular defects for the second class of mutants."
INFORMATION:
The study's co-first authors are Leslie Epling, Christy Grace and Brandon Lowe, all of St. Jude.
The research was funded in part by a grant (CA21765) from the National Institutes of Health and ALSAC.
St. Jude Media Relations Contacts:
Carrie Strehlau
Desk: (901) 595-2295
Cell: (901) 297-9875
carrie.strehlau@stjude.org
Summer Freeman
Desk: (901) 595-3061
Cell: (901) 297-9861
summer.freeman@stjude.org
St. Jude Children's Research Hospital
St. Jude Children's Research Hospital is leading the way the world understands, treats and defeats childhood cancer and other life-threatening diseases. It is the only National Cancer Institute-designated Comprehensive Cancer Center devoted solely to children. Treatments developed at St. Jude have helped push the overall childhood cancer survival rate from 20 percent to 80 percent since the hospital opened more than 50 years ago. St. Jude is working to increase the overall survival rate for childhood cancer to 90 percent in the next decade. St. Jude freely shares the breakthroughs it makes, and every child saved at St. Jude means doctors and scientists worldwide can use that knowledge to save thousands more children. Families never receive a bill from St. Jude for treatment, travel, housing and food -- because all a family should worry about is helping their child live. To learn more, visit stjude.org or follow St. Jude at @stjuderesearch.
PITTSBURGH -- Scientists have been manipulating genes for a while. The University of Pittsburgh's Alexander Deiters just found a way to control the process with higher precision.
By using light.
Deiters and his group are the first to achieve this. The resulting paper was recently published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
Since 2013, scientists have used a gene-editing tool called CRISPR/Cas9. The method employs a bacterially derived protein (Cas9) and a synthetic guide RNA to induce a double-strand break at a specific location in the genome. This ...
Object recognition -- determining what objects are where in a digital image -- is a central research topic in computer vision.
But a person looking at an image will spontaneously make a higher-level judgment about the scene as whole: It's a kitchen, or a campsite, or a conference room. Among computer science researchers, the problem known as "scene recognition" has received relatively little attention.
Last December, at the Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, MIT researchers announced the compilation of the world's largest database of images ...
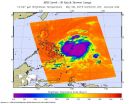
The Philippines warning center has raised a #2 warning for its citizens in the Luzon province of Catanduanes. This warning indicates, among other things, that the tropical cyclone will affect the locality and that winds of greater than 100 kph up to 185 kph (62 to 114 mph) may be expected in at least 18 hours.
Philippines know the storm as Dodong and have also raised warning #1 for the areas of Luzon provinces of Sorsogon. Albay, Camarines Norte, Camarines Sur, Quezon, Polillo Island, Aurora, Quirino, Isabela and the Visayas provinces of Northern and Eastern Samar.
Warning ...
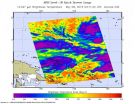
Forecasters expect Tropical Depression 07W which is riding behind Typhoon Noul to intensify to typhoon strength within the next five days. Currently 07W is located 298 miles southeast of Pohnopei, one of the Federated States of Micronesia. It is moving at a slow 5 knots on a east northeast trajectory with maximum sustained winds of 30 knots gusting to 40 (18 to 24 mph). Maximum wave height is 11 feet. 07W is moving east, but will turn round to a northwesterly course.
A tropical storm WARNING is in force for Kosrae, Pingelap and Mokil in Pohnpei State. A tropical storm ...
For the last decade, scientists have deployed increasingly capable underwater robots to map and monitor pockets of the ocean to track the health of fisheries, and survey marine habitats and species. In general, such robots are effective at carrying out low-level tasks, specifically assigned to them by human engineers -- a tedious and time-consuming process for the engineers.
When deploying autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs), much of an engineer's time is spent writing scripts, or low-level commands, in order to direct a robot to carry out a mission plan. Now a new ...
The EU-funded MycoSynVac project combines gene engineering and biotechnology to design a novel veterinary vaccine chassis based on the bacterium Mycoplasma pneumoniae.
By combining their systems biology expertise with cutting-edge synthetic biology methodologies, researchers will engineer a universal chassis, which will be free of virulence and optimized for fast growth in a serum-free medium.
This chassis will be used to create specific vaccines against two highly detrimental pathogens that are causing suffering in livestock animals and large financial losses to the ...
TAMPA, Fla. -- Androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) is a common treatment option for patients with advanced stage prostate cancer. But nearly 80 percent of patients who receive ADT report experiencing hot flashes during and after treatment. Moffitt Cancer Center researchers are working to determine what genetic factors and other characteristics might make prostate cancer patients more likely to experience hot flashes during and after therapy.
Cancer therapies often are associated with unwanted side effects. Some side effects can be so debilitating that patients decide ...
Mexico is undergoing a transformation: ranked as the second largest economy in Latin America, it's an increasingly dynamic middle-income country -- and its population is ageing rapidly. How will this relate to the burden of cancer?
Mexico is an interesting case study for the relationship between population ageing and cancer burden, according to new research published in ecancermedicalscience.
Researchers led by Dr Ajay Aggarwal of the Institute of Cancer Policy, Kings College London, UK, examined population data, cancer databases, and the research output of Mexican ...
The ability that some people have to use echoes to determine the position of an otherwise silent object, in a similar way to bats and dolphins, requires good high-pitch hearing in both ears, according to new research from the University of Southampton.
The study, published in Hearing Research, found that locating an object by listening to echoes, without moving the head, requires good hearing at high frequencies and in both ears. This builds on research published in 2013 by the team at the University's Institute of Sound and Vibration Research (ISVR) that demonstrated ...
Scientists at LSTM have come a step closer to understanding why people exposed to household air pollution (HAP) are at higher risk of lung infections such as pneumonia and tuberculosis.
Three billion people worldwide are exposed to HAP from the fuels they burn to cook, light and heat with at home. Frequently, charcoal, wood and food waste are burned and generate high concentrations of smoke particles. This exposure is associated with increased risk of pneumonia, particularly in low and middle income countries where bacterial pneumonia is the biggest cause of infant mortality. ...