(Press-News.org) A promising type of vaccine designed to eradicate malaria by blocking parasite transmission could be a step closer, as a result of experts uncovering new information about the targeted protein.
The international team of researchers co-led by Dr Natalie Borg from the Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology at Monash University, and Dr Rhoel Dinglasan from the Malaria Research Institute at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health in Baltimore, USA, focused on a protein in the Anopheles mosquito midgut called AnAPN1.
The research, published in the journal Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, provides for the first time, detailed information on the shape of AnAPN1 and where antibodies against AnAPN1 that can and can't block parasite development, bind to the protein.
Malaria is transmitted to humans by the bite of a mosquito infected with the Plasmodium parasite. Malaria transmission-blocking vaccines are designed to prevent the spread of malaria by interrupting parasite transmission.
Vaccinated individuals in malaria-endemic countries produce antibodies to AnAPN1. During routine disease transmission, when these same immunised individuals become infected with malaria parasites, both antibodies and parasites are ingested by a mosquito during blood feeding. The antibodies block parasite development in the mosquito, breaking the cycle of transmission.
The AnAPN1 protein is a leading candidate for a mosquito-based malaria transmission-blocking vaccine that is being developed by Dr Dinglasan.
"This type of vaccine won't boost people's immunity to malaria, but instead it will provide a delayed benefit to the individual by protecting the entire community from parasite transmission," Dr Dinglasan said.
"Ultimately it could lead to a reduced number of infected mosquitoes and the eventual elimination and eradication of the disease," he said.
AnAPN1 is found on the mosquito gut and is potentially a receptor for the parasite. Dr Dinglasan said as a vaccine antigen, AnAPN1 prompts people to make antibodies; however only some of these antibodies block parasite transmission, while others do not.
"This dilution of the overall antibody response to AnAPN1 is problematic. To further improve vaccine immunogenicity at the preclinical stage, we need to immuno-focus the antibody response to only the critical, 'transmission-blocking' regions of the protein," he said.
An understanding of how AnAPN1 antibodies that are generated can block parasite transmission to mosquitoes and their binding region on AnAPN1 has remained elusive until now. Using the Australian Synchrotron, Dr Borg's team at Monash University were able to visualise the crystal structure of the AnAPN1 protein for the first time, providing valuable insights. Dr Dinglasan's team then provided the critical functional data to support the hypotheses generated by the AnAPN1 structure.
"The Australian Synchrotron was critical in providing detailed imaging of the structure of AnAPN1. In combination with other experimental data, the structure enabled us to pinpoint the binding site of AnAPN1 antibodies that can and can't block parasite development," Dr Borg said.
"We now know much more about which parts of the AnAPN1 protein are involved in generating transmission-blocking antibodies and have a new hypothesis as to how they might work," she said.
This discovery will fuel further work to understand what critical interaction the AnAPN1 transmission-blocking antibodies are blocking. It will also prompt the redesign of the AnAPN1 antigen to make it more effective.
INFORMATION:
Restricting teenagers from driving unsupervised at night, and introducing strict penalties and other licensing requirements, could reduce crashes significantly, according to research.
Published in Health Affairs, the study by researchers from Monash University and Harvard Medical School, shows that driving laws that eliminate or deter unsupervised night driving by people younger than 18 achieve substantial reductions in car crashes.
Car crashes are the leading cause of death among people aged 15-19 worldwide. In the US, where the study was based, teen drivers experience ...
This news release is available in German.
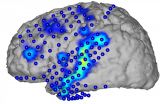
Speech is produced in the human cerebral cortex. Brain waves associated with speech processes can be directly recorded with electrodes located on the surface of the cortex. It has now been shown for the first time that is possible to reconstruct basic units, words, and complete sentences of continuous speech from these brain waves and to generate the corresponding text. Researchers at KIT and Wadsworth Center, USA present their "Brain-to-Text" system in the scientific journal Frontiers in Neuroscience (doi: 10.3389/fnins.2015.00217). ...
For breast cancer to be fatal, the tumor has to send out metastases to other parts of the body. The cancer cells are spread via the blood vessels, and a research team at Lund University in Sweden has now proven that the protein ALK1 determines the extent of the tumor's spread in the body. The higher the levels of the protein on the surface of the blood vessels, the greater their permeability to tumor cells and therefore the greater the risk of metastases.
The new study also shows that the drug Dalantercept can prevent the spread of tumour cells in breast cancer by blocking ...
This news release is available in German.
In 1915 Albert Einstein formulated the theory of general relativity which fundamentally changed our understanding of gravity. He explained gravity as the manifestation of the curvature of space and time. Einstein's theory predicts that the flow of time is altered by mass. This effect, known as "gravitational time dilation", causes time to be slowed down near a massive object. It affects everything and everybody; in fact, people working on the ground floor will age slower than their colleagues a floor above, by about 10 nanoseconds ...
The same kind of contraction that fires our muscles also controls a key stage of mammalian embryo development, according to a new study published in Nature Cell Biology. The research, conducted at EMBL Heidelberg, measured and mapped how cells in very early stage embryos bond tightly together. The scientists also discovered a cellular behaviour that hadn't been observed before: cells in the embryo 'dance', each one making the same rhythmic movement.
The focus of the study was a stage of development known as compaction, which takes place when the embryo has eight cells. ...
In recent decades, enormous successes have been achieved in the field of public health. Three examples of these are the fight against HIV, the reduction in cardiovascular disease, and protection for non-smokers. For Germany to make even better use of the potential of public health, it needs more political support, improved research structures, and stronger international involvement. The German National Academy of Sciences Leopoldina, acatech - the National Academy of Science and Engineering, and the Union of the German Academies of Sciences and Humanities point this out ...
Starfish have strange talents. Two biology students from University of Southern Denmark have revealed that starfish are able to squeeze foreign bodies along the length of their body cavities and out through their arm tips. This newly discovered talent gives insight into how certain animals are able to quickly heal themselves.
The two biology students, Frederik Ekholm Gaardsted Christensen and Trine Bottos Olsen have discovered a starfish behaviour that has never previously been described in the scientific literature. As part of their studies they were asked to tag some ...
Chimpanzees and bonobos are the two closest living relatives of the human species - the ultimate tool-using ape. Yet, despite being so closely related on the evolutionary tree, wild chimpanzees and bonobos differ hugely in the way they use tools.
Chimpanzees show the most diverse range of tool use outside of humans. For example, chimpanzees use sticks to 'fish' for ants and termites, stones to crack nuts, as well as tools for grooming and communication. Bonobos rarely use tools and never to forage for food.
The question of 'what makes a tool user?' is a key one in ...
AUSTIN, Texas -- Improving air quality -- in clean and dirty places -- could reduce pollution-related deaths worldwide by millions of people each year. That finding comes from a team of environmental engineering and public health researchers who developed a global model of how changes in outdoor air pollution could lead to changes in the rates of health problems such as heart attack, stroke and lung cancer.
Outdoor particulate air pollution results in 3.2 million premature deaths annually, more than the combined impact of HIV-AIDS and malaria. The researchers found that ...
Lisbon, 16 June 2015: Despite a prevalence of anonymous sperm donation in European countries, the use of the same sperm donor for subsequent conceptions is of paramount importance to those couples needing sperm donation to have children. "We found a marked tendency to favour full genetic bonds where possible," said midwife Sara Somers presenting study results today at the Annual Meeting of ESHRE.
The study, performed by Ms Somers and colleagues at the Ghent University Hospital and Ghent University in Belgium, included 34 lesbian and heterosexual couples using sperm donation ...