(Press-News.org) Offenders enrolled in alcohol treatment programmes as part of their sentence are significantly less likely to be charged or reconvicted in the 12 months following their programme, a study led by Plymouth University has shown.
Researchers from the University's School of Psychology led a project, supported by the European Social Fund, which saw males with alcohol problems related to offending being assigned to a range of different treatments when convicted.
They then calculated the participants' charged and reconviction rates over the following year, with the results indicating that offenders who did not participate in such programmes were twice more likely to be charged and 2.5 times more likely to be reconvicted.
The study, published in the journal Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research, also involved the former Devon and Cornwall Probation Service, the University of Exeter and the Virginia Commonwealth University in the United States.
In the paper, the authors - led by PhD student Marie Needham, Dr Michaela Gummerum and Dr Yaniv Hanoch from Plymouth University - also note that as well as the reduction in reoffending, such programmes could also have cost benefits, with the bill for placing one person in prison being up to 37 times higher than assigning that person to a community-based alcohol treatment programme.
They say: "Cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) has been one of the most common methods to reduce alcohol use and the judicial systems in the United Kingdom and the United States have specifically identified CBT alcohol treatment programs as the chief method to break the link between alcohol and crime. Our findings provide novel and valuable evidence to support the practice of assigning male offenders to alcohol treatment interventions, as they show an indication that alcohol treatment programs could help reduce recidivism. Given the hundreds if not thousands of offenders who might be eligible to attend an alcohol treatment program each year, this could amount to substantial public savings. Beyond financial gains, committing fewer offences and staying out of prison have strong and continued benefits for the offenders, their families, and the community."
Alcohol misuse is associated with about 50 per cent of all violent crimes and 73 per cent of all domestic violence incidents in the United Kingdom and the United States, with nearly 1million violent attacks every year in the United Kingdom alone.
It is estimated that alcohol-related crime has a price tag of £8 to 13 billion a year in the UK, and the link between alcohol and criminal behaviour has reached such proportions that the World Health Organization now considers it a public health issue.
This study involved 564 male offenders, with 141 of them each assigned by the courts to one of three alcohol treatment programmes: a Low Intensity Alcohol Program (LIAP), an Alcohol Specified Activity Requirement (ASAR), and Addressing Substance-Related Offending (ASRO). A fourth group of 141 was not assigned to a programme and served as a control group.
The results indicate a significant reduction in being charged with or reconvicted of a crime among those on the programmes, with the LIAP being deemed by researchers as the most successful in reducing reconviction rates and the most cost effective.
Ian Clewlow, Deputy Chief Executive of the Dorset Devon and Cornwall Community Rehabilitation Company, commented: "In the delivery of probation services to offenders we always try to do things that are evidenced to work. We welcome the news from this Plymouth University research that offenders and service users who participate on alcohol programmes are less likely to reoffend and be convicted than those that do not and this is a testament to the hard work of staff to make these programmes a success in the community. The newly created Dorset Devon and Cornwall Community Rehabilitation Company with responsibility for probation services, alongside the National Probation Service, is committed to maintaining this activity."
INFORMATION:
This news release is available in German.
Mainz-based researchers have made significant advances with regard to the development of individualized immunotherapy strategies for treating cancer. They have managed to identify the relevant genetic changes or mutations associated with various types of cancer and have determined their individual blueprints. This makes it possible for the scientists to readily produce customized cancer vaccines of the kind that have already been demonstrated to be effective in animal models. Here they have proven effective in the regression ...
PITTSBURGH--Bragging to coworkers about a recent promotion, or posting a photo of your brand new car on Facebook, may seem like harmless ways to share good news.
However, a new study from City University London, Carnegie Mellon University and Bocconi University shows that self-promotion or a "humblebrag" often backfires.
Published in Psychological Science, Irene Scopelliti, George Loewenstein and Joachim Vosgerau wanted to find out why so many people frequently get the trade-off between self-promotion and modesty wrong. They found that self-promoters overestimate how ...
Pollution from historic mining activities in south west England has led to a reduction in genetic diversity of brown trout according to new research from the University of Exeter. The findings, which will be published on Friday 15 May in the journal Evolutionary Applications, indicate that human activity can alter the genetic patterns of wild populations - an important issue in modern conservation.
The prevalence of metal contaminants in rivers across the south west of England is directly linked to mining activities dating back hundreds of years. Exposure to high concentrations ...
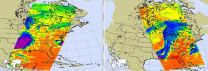
Today's imagery from NASA's AIRS instrument on the Aqua satellite indicates more severe weather is in store for the Midwest from Texas to Michigan. There is another extremely strong storm that is stretching from south to north and into Canada, and that system can be seen in this AIRS image from May 11, 2015. The first image (left) was taken at 3:35 am EDT, by the time the second image (right) was taken at 2:41 pm EDT the system had come together and was stretching across the nation vertically across the country.
Current weather forecasting predicts that Monday evening ...
CORVALLIS, Ore. - Researchers have discovered why many animal species can spend their whole lives outdoors with no apparent concern about high levels of solar exposure: they make their own sunscreen.
The findings, published today in the journal eLife by scientists from Oregon State University, found that many fish, amphibians, reptiles, and birds can naturally produce a compound called gadusol, which among other biologic activities provides protection from the ultraviolet, or sun-burning component of sunlight.
The researchers also believe that this ability may have ...
Using a smart tablet and a red beam of light, Georgia Institute of Technology researchers have created a system that allows people to control a fleet of robots with the swipe of a finger. A person taps the tablet to control where the beam of light appears on a floor. The swarm robots then roll toward the illumination, constantly communicating with each other and deciding how to evenly cover the lit area. When the person swipes the tablet to drag the light across the floor, the robots follow. If the operator puts two fingers in different locations on the tablet, the machines ...
Diet exerts a major impact on health and ageing. The nervous system plays an important role in this process but, thus far, how food signals are interpreted by the nervous system has been a mystery. This is an important question because the perception of food by the nervous system impacts not just ageing, but also other processes associated with health and disease, including metabolism, reproduction, and development.
A new study published in eLife by researchers from the MRC Centre for Developmental Neurobiology (MRC CDN) at the Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology & Neuroscience ...
To measure distances in the Universe, astronomers use Cepheids, a family of variable stars whose luminosity varies with time. Their role as distance calibrators has brought them attention from researchers for more than a century. While it was thought that nearly everything was known about the prototype of Cepheids, named Delta Cephei, a team of researchers at the University of Geneva (UNIGE), the Johns Hopkins University, and the European Space Agency (ESA), have now discovered that this star is not alone, but that it has a hidden companion. A revelation published in The ...
MADISON, Wis. -- Expansion of cattle pastures has led to the destruction of huge swaths of rain forest in Brazil, home to the world's largest herd of commercial beef cattle. But a new study led by the University of Wisconsin-Madison's Holly Gibbs shows that market-driven "zero deforestation agreements" have dramatically influenced the behavior of ranchers and the slaughterhouses to which they sell.
Publishing today [May 12, 2015] in the journal Conservation Letters, the research team - including other UW-Madison scientists, the National Wildlife Federation, and IMAZON ...
Scientists from Oregon State University have discovered that fish can produce their own sunscreen. They have copied the method used by fish for potential use in humans.
In the study published in the journal eLife, scientists found that zebrafish are able to produce a chemical called gadusol that protects against UV radiation. They successfully reproduced the method that zebrafish use by expressing the relevant genes in yeast. The findings open the door to large-scale production of gadusol for sunscreen and as an antioxidant in pharmaceuticals.
"The fact that the compound ...