(Press-News.org) A "look back" study of Medicare fee-for-service claims for more than 1.2 million patients over age 65 has directly affirmed and quantified a long-suspected link between lower rates of coordinated health care services and higher rates of unnecessary medical tests and procedures.
In a report on the study published online May 18 in JAMA Internal Medicine, a trio of Johns Hopkins researchers say they analyzed 5 percent of Medicare claims using a previously validated set of 19 over-used procedures and a measure of so-called continuity of care.
Their results showed that 14.7 percent of patients were subjected to at least one potentially overused diagnostic, screening, monitoring or treatment procedure in 2008. Overall, patients who had more continuity in their medical care had a lower chance of having an overused procedure. In particular, higher continuity was significantly associated with lower odds of nine procedures (six out of 13 diagnostic tests and three out of three therapeutic procedures).
Higher continuity was associated with increased overuse for just three procedures: routine monitoring of digoxin, an MRI of the lumbar spine for low back pain prior to conservative therapy, and thorax CT scans with and without contrast.
"Increased continuity was associated with lower rates of overuse," says lead author Max Romano, M.D., M.P.H, a medical student at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine and the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, "suggesting a potential benefit of high-continuity care," although the strength and direction of the association varied according to the specific procedure.
"Conservative estimates suggest that 30 percent of all health care spending nationwide -- roughly $600 billion annually -- could be eliminated without any decrease in health care quality," says Romano. "This research is important because it suggests that fractured patient care is related to this massive amount of overuse."
Each year, Romano says, the average Medicare patient racks up 13 medical visits in four different practices, split among an average of two primary care physicians and five specialists. This lack of continuity has previously been associated with higher costs and lower quality health care, but the links between continuity and specific patterns of procedure overuse had not been examined.
For the study, Romano and his colleagues measured the number of procedures each Medicare patient received that could be classified as potentially overused. The researchers defined overuse as services that may be provided in the absence of a clear medical basis, when the risk of harm exceeds its likely benefit. Examples of commonly overused procedures are antibiotics given for simple respiratory infections. Causes of overuse, according to Romano, include physicians who may not follow clinical guidelines and providers who inadvertently order procedures that a patient has already received.
"Our patients receive too much care that doesn't improve their health, and there is often a lack of continuity in the care they receive," says senior author Craig Evan Pollack, M.D., M.H.S., an associate professor of medicine at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine. "This work finds that poor continuity is linked with overuse of medical care."
"The scale of overuse is mindboggling," says Romano. "Unfortunately, patients just don't know which procedures are necessary and which aren't. They have to put a lot of trust in the health care system and providers. The fragmented health care system may make it harder for their providers to make the best decisions."
Romano cautioned that the current study had limitations. For example, it only examined correlations between continuity and overuse. But Romano hopes that his team's results will inspire a deeper investigation. "If further research can validate our findings and establish a causal relationship between continuity driving overuse," Romano says, "then it could really lead to a variety of policy decisions that could change our health care system for the better."
INFORMATION:
The work was funded by the Johns Hopkins Institute for Clinical and Translational Research (ICTR), which is funded in part by Grant Number TL1 TR001078 from the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS), a component of the National Institutes of Health (NIH); the NIH Roadmap for Medical Research and the National Cancer Institute (K07CA151910).
The other investigator on the study is Jodi Segal from the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine and the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
Johns Hopkins Medicine
Media Relations and Public Affairs
Media contacts:
Marin Hedin, (410) 502-9429, mhedin2@jhmi.edu,
Helen Jones, (410) 502-9422, hjones49@jhmi.edu
An analysis of extended follow-up data from the Women's Health Initiative clinical trials suggests that postmenopausal women who were overweight and obese had an increased risk of invasive breast cancer compared to women of normal weight, according to an article published online by JAMA Oncology.
Obesity is a major public health problem in the United States and obesity has been associated with breast cancer risk in observational studies, systematic reviews and meta-analyses. However, questions remain.
Marian L. Neuhouser, Ph.D., R.D., of the Fred Hutchison Cancer Research ...
DARIEN, IL - A new study suggests that students who initiate and/or continue drinking and engage in binge drinking in college have more delayed sleep timing and more variable sleep schedules.
Results show that heavier drinkers had later bedtimes and rise times, and more day-to-day variability in sleep length, bedtime and rise time.
"These data indicate that students who initiate drinking and engage in binge drinking in college have more delayed sleep timing and a greater mismatch between circadian phase and sleep timing," said lead author Eliza Van Reen, assistant professor, ...
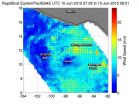
The third tropical depression of the active Eastern Pacific Ocean hurricane season formed and NASA's RapidScat saw its winds coming together as it formed. NASA's Terra satellite provided an image of the storm's cloud extent showing bands of thunderstorms wrapping into its center.
RapidScat is a scatterometer instrument that flies aboard the International Space Station and can measure surface winds over the ocean. On June 10 from 07:28 to 09:01 UTC (3:28 to 5:01 a.m. EDT) RapidScat collected wind data on the strengthening tropical low pressure area known as System 94E. ...
Researchers have identified two critical mutations allowing the deadly Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) virus to transmit from bats to humans. The findings were published in the most recent edition of the Journal of Virology.
Leading the research was Fang Li, Ph.D., associate professor of Pharmacology at the University of Minnesota Medical School. Graduate students Yang Yang and Chang Liu from Professor Fang Li's lab participated in the research. The study was conducted in collaboration with Shibo Jiang, M.D. , Ph.D., and Lanying Du, Ph.D., from the New York Blood ...
Comparing the genomes of different species -- or different members of the same species -- is the basis of a great deal of modern biology. DNA sequences that are conserved across species are likely to be functionally important, while variations between members of the same species can indicate different susceptibilities to disease.
The basic algorithm for determining how much two sequences of symbols have in common -- the "edit distance" between them -- is now more than 40 years old. And for more than 40 years, computer science researchers have been trying to improve upon ...
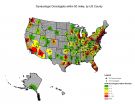
PHILADELPHIA -- More than one-third of counties in the Unites States are located more than 50 miles from the nearest gynecologic oncologist, making access to specialty care for ovarian and other gynecologic cancers difficult for nearly 15 million women. While most of these "low access" counties are located in the Mountain-West and Midwest regions, the findings of a recent study from researchers at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania also reveal that 47 states have at least one county located more than 50 miles from the nearest gynecologic oncologist. ...
PHILADELPHIA - According to a new study, women experiencing difficulty with time management, attention, organization, memory, and problem solving - often referred to as executive functions - related to menopause may find improvement with a drug already being used to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). The study led by researchers at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania is the first to show that lisdexamfetamine (LDX) improved subjective and objective measures of cognitive decline commonly experienced in menopausal women. Results ...
Researchers from Boston Children's Hospital and Merck have built the beginnings of "digital phenotype" of insomnia and other sleep disorders based on data from Twitter. This study, published today in the Journal of Medical Internet Research, is one of the first to look at relationships between social media use and sleep issues, and--based on assessments the sentiments expressed in users' tweets--gives preliminary hints that patients with sleep disorders may be a greater risk of psychosocial issues.
The study--led by Jared Hawkins, PhD; David McIver, PhD; and John Brownstein, ...
Philadelphia, PA - "The impact of human mobility on disease dynamics has been the focus of mathematical epidemiology for many years, especially since the 2002-03 SARS outbreak, which showed that an infectious agent can spread across the globe very rapidly via transportation networks," says mathematician Gergely Röst. Röst is co-author of a paper to be published this week in the SIAM Journal on Applied Dynamical Systems that presents a mathematical model to study the effects of individual movement on infectious disease spread.
"More recently, the risk of polio ...
Washington D.C., June 11, 2015 - A study published in the June 2015 issue of the Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry demonstrates that the atypical trajectory of cortical/brain development in autism spectrum disorder (ASD) extends well beyond young childhood and into late adolescence and young adulthood.
A considerable amount of work has focused on early structural brain development in ASD utilizing magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). This body of work has revealed evidence for brain overgrowth during the early postnatal years that appears ...