(Press-News.org) URBANA, Ill. - Much attention has been given to dedicated, perennial bioenergy crops to meet the revised Renewable Fuel Standard mandating production of 36 billion gallons of biofuel by the year 2022. Even so, concern remains over the impending need to convert as much as 30 million acres of U.S. crop land, which would include food crops, to land for perennial energy crops in order to meet that demand.
Researchers realize that biomass feedstocks will need to come from many different sources, including crop residues, forest residues, and municipal waste, for example, said Marty Williams, a University of Illinois crop scientist and ecologist with the USDA-Agricultural Research Service. The use of double-cropping systems--a winter annual biomass crop is grown then harvested in the spring, followed by a summer annual crop--has been suggested as an additional option.
Knowing that many large-seeded vegetables in the Midwest must be planted later than agronomic crops into warmer soils, Williams was interested in the possibility of developing a bioenergy feedstock/vegetable double-cropping system. He explained that no such system had been developed and tested yet.
"Some vegetables have relatively short growing seasons, too. Rather than the standard fallow period for certain vegetables, what about integrating a bioenergy crop as a part of a double-cropping system?" Williams said.
Williams chose a vegetable crop popular in the state of Illinois, pumpkin, to be used in the double-cropping system study. "We took a fairly simplistic look at comparing this bioenergy/vegetable double-cropping system with traditional vegetable production using processing pumpkin," Williams explained. "Illinois leads the nation in pumpkin production, providing some 90 percent of the processing pumpkin in the United States."
Field trials were conducted over three environments. During the study, Williams compared crop productivity and weed communities in four different pumpkin production systems, varying in tillage, cover crop, and bioenergy feedstock/pumpkin double-cropping. A fall-planted rye (Secale cereale) mix was used as the biomass feedstock.
"In the end, winter rye may not be the best feedstock crop to use," he explained. "It was more of a model crop for us for our system. It grows well and has several desirable traits. Seed is relatively inexpensive and the plant is hardy."
Interestingly, the researchers saw pumpkin yields in the double-cropping system were comparable to conventional pumpkin production. However, the biomass feedstock also yielded an average of 4.4 tons per acre of dry biomass prior to pumpkin planting. "We saw a theoretical yield of 349 gallons of ethanol per acre, and a higher farm gate value than typical pumpkin production," Williams said.
"It looks promising," he added. "The biomass yield wasn't as high as something like Miscanthus, but we're producing feedstock and not taking land away from food production. Moreover, the cropping systems were not optimized, such as for soil fertility, so our economic estimates are likely conservative."
Overall, the biomass yield was comparable to that of 'Shawnee' switchgrass, but only one-half the yield of a hybrid switchgrass, the study reported.
"Perhaps some of our vegetable-cropping systems could contribute to bioenergy production, while still producing veggies," Williams said. "Also, there may be certain vegetable crops that are better suited to double-cropping. Given the potential competition between food and fuel production globally, systems making contributions towards both goals appear worth further consideration," he added.
"A bioenergy feedstock/vegetable double-cropping system" was recently published in Industrial Crops and Products.
INFORMATION:
Livermore - New results from the NASA NuSTAR telescope show that a supernova close to our galaxy experienced a single-sided explosion.
A team of scientists including Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory researchers found that X-ray emissions taken with the Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) show that the Supernova 1987A explosion was highly asymmetric. The results appear in the May 8 edition of the journal, Science.
NuSTAR observations, including those of 1987A, provide strong and compelling observational evidence that supernovae are not symmetric.
Supernova ...
El Salvador, Niger, and Pakistan are performing better in improving water and sanitation for their citizens than industrial giants like Russia and Brazil according to the new WaSH Performance Index developed by The Water Institute at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill's Gillings School of Global Public Health. The new index to be released Friday, May 8 during a live webcast shows which countries are leaders in improving access to water and sanitation for their citizens. Sub-Saharan Africa countries including Mali, South Africa, and Ethiopia are also among the ...
(MEMPHIS, Tenn. -- May 8, 2015) St. Jude Children's Research Hospital scientists have gained ground toward developing more targeted therapies for the most common childhood brain tumor. The findings appear today in the Journal of Molecular Biology.
The findings involve the DDX3X gene. In 2012, the St. Jude Children's Research Hospital -- Washington University Pediatric Cancer Genome Project highlighted DDX3X as a promising focus for efforts to develop targeted therapies against medulloblastoma. Such treatments target the genetic mistakes that give rise to the brain tumor's ...
PITTSBURGH -- Scientists have been manipulating genes for a while. The University of Pittsburgh's Alexander Deiters just found a way to control the process with higher precision.
By using light.
Deiters and his group are the first to achieve this. The resulting paper was recently published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
Since 2013, scientists have used a gene-editing tool called CRISPR/Cas9. The method employs a bacterially derived protein (Cas9) and a synthetic guide RNA to induce a double-strand break at a specific location in the genome. This ...
Object recognition -- determining what objects are where in a digital image -- is a central research topic in computer vision.
But a person looking at an image will spontaneously make a higher-level judgment about the scene as whole: It's a kitchen, or a campsite, or a conference room. Among computer science researchers, the problem known as "scene recognition" has received relatively little attention.
Last December, at the Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, MIT researchers announced the compilation of the world's largest database of images ...
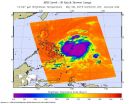
The Philippines warning center has raised a #2 warning for its citizens in the Luzon province of Catanduanes. This warning indicates, among other things, that the tropical cyclone will affect the locality and that winds of greater than 100 kph up to 185 kph (62 to 114 mph) may be expected in at least 18 hours.
Philippines know the storm as Dodong and have also raised warning #1 for the areas of Luzon provinces of Sorsogon. Albay, Camarines Norte, Camarines Sur, Quezon, Polillo Island, Aurora, Quirino, Isabela and the Visayas provinces of Northern and Eastern Samar.
Warning ...
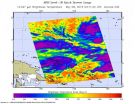
Forecasters expect Tropical Depression 07W which is riding behind Typhoon Noul to intensify to typhoon strength within the next five days. Currently 07W is located 298 miles southeast of Pohnopei, one of the Federated States of Micronesia. It is moving at a slow 5 knots on a east northeast trajectory with maximum sustained winds of 30 knots gusting to 40 (18 to 24 mph). Maximum wave height is 11 feet. 07W is moving east, but will turn round to a northwesterly course.
A tropical storm WARNING is in force for Kosrae, Pingelap and Mokil in Pohnpei State. A tropical storm ...
For the last decade, scientists have deployed increasingly capable underwater robots to map and monitor pockets of the ocean to track the health of fisheries, and survey marine habitats and species. In general, such robots are effective at carrying out low-level tasks, specifically assigned to them by human engineers -- a tedious and time-consuming process for the engineers.
When deploying autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs), much of an engineer's time is spent writing scripts, or low-level commands, in order to direct a robot to carry out a mission plan. Now a new ...
The EU-funded MycoSynVac project combines gene engineering and biotechnology to design a novel veterinary vaccine chassis based on the bacterium Mycoplasma pneumoniae.
By combining their systems biology expertise with cutting-edge synthetic biology methodologies, researchers will engineer a universal chassis, which will be free of virulence and optimized for fast growth in a serum-free medium.
This chassis will be used to create specific vaccines against two highly detrimental pathogens that are causing suffering in livestock animals and large financial losses to the ...
TAMPA, Fla. -- Androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) is a common treatment option for patients with advanced stage prostate cancer. But nearly 80 percent of patients who receive ADT report experiencing hot flashes during and after treatment. Moffitt Cancer Center researchers are working to determine what genetic factors and other characteristics might make prostate cancer patients more likely to experience hot flashes during and after therapy.
Cancer therapies often are associated with unwanted side effects. Some side effects can be so debilitating that patients decide ...