What controls blood flow in the brain?
2015-06-25
(Press-News.org) When neurons become active, they call for an extra boost of oxygenated blood -- this change in the presence of blood in different regions of the brain is the basis for functional brain scans. However, what controls this increase or decrease in blood supply has been a long-standing debate.
In a paper published on June 25 in Neuron, Yale University scientists present the strongest evidence yet that smooth muscle cells surrounding blood vessels in the brain are the only cells capable of contracting to control blood vessel diameter and thus regulate blood flow. This basic anatomical understanding may also have important implications for phenomena observed in stroke and migraines.
Smooth muscle cells line the thicker blood vessels in the brain, while the branching capillaries are covered by a mysterious cell type called pericytes. Pericytes are not muscle cells or neurons, but they are found in large numbers in the brain and are thought to play a role in blood vessel formation. Previous studies have suggested that pericytes could contract to regulate blood flow in the smaller blood vessels, but the new Neuron paper contradicts this theory.
'We found that when neurons fire more actively (either during normal brain activity or events such as migraines) there is a response in small blood vessels that are covered by smooth muscle cells, but not those that are covered by pericytes,' says senior study author Jaime Grutzendler, director of Yale School of Medicine's Center for Experimental Neuroimaging.
His team, including co-lead authors Robert Hill, Lei Tong, and Peng Yuan, made these observations in mice using high-resolution optical imaging and optogenetics, an emerging laboratory tool that allows researchers to distinctly activate single cells. With these tools, they could map out the location and identity of the cells that were making use of a spring-like protein called actin to contract -- which pericytes were never observed to do.
If capillaries do not regulate blood flow, then the next question is how individual neurons around the capillaries can request blood when they need to be active: 'While there is a local response, this response is not so local that a single capillary dilation/contraction will be triggered by the few adjacent neural cells surrounding it.' Grutzendler says. 'Our data supports the idea that flow control requires a certain threshold of cumulative neural activity within an area to trigger blood vessel dilation, which would then increase the flow to all its downstream capillary branches.'
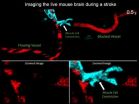
He notes that if this is how blood vessels function, it could provide insight into the 'no reflow' phenomenon that occurs after stroke. Even after the blood clot or other blockage that causes a stroke is removed, blood does not start reflowing downstream to the tissue. The reason could be that abnormal constrictions in smooth muscle-covered blood vessels result in permanent vessel block in downstream vessels through formation of new clots and other mechanisms (see video). Grutzendler plans to explore therapeutic interventions that could help smooth muscle-covered blood vessels dilate on their own after stroke in hopes that it can limit the damage.
INFORMATION:
Neuron, Hill, Tong & Yuan et al.: 'Regional Blood Flow in the Normal and Ischemic Brain Is Controlled by Arteriolar Smooth Muscle Cell Contractility and Not by Capillary Pericytes'
Neuron, published by Cell Press, is a bimonthly journal that has established itself as one of the most influential and relied upon journals in the field of neuroscience and one of the premier intellectual forums of the neuroscience community. It publishes interdisciplinary articles that integrate biophysical, cellular, developmental, and molecular approaches with a systems approach to sensory, motor, and higher-order cognitive functions. For more information, please visit http://www.cell.com/neuron. To receive media alerts for Neuron or other Cell Press journals, please contact press@cell.com.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-06-25
Think the nest of cables under your desk is bad? Try keeping the trillions of connections crisscrossing your brain organized and free of tangles. A new study coauthored by researchers at UC San Francisco and the Freie Universität Berlin reveals this seemingly intractable job may be simpler than it appears.
The researchers used high-resolution time-lapse imaging of the developing brains of pupal fruit flies (Drosophila melanogaster) paired with mathematical simulations to unravel a trick of neural wiring that had stumped neuroscientists for decades. They discovered ...
2015-06-25
Adult fruit flies given a cancer drug live 12% longer than average, according to a UCL-led study researching healthy ageing. The drug targets a specific cellular process that occurs in animals, including humans, delaying the onset of age-related deaths by slowing the ageing process.
The study published today in Cell and funded by the Max Planck Society and Wellcome Trust shows for the first time that a small molecule drug, which limits the effects of a protein called Ras, can delay the ageing process in animals. The treated fruit flies outlived the control group by staying ...
2015-06-25
Boston, MA -- A new study led by researchers at Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health finds that a malaria parasite protein called calcineurin is essential for parasite invasion into red blood cells. Human calcineurin is already a proven target for drugs treating other illnesses including adult rheumatoid arthritis and lupus, and the new findings suggest that parasite calcineurin should be a focus for the development of new antimalarial drugs.
"Our study has great biological and medical significance, particularly in light of the huge disease burden of malaria," said ...
2015-06-25
LA JOLLA--As a tumor grows, its cancerous cells ramp up an energy-harvesting process to support its hasty development. This process, called autophagy, is normally used by a cell to recycle damaged organelles and proteins, but is also co-opted by cancer cells to meet their increased energy and metabolic demands.
Salk Institute and Sanford Burnham Prebys Medical Discovery Institute (SBP) scientists have developed a drug that prevents this process from starting in cancer cells. Published June 25, 2015 in Molecular Cell, the new study identifies a small molecule drug that ...
2015-06-25
Washington, DC (June 25, 2015) - Comment sections on websites continue to be an environment for trolls to spew racist opinions. The impact of these hateful words shouldn't have an impact on how one views the news or others, but that may not be the case. A recent study published in the journal Human Communication Research, by researchers at the University of Canterbury, New Zealand, found exposure to prejudiced online comments can increase people's own prejudice, and increase the likelihood that they leave prejudiced comments themselves.
Mark Hsueh, Kumar Yogeeswaran, ...
2015-06-25
June 25 -- During the wars in Iraq and Afghanistan, U.S. combat support hospitals treated at least 650 children with severe, combat-related head injuries, according to a special article in the July issue of Neurosurgery, official journal of the Congress of Neurological Surgeons. The journal is published by Wolters Kluwer.
"Given the challenging environment and limited available resources, coalition forces were able to provide quality, timely, and life-saving care to many children" with severe head injuries, write Dr. Paul Klimo, Jr., of Semmes-Murphy Neurologic & Spine ...
2015-06-25
A large number of patients use online communication tools such as email and Facebook to engage with their physicians, despite recommendations from some hospitals and professional organizations that clinicians limit email contact with patients and avoid "friending" patients on social media, new research suggests.
The findings from Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health researchers suggest a disconnect between what patients expect and what physicians -- concerned about confidentiality and being overwhelmed in off-hours -- are willing to do when it comes to online ...
2015-06-25
June 25, 2015 - New results in animals highlight a major safety concern regarding a class of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast agents used in millions of patients each year, according to a paper published online by the journal Investigative Radiology. The journal is published by Wolters Kluwer.
The study adds to concerns that repeated use of specific "linear"-type gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) lead to deposits of the heavy-metal element gadolinium in the brain. The results will have a major impact on the multimillion-dollar market for MRI contrast agents, ...
2015-06-25
Many patients in the latter stage of Parkinson's disease are at high risk of dangerous, sometimes fatal, falls. One major reason is the disabling symptom referred to as Freezing of Gait (FoG) -- brief episodes of an inability to step forward that typically occurs during gait initiation or when turning while walking. Patients who experience FoG often lose their independence, which has a direct effect on their already degenerating quality of life. In the absence of effective pharmacological therapies for FoG, technology-based solutions to alleviate the symptom and prolong ...
2015-06-25
While the use of antiangiogenesis drugs that block the growth of new blood vessels can improve the treatment of some cancers, clinical trials of their ability to prevent the development of new metastases have failed. Now a study from the Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) Cancer Center may have found at least one reason why. In their paper published online in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute, an MGH research team reports finding that the growth of metastases in lymph nodes -- the most common site of cancer spread -- does not require new blood vessels but instead ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] What controls blood flow in the brain?