(Press-News.org) This news release is available in Japanese.
Right before a cell starts to divide to give birth to a daughter cell, its biochemical machinery unwinds the chromosomes and copies the millions of protein sequences comprising the cell's DNA, which is packaged along the length of the each chromosomal strand. These copied sequences also need to be put back together before the two cells are pulled apart. Mistakes can lead to genetic defects or cancerous mutations in future cell generations.
Just like raising a building requires scaffolding be erected first, cells use biochemical scaffolding machinery to reassemble copied genomic fragments back into chromosomes. Researchers at the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology Graduate University (OIST) have mapped the points along the genome where a scaffolding protein crucial to maintaining the genome's structure binds. The paper was published in Genes to Cells.
The protein complex, called condensin, is one of many that become active when cells replicate. Researchers in OIST's G0 Cell Unit used fission yeast to find the binding sites of this particular protein complex along chromosomal DNA. This type of yeast shares many important genes with us and also has one of the two known condensin complexes in humans. It also undergoes cell division by first creating copies of chromosomes like most human cells and has a very fast replication cycle, all of which facilitated the study.
The OIST researchers found that the largest amount of condensin aggregates at the centromere, the central knot tying together the two replicated chromosomes. In a lot of cancerous cells, the centromere has an unnatural shape, which could be caused by a malfunction in the relevant cell's scaffolding machinery.
Large amounts of condensin also accumulate at areas where RNA is created. In humans and all multicellular organisms, three different types of RNA producing enzymes control how genes are transcribed. Thus, condensin is crucial to passing on genes correctly.
Condensin also helps preserve the genome in challenging environments. OIST researchers bumped up the heat from 20 degrees to 36 degrees centigrade over 9 minutes, and found that condensin accumulated around heat-shock protein (Hsp) genes after replication. Hsp genes are a family of proteins produced by cells in stressful situations, ranging from high temperatures to ultraviolet light exposure to maintain genomic integrity.
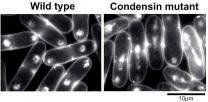
The researchers also engineered a yeast strain where a mutant condensin was produced by the cell when it went into figurative labor. In this mutated strain, there were massive errors in disentangling the separately copied chromosomes from the original. DNA content in the mutant cells increased and some of the resulting cell sizes were larger.
Larger cells need more energy to survive and condensin could be crucial to maintaining appropriate DNA content and cell sizes across cellular generations.
Extraneous structures like RNA and bound proteins are typically present along the length of chromosomes. Accommodating these extra structures into the daughter cell's nucleus might be what increases the overall cell size.
"While these macromolecules are important for the parent cell, they pose hindrances during cell division to segregating the copied chromosomes to daughter cells properly," said Dr. Norihiko Nakazawa, of OIST's G0 Cell Unit, the paper's first author.
The OIST researchers speculate that condensin is trimming the hedgerow of the genome during the replication and dividing phase. They further speculate that these eliminated macromolecules might be regenerated by the cellular machinery of the daughter cell when necessary.
At this point, the relevant biochemical processes by which condensin works remain to be apprehended. The OIST study concentrates on only one type of condensin. Where the second type of condensin, which is present in humans and other multicellular organisms, binds during cell division is another future line of enquiry.
INFORMATION:
The method used to calculate Standard & Poor's Case-Shiller Home Price Indices, the most trusted benchmark for U.S. residential real estate prices, contains a flaw that likely could lead to misstating its monthly estimates, according to a newly published study led by faculty at Florida Atlantic University.
The paper published in the Journal of Real Estate Research identifies an important deficiency in the Weighted Repeated Sales (WRS) method developed by economists Karl Case and Robert Shiller, which compares repeat sales of the same homes in an effort to study home ...
Anti-osteoporotic medication is not an effective means for preventing hip fractures among the elderly, concludes a study recently published in the BMJ.
Proximal femoral fractures (i.e., hip fractures) occur in the world at a rate of 1.5 million per year, or 7,000 per year in Finland. As most such fractures occur among older people, their number is expected to grow as the population ages. Hip fractures often lead to permanently reduced mobility, quality of life and general health, as well as result in significant social costs.
Since the early 1990s, anti-osteoporotic ...
The teacher's interaction style can either foster or slow down the development of math skills among children with challenging temperaments. This was shown in the results of the study "Parents, teachers and children's learning" carried out at the University of Jyväskylä, Finland.
Ph.D. Jaana Viljaranta, along with her colleagues, studied the role of teachers' interaction styles in academic skill development among children with different temperamental characteristics.
A child's challenging temperament may show up in the classroom, for example, as low task-orientation ...
When Niels Bohr hypothesised his model of atom with the electrons orbiting the nucleus just like satellites orbit a planet, he was engaging in analogical reasoning. Bohr transferred to atoms the concept of "a body orbiting another", that is, he transferred a relation between objects to other, new objects. Analogical reasoning is an extraordinary ability that is unique to the human mind, is not seen in animals (except very rarely in primates) and that forms the basis of highly sophisticated human thoughts. Scientists have wondered about the origin of this cognitive function: ...
Jena (Germany) March 1938: The Italian elementary particle physicist Ettore Majorana boarded a post ship in Naples, heading for Palermo. But he either never arrives there - or he leaves the city straight away - ever since that day there has been no trace of the exceptional scientist and until today his mysterious disappearance remains unresolved. Since then, Majorana, a pupil of the Nobel Prize winner Enrico Fermi, has more or less been forgotten. What the scientific world does remember though is a theory about nuclear forces, which he developed, and a very particular elementary ...
Hodgkin's lymphoma--cancer of the lymph nodes--arises in more than 150 children and adolescents in Germany each year. Nine out of ten patients survive the disease, thanks to the highly effective treatments that are now available. Depending on the type of treatment given, however, there may be late sequelae, as discussed by Wolfgang Dörffel and colleagues in an original article in the current issue of Deutsches Ärzteblatt International (Dtsch Arztebl Int 2015; 112: 320-7). These authors studied the question of which types of treatment were more likely to be followed ...
An international team of researchers has for the first time predicted the occurrence of aurorae visible to the naked eye on a planet other than Earth.
Mars' upper atmosphere may be indeed closer to Earth's than previously thought. Researchers showed that the upper atmosphere of Mars glows blue depending on the activity of the Sun. The result was achieved through numerical simulation and a laboratory experiment, called the Planeterrella, used to simulate the aurora. The study was published in the leading planetology publication Planetary and Space Science on 26 May.
'The ...
GAINESVILLE, FL -- As the container nursery industry faces severe restrictions on water use, researchers are looking to identify ways to minimize watering needs and eliminate excess watering. The authors of a new study say that understanding container-grown plants' capacity to "capture" sprinkler irrigation water can give growers important tools that help them adjust irrigation rates, reduce water use, and produce healthy plants.
Jeff Million and Thomas Yeager from the Department of Environmental Horticulture at the University of Florida say that there has been limited ...
Brisbane flood victims suffered more psychological distress during the rebuilding phase than as waters inundated their homes and businesses, a Queensland University of Technology study has found.
Kelly Dixon, from QUT's School of Psychology and Counselling, has looked at the mental health impacts caused by the Brisbane 2011 and the Mackay 2008 flood disasters.
"The findings showed that aftermath stress contributed to poor mental health outcomes over and above the flood itself, prior mental health issues and demographic factors," Ms Dixon said.
Presenting her findings ...
In a groundbreaking study published recently in the Journal Psychology, Professor Lea Waters from the Melbourne Graduate School of Education outlines how children can draw on their personal strengths to cope with the demands that lead to stress.
"While some stress such as toxic stress caused by a long lasting intense negative experience can have a debilitating effect on the wellbeing of children, not all stress is bad or damaging," Professor Waters said.
"Positive stress is a normal part of the developmental process. When managed well, it has the potential to help children ...