(Press-News.org) A spider's web is one of the most intricate constructions in nature, but its precious silk has more than one use. Silk threads can be used as draglines, guidelines, anchors, pheromonal trails, nest lining, or even food. And each use requires a slightly different type of silk, optimized for its function.
"Each type of silk has similar proteins, but they are synthesized differently," said Sinan Keten, assistant professor of mechanical and civil engineering at Northwestern University's McCormick School of Engineering. "Then the spider knows how fast to reel the silk to get different properties. Nature is smart. It can tailor a structure to get different mechanical properties."
Spider silk is one biological material that Keten discusses in his new paper "The role of mechanics in biological and bio-inspired systems," published in the July 6 issue of Nature Communications. Surveying everything from sea cucumbers and Venus flytraps to human muscles and trees, the review paper broadly explores the strategies that biology employs to create different functions and the mechanics at play within those functions. Discovering how and why biological systems attain desirable static and dynamic mechanical functionalities often reveals principles that inform new synthetic designs based on biological systems.
Coauthored by Philip LeDuc of Carnegie Mellon University, Keten's paper covers three themes: bottom-up assembly, multiscale and multiphasic organization, and the passive and active features found in different materials.
"We wanted to point out some of the overarching principles that many systems share," Keten said. "By understanding these and learning from biology, we can speed up discovery."
Much of the paper focuses on nanoconfinement, a major part of Keten's research. The term describes the ability to control the building blocks of a material at the smallest level in order to ensure specific properties. When a spider creates its dragline, for example, it spins silk faster than when its constructing a web. The crystals comprising the silk are smaller when it's spun faster, resulting in stronger material. When the crystals are larger, the silk is less structured and contains more defects.
Although Keten spent the early part of his career studying spider silk, he has more recently shifted his focus to cellulose in tree branches. "We see the same things in silk as we do wood," Keten said. "Small crystals are preferred to larger crystals. It call comes back to nanoconfinement, which is to make the material's building blocks small enough that you don't have defects and therefore get stronger features. Additionally, nanoscale building blocks give rise to more interfaces in materials where intriguing physical phenomena may emerge from the large surface of nanoparticles."
Funded by the Army Research Office, Keten's team discovered that, on the nanolevel, cellulose crystals are transparent and as tough as Kevlar. He suggests that these properties could be mimicked to develop bulletproof glass and goggles and uses computation to explore the best ways to arrange the crystals to achieve different properties.
"You never mimic the biological system one-to-one," Keten said. "Like flight, for example. We can learn about aerodynamics from birds, but we don't design an airplane like a bird. That also applies to spider silk, which is a very tough and strong material. We don't use the exact same building blocks to develop a tough, man-made material. We use other building blocks but arrange them using the same methods we learn from biology."
INFORMATION:
An ambitious policy package is essential for the UK to transform its energy system to achieve the deep reductions in carbon emissions required to avoid dangerous climate change, according to research led by UCL scientists. To meet climate targets set for 2050, policies need to ensure strong action is taken now, while preparing for fundamental changes in how energy is provided and used in the long term.
The study is part of the Deep Decarbonization Pathway Project (DDPP) which is coordinated by the Institute for Sustainable Development and International Relations (IDDRI) ...
It may sound counter-intuitive, but crushing up bees into a 'DNA soup' could help conservationists understand and even reverse their decline - according to University of East Anglia scientists.
Research published today in the journal Methods in Ecology and Evolution shows that collecting wild bees, extracting their DNA, and directly reading the DNA of the resultant 'soup' could finally make large-scale bee monitoring programmes feasible.
This would allow conservationists to detect where and when bee species are being lost, and importantly, whether conservation interventions ...
BARCELONA-LUGANO, 4 July 2015 - Patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) that are mutation-free in the KRAS, NRAS, BRAF and PIK3CA genes showed significant benefit from continuing anti-epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) therapy beyond progression following first-line chemotherapy and an anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody, according to study results (1) presented today at the ESMO 17th World Congress on Gastrointestinal Cancer in Barcelona, Spain.
Prof Fortunato Ciardiello from Seconda Università degli Studi di Napoli, Italy, presented results from the CAPRI-Goim ...
Mice that are exposed to the powerful smell of cat urine early in life do not escape from cats later in life. Researchers at the A. N. Severtsov Institute of Ecology and Evolution, Russia, have discovered that mice that smell cat urine early in life, do not avoid the same odour, and therefore do not escape from their feline predators, later in life.
"Because the young mice (less than 2 weeks-old) are being fed milk while being exposed to the odour, they experience positive reinforcement," says Dr Vera Voznessenskaya, one of the lead researchers behind this study. "So ...
To mark the final day of the 65th Lindau Nobel Laureate Meeting, on Friday, 3 July, over 30 Nobel laureates assembled on Mainau Island on Lake Constance signed a declaration on climate change. The "Mainau Declaration 2015 on Climate Change" states "that the nations of the world must take the opportunity at the United Nations Climate Change Conference in Paris in December 2015 to take decisive action to limit future global emissions." It is expected that a new international agreement on climate protection will be approved at the 21st UN Climate Conference to succeed the ...
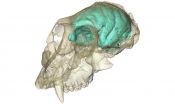
DURHAM, N.C. -- The brain hidden inside the oldest known Old World monkey skull has been visualized for the first time. The creature's tiny but remarkably wrinkled brain supports the idea that brain complexity can evolve before brain size in the primate family tree.
The ancient monkey, known scientifically as Victoriapithecus, first made headlines in 1997 when its fossilized skull was discovered on an island in Kenya's Lake Victoria, where it lived 15 million years ago.
Now, thanks to high-resolution X-ray imaging, researchers have peered inside its cranial cavity ...
BARCELONA-LUGANO, 3 July 2015 - The phase IIIb CONSIGN study has confirmed the benefit of regorafenib in patients with previously treated metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC), researchers announced at the ESMO 17th World Congress on Gastrointestinal Cancer 2015 in Barcelona.(1) The safety profile and progression free survival were similar to phase III trial results.
CONSIGN was a prospective, observational study that was initiated to allow patients with mCRC access to regorafenib before marketing authorisation and to assess safety, which was the primary endpoint. The randomised ...
Spiders travel across water like ships, using their legs as sails and their silk as an anchor, according to research published in the open access journal BMC Evolutionary Biology. The study helps explain how spiders are able to migrate across vast distances and why they are quick to colonise new areas.
Common spiders are frequently observed to fly using a technique called 'ballooning'. This involves using their silk to catch the wind which then lifts them up into the air. Ballooning spiders are estimated to move up to 30 km per day when wind conditions are suitable, helping ...
Scientists have developed a new technique allowing the bioprinting at ambient temperatures of a strong paste similar to 'play dough' capable of incorporating protein-releasing microspheres.
The scientists demonstrated that the bioprinted material, in the form of a micro-particle paste capable of being injected via a syringe, could sustain stresses and strains similar to cancellous bone - the 'spongy' bone tissue typically found at the end of long bones.
This work, published today (3 July 2015) in the journal Biofabrication, suggests that bioprinting at ambient temperatures ...
A therapy that replaces the faulty gene responsible for cystic fibrosis in patients' lungs has produced encouraging results in a major UK trial.
One hundred and thirty six patients aged 12 and over received monthly doses of either the therapy or the placebo for one year.
The clinical trial reached its primary endpoint with patients who received therapy having a significant, if modest benefit in lung function compared with those receiving a placebo.
Patients from across England and Scotland participated, and were treated in two centres, Royal Brompton Hospital in ...