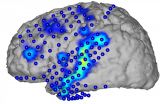
(Press-News.org) Restricting teenagers from driving unsupervised at night, and introducing strict penalties and other licensing requirements, could reduce crashes significantly, according to research.
Published in Health Affairs, the study by researchers from Monash University and Harvard Medical School, shows that driving laws that eliminate or deter unsupervised night driving by people younger than 18 achieve substantial reductions in car crashes.
Car crashes are the leading cause of death among people aged 15-19 worldwide. In the US, where the study was based, teen drivers experience motor vehicle crashes at more than twice the rate of the total population of licensed drivers.
Researchers evaluated the impact of changes to the Massachusetts graduated driver licensing program. Designed to allow young drivers under 18 years to gain experience before receiving their full license, the program prohibits driving unsupervised at night. It also imposes penalties for those violating the restriction and includes compulsory drowsy driving education programs.
Police crash records of drivers aged 16-17 were analysed for one year before and five years after the law's implementation in 2007. Two comparison groups were also evaluated.
The results showed that crash rates for drivers aged 16-17 fell 19 per cent, nighttime crashes for this age group fell by 29 per cent, and crashes causing fatal or incapacitating injury fell by 40 per cent.
The lead author, Professor Shantha Rajaratnam from the School of Psychological Sciences at Monash University, and the Brigham and Women's Hospital and Harvard Medical School in Boston, said the 18-19 age group should be the focus of targeted night driving interventions strategies in the future.
"Young people are strikingly overrepresented in sleep-related crashes. That's because they are more vulnerable than older people to performance impairment as a result of sleep deprivation, particularly during the night time when the biological clock in the brain is signalling sleep," he said.
"In the US, and similarly in Australia, drowsy driving is responsible for about 20 per cent of fatal crashes. This study provides strong evidence for policy makers, not only in the US, but more broadly, that graduated driver licensing programs that include tough penalties for violating restrictions on night driving among teenagers, are highly effective in reduce motor vehicle crashes,."
Night driving restrictions are already a feature of graduated driving licensing laws in nearly all states in the US. This study recommends that these restrictions have a much greater impact when they are accompanied by strict penalties, including enforcing drivers' license suspensions as the penalty for intermediate stage drivers who violate night driving prohibitions, with incremental increases in the duration of the suspension for subsequent violations.
Education about the risks associated with night driving, including driver sleepiness; through mandatory driver training courses are among other measures suggested.
Senior author Dr Charles Czeisler from Harvard Medical School and Brigham and Women's Hospital in Boston said: "Our data indicate that the 2007 revisions to the Massachusetts Junior Operator Law have prevented about 320 fatal and incapacitating injuries and 13,000 motor vehicle crashes among Massachusetts teen drivers over the past eight years."
INFORMATION:
This news release is available in German.
Speech is produced in the human cerebral cortex. Brain waves associated with speech processes can be directly recorded with electrodes located on the surface of the cortex. It has now been shown for the first time that is possible to reconstruct basic units, words, and complete sentences of continuous speech from these brain waves and to generate the corresponding text. Researchers at KIT and Wadsworth Center, USA present their "Brain-to-Text" system in the scientific journal Frontiers in Neuroscience (doi: 10.3389/fnins.2015.00217). ...
For breast cancer to be fatal, the tumor has to send out metastases to other parts of the body. The cancer cells are spread via the blood vessels, and a research team at Lund University in Sweden has now proven that the protein ALK1 determines the extent of the tumor's spread in the body. The higher the levels of the protein on the surface of the blood vessels, the greater their permeability to tumor cells and therefore the greater the risk of metastases.
The new study also shows that the drug Dalantercept can prevent the spread of tumour cells in breast cancer by blocking ...
This news release is available in German.
In 1915 Albert Einstein formulated the theory of general relativity which fundamentally changed our understanding of gravity. He explained gravity as the manifestation of the curvature of space and time. Einstein's theory predicts that the flow of time is altered by mass. This effect, known as "gravitational time dilation", causes time to be slowed down near a massive object. It affects everything and everybody; in fact, people working on the ground floor will age slower than their colleagues a floor above, by about 10 nanoseconds ...
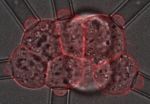
The same kind of contraction that fires our muscles also controls a key stage of mammalian embryo development, according to a new study published in Nature Cell Biology. The research, conducted at EMBL Heidelberg, measured and mapped how cells in very early stage embryos bond tightly together. The scientists also discovered a cellular behaviour that hadn't been observed before: cells in the embryo 'dance', each one making the same rhythmic movement.
The focus of the study was a stage of development known as compaction, which takes place when the embryo has eight cells. ...
In recent decades, enormous successes have been achieved in the field of public health. Three examples of these are the fight against HIV, the reduction in cardiovascular disease, and protection for non-smokers. For Germany to make even better use of the potential of public health, it needs more political support, improved research structures, and stronger international involvement. The German National Academy of Sciences Leopoldina, acatech - the National Academy of Science and Engineering, and the Union of the German Academies of Sciences and Humanities point this out ...
Starfish have strange talents. Two biology students from University of Southern Denmark have revealed that starfish are able to squeeze foreign bodies along the length of their body cavities and out through their arm tips. This newly discovered talent gives insight into how certain animals are able to quickly heal themselves.
The two biology students, Frederik Ekholm Gaardsted Christensen and Trine Bottos Olsen have discovered a starfish behaviour that has never previously been described in the scientific literature. As part of their studies they were asked to tag some ...
Chimpanzees and bonobos are the two closest living relatives of the human species - the ultimate tool-using ape. Yet, despite being so closely related on the evolutionary tree, wild chimpanzees and bonobos differ hugely in the way they use tools.
Chimpanzees show the most diverse range of tool use outside of humans. For example, chimpanzees use sticks to 'fish' for ants and termites, stones to crack nuts, as well as tools for grooming and communication. Bonobos rarely use tools and never to forage for food.
The question of 'what makes a tool user?' is a key one in ...
AUSTIN, Texas -- Improving air quality -- in clean and dirty places -- could reduce pollution-related deaths worldwide by millions of people each year. That finding comes from a team of environmental engineering and public health researchers who developed a global model of how changes in outdoor air pollution could lead to changes in the rates of health problems such as heart attack, stroke and lung cancer.
Outdoor particulate air pollution results in 3.2 million premature deaths annually, more than the combined impact of HIV-AIDS and malaria. The researchers found that ...
Lisbon, 16 June 2015: Despite a prevalence of anonymous sperm donation in European countries, the use of the same sperm donor for subsequent conceptions is of paramount importance to those couples needing sperm donation to have children. "We found a marked tendency to favour full genetic bonds where possible," said midwife Sara Somers presenting study results today at the Annual Meeting of ESHRE.
The study, performed by Ms Somers and colleagues at the Ghent University Hospital and Ghent University in Belgium, included 34 lesbian and heterosexual couples using sperm donation ...
Lisbon, 16 June 2015: Dilatation and curettage (D&C) is one of the most common minor surgical procedures in obstetrics and gynaecology, used mainly for miscarriage or terminations.(1) Today, use of the 15-minute procedure is declining in favour of less invasive medical methods, but it still remains common in O&G.
Although D&C is generally considered safe and easy to perform, it is associated with some serious (if rare) side effects, including perforations to the cervix and uterus, infection, and bleeding. Now, an analysis 21 cohort studies which included almost 2 million ...