(Press-News.org) An anti-poverty program tested extensively on three continents has produced sustained gains in individuals' income, wealth, and well-being, according to a study published today in the journal Science.
The program provides very poor people with productive assets, such as livestock, as well as job training, life-skills coaching, and health information. Known as the "Graduation" program, its intention was to examine whether helping the poor in multiple ways simultaneously could be especially effective in fighting poverty.
Overall, with more than 20,000 people enrolled across six countries over a three-year period, the experiment produced a 5 percent increase in per capita income, an 8 percent increase in food consumption, a 15 percent increase in assets, and a 96 percent increase in savings, compared with similar groups of people not enrolled in the program.
"The results show that three years after the intervention, hunger is down, consumption is up, and income is up," says Abhijit Banerjee, the Ford Professor of International Economics at MIT, and a co-author of the paper detailing the findings.
The "Graduation" program was targeted at substantial groups of very poor citizens in Ethiopia, Ghana, Honduras, India, Pakistan, and Peru; about 48 percent of households in the experiment had daily per capita consumption of less than $1.25. While the welfare of recipients was expected to increase in the short run, those gains proved durable.
"It seems to be an improvement that happens and stays intact," Banerjee says, noting that the self-reported mental health of participants improved as well: "They are happier, too."
Providing a "big push"
There are nine co-authors of the Science paper, including Banerjee and Esther Duflo, co-founders of MIT's Abdul Latif Jameel Poverty Action Lab (J-PAL). The paper's corresponding author is Dean Karlan, a development economist at Yale University and a member of J-PAL's executive committee.
J-PAL was founded in 2003 and named in 2005 after the father of MIT alumnus Mohammed Abdul Latif Jameel '78, whose substantial gift to the lab greatly expanded the scope of its activities.
The study examined results from 21,063 adults in 10,495 rural households. The "Graduation" program concept was first used deployed in Bangladesh by a large non-governmental organization known as BRAC. As the paper notes, the idea was to provide the poor with a "big push" intended to alleviate poverty.
"The intellectual impetus came from asking the question: Can we have durable consequences from a one-time intervention into the lives of the poor?" Banerjee says.
The "Graduation" program gave participants a one-time asset transfer, often providing people with animals, such as cows or chickens, from which they could earn income. It supplemented that asset donation with temporary spending support; training on running a business; frequent home visits from project staff; and information about health care. Participants were also encouraged to save money.
Some specifics were tailored to each country, but in each case, participants' results were compared to those of people with similar income levels who did not take part in the project. The wealth gains were observed in five of the six countries; only Honduras was an exception.
"The overall bottom line is that the program appears to be effective in most places," the authors write in the Science paper.
"A battle that could be won"
The "Graduation" project has also produced a number of questions the researchers hope to explore. Some pertain to costs; the program is intensive, with home visits and personalized coaching. Future variations, Banerjee notes, may modify some elements of the program, to see if the same outcomes can be achieved at lower cost.
For now, Banerjee thinks the experiment has demonstrated that the world's poorest people are not inherently incapable of improving their own lives.
"We wanted to show it's a battle that could be won," Banerjee says.
INFORMATION:
The other co-authors of the Science paper are Nathaniel Goldberg of Innovations for Poverty Action; Robert Osei of the University of Ghana-Legon; William Pariente of the Catholic University of Louvain in Belgium; Jeremy Shapiro of Princeton University; Bram Thuysbaert of the University of Ghent; and Christopher Udry of Yale University.
Funding for the project was provided by the Ford Foundation, 3ie, and the U.S. Agency for International Development.
A new paper, co-authored by Woods Hole Research Center Senior Scientist Richard A. Houghton, entitled, "Audit of the global carbon budget: estimate errors and their impact on uptake uncertainty", was published in the journal Biogeosciences. The paper confirms that as carbon emissions continue to climb, so too has the Earth's capacity to absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. About half of the emissions of CO2 each year remain in the atmosphere; the other half is taken up by the ecosystems on land and the oceans.
For Dr. Houghton, "There is no question that land ...
A new work based on 3-D supercomputer simulations of earthquake data has found hidden rock structures deep under East Asia. Researchers from China, Canada, and the U.S. worked together to publish their results in March 2015 in the American Geophysical Union Journal of Geophysical Research, Solid Earth.
The scientists used seismic data from 227 East Asia earthquakes during 2007-2011, which they used to image depths to about 900 kilometers, or about 560 miles below ground.
Notable structures include a high velocity colossus beneath the Tibetan plateau, and a deep mantle ...
GAINESVILLE, Fla. -- Raising awareness of the dangers of mouth and throat cancer increased the number of black men in some of Florida's poorest counties who sought screening for the first time, opening the door to improved survival rates through early detection and treatment, UF Health researchers report.
Black men have the lowest survival rates of mouth and throat cancer in the United States, and these rates have decreased even more in recent years. To combat this problem, UF Health researchers launched a five-month media campaign targeted at black men in some of Florida's ...
A new study led by investigators at Brigham and Women's Hospital (BWH) reports the discovery of a genetic variant that is associated with a patient's likelihood of responding to interferon-beta, one of the medications used in treating multiple sclerosis (MS). Published in the Annals of Neurology on May 14, the study also presents evidence that the affected gene, SLC9A9, may have a broader role in regulating the development and activity of certain immune cells that play important roles in inflammatory diseases like MS.
A proportion of MS patients experience disease activity ...
May 14, 2015 -- Researchers at Columbia University's Mailman School of Public Health and Leiden University in the Netherlands found that children whose mothers were malnourished at famine levels during the first 10 weeks of pregnancy had changes in DNA methylation known to suppress genes involved in growth, development, and metabolism documented at age 59. This is the first study to look at prenatal nutrition and genome-wide DNA patterns in adults exposed to severe under-nutrition at different periods of gestation. Findings are published in the International Journal of ...
Army scientists working to support the Ebola virus outbreak response in West Africa have established the first genomic surveillance capability in Liberia, enabling them to monitor genetic changes in the virus within one week of sample collection. An article describing their work was recently published ahead of print in the online edition of Emerging Infectious Diseases.
In the paper, the team offers a concise evaluation of the potential impact of the evolution of Ebola virus Makona, the strain responsible for the current outbreak, based on genome reconstruction of 25 ...
LAWRENCE -- For centuries, people have imagined the possibility of life on Mars. But long-held dreams that Martians could be invaders of Earth, or little green men, or civilized superbeings, all have been undercut by missions to our neighboring planet that have, so far, uncovered no life at all.
Yet visits to the Red Planet by unmanned probes from NASA and the European Space Agency have found evidence that a prime condition for life once may have existed: water.
"There has been a tremendous amount of very exciting findings this year that Mars once contained actively ...
The Aqua satellite's MODIS (Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) instrument took this image of the fires in Siberia. The top image shows the full sized false color image of the area highlighting the burn scars from previous fires.
The sliding "before and after" image shows the real and false color images side-by-side for comparison. The left side shows current fires burning denoted by the red spots. These spots show areas where the thermal detectors on the MODIS instrument recognized temperatures higher than background. When accompanied by plumes of smoke, ...
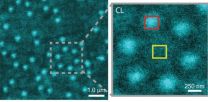
Soft matter encompasses a broad swath of materials, including liquids, polymers, gels, foam and - most importantly - biomolecules. At the heart of soft materials, governing their overall properties and capabilities, are the interactions of nano-sized components. Observing the dynamics behind these interactions is critical to understanding key biological processes, such as protein crystallization and metabolism, and could help accelerate the development of important new technologies, such as artificial photosynthesis or high-efficiency photovoltaic cells. Observing these ...
DNA damage caused by smoking can be detected in cheek swabs, finds research published today in JAMA Oncology. The study provides evidence that smoking induces a general cancer program that is also present in cancers which aren't usually associated with it - including breast and gynaecological cancers.
The research team, led by Professor Martin Widschwendter, Head of the Department of Women's Cancer at the UCL Institute for Women's Health and Dr Andrew Teschendorff (UCL Cancer Institute) looked at epigenetic alterations - changes to the DNA that switch genes on and off. ...