(Press-News.org) Researchers from the ARC Centre of Excellence for Coral Reef Studies at James Cook University have discovered that suspended sediment damages fish gills and can increase the rate of disease in fish.
"Suspended sediments result from flood plumes, coastal agricultural and industrial development and from dredging operations and are increasing in coastal waters worldwide," says study co-author, Dr Amelia Wenger.
"Fish gills are in direct contact with their environment and are the first line of defence in the animal's immune response, which makes them the perfect place to look for damage associated with sediment," adds co-author Dr Jodie Rummer.
"Plus, harm to this vital organ affects every activity in the animal's body that requires oxygen," Dr Rummer says.
For the study, the researchers simulated sediment conditions frequently found on inshore reefs on the Great Barrier Reef, but they say the problem isn't limited to Australian waters.
Coastal oceans affected by suspended sediment tend to overlap critical fish habitats and nurseries. The research highlights the need for the continued protection of these crucial habitats.
Juvenile reef fish are often exposed to sediment as they swim in open waters before settling on a chosen reef. During this critical developmental stage they need great amounts of oxygen, but damage to their gills makes it hard for them to get it.
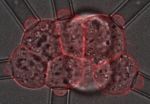
"The gills in sediment-exposed larval clownfish fish were congested, exhibiting twice as much mucous of what could be found in clean-water exposed fish," says study lead author, PhD Student Sybille Hess.
"Sediment-exposed fish also increased the number of protective cells on their gills, presumably safeguarding the delicate tissue from the damage that sediment particles could cause."
"Larval fish have very high growth rates. They're swimming a lot, often over long distances. They have a very high metabolic rate and high-energy costs and need their gills to be working as efficiently as possible," says co-author Dr Jodie Rummer.
The gills of affected fish were also found to harbour disease-causing bacteria.
"The presence of bacteria linked to fish disease on the gills of sediment-exposed fish suggests that exposure to, and accumulation of sediment, may trigger the development of fish diseases," says co-author Dr Tracy Ainsworth.
"This research underscores the necessity for future coastal developments to consider the adverse effects of sediment on fish and reef ecosystems," adds Dr Wenger.
Exposure of clownfish larvae to suspended sediment levels found on the Great Barrier Reef: Impacts on gill structure and microbiome by Sybille Hess, Amelia Wenger, Tracy Ainsworth and Jodie L. Rummer is published in the journal, Nature Scientific Reports.
INFORMATION:
Images
https://www.dropbox.com/sh/mzrqr6t9cbzuw2s/AADlBdY__qQfKovTxgog3vQfa?dl=0
Photo credit: Ian McLeod
Contacts
Ms Sybille Hess - sybille.hess@my.jcu.edu.au
Dr Amelia Wenger - amelia.wenger@my.jcu.edu.au +61 (0) 4 0655 9711
Dr Tracy Ainsworth, tracy.ainsworth@jcu.edu.au
Dr Jodie Rummer - jodie.rummer@jcu.edu.au +61 (0) 4 3916 6171, +61 (0) 7 4781 5300
Eleanor Gregory, (Communications) eleanor.gregory@jcu.edu.au +61 (0) 428 785 895
University of Tokyo researchers have discovered the structure and transport properties of the "intermediate state" in lithium-ion batteries - key to understanding the mechanisms of charge and discharge in rechargeable batteries. These findings may help accelerate battery reaction speed and significantly shorten battery charging time.
Although there is strong demand to minimize battery-charging time, the mechanisms of battery charge and discharge reactions have yet to be fully understood. While the existence of an "intermediate state" that accelerates battery charge and ...
Researchers have discovered that extreme exercise can cause intestinal bacteria to leak into the bloodstream, leading to blood poisoning.
Experts at Monash University monitored people participating in a range of extreme endurance events, including 24-hour ultra-marathons and multi-stage ultra-marathons, run on consecutive days.
"Blood samples taken before and after the events, compared with a control group, proved that exercise over a prolonged period of time causes the gut wall to change, allowing the naturally present bacteria, known as endotoxins, in the gut to ...
A promising type of vaccine designed to eradicate malaria by blocking parasite transmission could be a step closer, as a result of experts uncovering new information about the targeted protein.
The international team of researchers co-led by Dr Natalie Borg from the Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology at Monash University, and Dr Rhoel Dinglasan from the Malaria Research Institute at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health in Baltimore, USA, focused on a protein in the Anopheles mosquito midgut called AnAPN1.
The research, published in the journal ...
Restricting teenagers from driving unsupervised at night, and introducing strict penalties and other licensing requirements, could reduce crashes significantly, according to research.
Published in Health Affairs, the study by researchers from Monash University and Harvard Medical School, shows that driving laws that eliminate or deter unsupervised night driving by people younger than 18 achieve substantial reductions in car crashes.
Car crashes are the leading cause of death among people aged 15-19 worldwide. In the US, where the study was based, teen drivers experience ...
This news release is available in German.
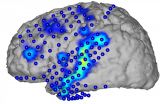
Speech is produced in the human cerebral cortex. Brain waves associated with speech processes can be directly recorded with electrodes located on the surface of the cortex. It has now been shown for the first time that is possible to reconstruct basic units, words, and complete sentences of continuous speech from these brain waves and to generate the corresponding text. Researchers at KIT and Wadsworth Center, USA present their "Brain-to-Text" system in the scientific journal Frontiers in Neuroscience (doi: 10.3389/fnins.2015.00217). ...
For breast cancer to be fatal, the tumor has to send out metastases to other parts of the body. The cancer cells are spread via the blood vessels, and a research team at Lund University in Sweden has now proven that the protein ALK1 determines the extent of the tumor's spread in the body. The higher the levels of the protein on the surface of the blood vessels, the greater their permeability to tumor cells and therefore the greater the risk of metastases.
The new study also shows that the drug Dalantercept can prevent the spread of tumour cells in breast cancer by blocking ...
This news release is available in German.
In 1915 Albert Einstein formulated the theory of general relativity which fundamentally changed our understanding of gravity. He explained gravity as the manifestation of the curvature of space and time. Einstein's theory predicts that the flow of time is altered by mass. This effect, known as "gravitational time dilation", causes time to be slowed down near a massive object. It affects everything and everybody; in fact, people working on the ground floor will age slower than their colleagues a floor above, by about 10 nanoseconds ...
The same kind of contraction that fires our muscles also controls a key stage of mammalian embryo development, according to a new study published in Nature Cell Biology. The research, conducted at EMBL Heidelberg, measured and mapped how cells in very early stage embryos bond tightly together. The scientists also discovered a cellular behaviour that hadn't been observed before: cells in the embryo 'dance', each one making the same rhythmic movement.
The focus of the study was a stage of development known as compaction, which takes place when the embryo has eight cells. ...
In recent decades, enormous successes have been achieved in the field of public health. Three examples of these are the fight against HIV, the reduction in cardiovascular disease, and protection for non-smokers. For Germany to make even better use of the potential of public health, it needs more political support, improved research structures, and stronger international involvement. The German National Academy of Sciences Leopoldina, acatech - the National Academy of Science and Engineering, and the Union of the German Academies of Sciences and Humanities point this out ...
Starfish have strange talents. Two biology students from University of Southern Denmark have revealed that starfish are able to squeeze foreign bodies along the length of their body cavities and out through their arm tips. This newly discovered talent gives insight into how certain animals are able to quickly heal themselves.
The two biology students, Frederik Ekholm Gaardsted Christensen and Trine Bottos Olsen have discovered a starfish behaviour that has never previously been described in the scientific literature. As part of their studies they were asked to tag some ...