(Press-News.org) Pursuant to the Act on the Reform of the Market for Medicinal Products (AMNOG), the German Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG) reassessed fingolimod (trade name: Gilenya), a drug for the treatment of adults with highly active relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS). The Federal Joint Committee (G-BA) had limited its decision on the first assessment from 2012 to three years because it considered the certainty of the data as insufficient. This obliged the drug manufacturer to submit a second dossier.
It did not submit any new studies, but reanalysed studies that were already available. On this basis, IQWiG reached different conclusions: From the data, an added benefit was now derived for two instead of only one of a total of three patient groups. IQWiG now found an indication where it had found a hint before.
Indication instead of hint in severe course of disease
One study - the approval study TRANSFORMS - was decisive also for the new dossier assessment. The manufacturer presented new analyses with a more detailed differentiation between subgroups for two patient groups.
On the basis of the new analyses, there was an indication, and no longer a hint of an added benefit in patients with rapidly evolving severe RRMS. The extent of this added benefit depends on sex, however: It is considerable in women, and minor in men. While adverse events in the form of influenza-like symptoms are less frequent and certain adverse events (severe adverse events) occur more often in both sexes, only women have fewer relapses under fingolimod.
Added benefit for further patient group
The new analyses of TRANSFORMS showed that fingolimod has advantages for patients with highly active RRMS that has not been fully treated with interferon beta. In contrast, no added benefit had resulted from the first dossier.
Since both the annualized relapse rate is lower and adverse events in the form of influenza-like symptoms occur less frequently, IQWiG sees an indication of considerable added benefit in comparison with the appropriate comparator therapy.
Still no evaluable data for one group
However, also the new dossier contained no evaluable data for patients with highly active RRMS who have already received full previous treatment with interferon beta (IFN-β1a). The results of an indirect comparison again presented by the manufacturer are still unsuitable because the majority of the patients in the studies on the appropriate comparator therapy had not been fully pretreated.
Now added benefit for two thirds of the approval population
Overall, the current assessment showed an added benefit for approximately two thirds of all patients for whom fingolimod was approved in 2011. However, this assessment only referred to the therapeutic indication of the first approval from 2011, not to the indication "highly active RRMS with pretreatments other than interferon beta", which was also approved in 2014 and assessed according to AMNOG.
G-BA decides on the extent of added benefit
This dossier assessment is part of the early benefit assessment according to AMNOG supervised by the G-BA. After publication of the dossier assessment, the G-BA conducts a commenting procedure and makes a final decision on the extent of the added benefit.
INFORMATION:
An overview of the results of IQWiG's benefit assessment is given by a German-language executive summary. In addition, the website » http://www.gesundheitsinformation.de, published by IQWiG, provides easily understandable German-language Information.
More English-language information will be available soon (Sections 2.1 to 2.6 of the dossier assessment as well as subsequently published health information on » http://www.informedhealthonline.org). If you would like to be informed when these documents are available, please send an e-mail to » info@iqwig.de.
Scientists believe that a simple two-hour emotional awareness course aimed at making young offenders less aggressive could hold the key to significantly reducing the seriousness of their future crimes.
In the first ever study of its kind, psychologists from Cardiff University recorded a 44% drop in the severity of crimes committed by persistent reoffenders, six months following the completion of a course designed to improve their ability to recognise other people's emotions. The findings are published today in PLOS ONE journal.
Much has been published previously to ...
ITHACA, N.Y. - To protect consumers from foodborne illness, produce farmers should wait 24 hours after a rain or irrigating their fields to harvest crops, according to new research published in the journal Applied and Environmental Microbiology.
Rain or irrigation creates soil conditions that are more hospitable to Listeria monocytogenes, which when ingested may cause the human illness Listeriosis. Waiting to harvest crops reduces the risk of exposure to the pathogen, which could land on fresh produce.
Cornell scientists, along with other agricultural researchers from ...
Astronomers have found evidence for a large population of hidden supermassive black holes in the Universe.
Using NASA's Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) satellite observatory, the team of international scientists detected the high-energy x-rays from five supermassive black holes previously clouded from direct view by dust and gas.
The research, led by astronomers at Durham University, UK, supports the theory that potentially millions more supermassive black holes exist in the Universe, but are hidden from view.
The findings are being presented at the ...
For cell division to be successful, pairs of chromosomes have to line up just right before being swept into their new cells, like the opening of a theater curtain. They accomplish this feat in part thanks to structures called centrioles that provide an anchor for the curtain's ropes. Researchers at Johns Hopkins recently learned that most cells will not divide without centrioles, and they found out why: A protein called p53, already known to prevent cell division for other reasons, also monitors centriole numbers to prevent potentially disastrous cell divisions.
Details ...
Richland, Wash. -- Despite decades of industrial use, the exact chemical transformations occurring within zeolites, a common material used in the conversion of oil to gasoline, remain poorly understood. Now scientists have found a way to locate--with atomic precision--spots within the material where chemical reactions take place, and how these spots shut down.
Called active sites, the spots help rip apart and rearrange molecules as they pass through nanometer-sized channels, like an assembly line in a factory. A process called steaming causes these active sites to cluster, ...
Anti-inflammatory drug is one thousandth of the cost of the current drug which works in the same way
Discovery may open up cost effective treatment options not just for the NHS but also cancer patients across the world
Scientists at the University of Sheffield have discovered that a common drug given to arthritis sufferers could also help to treat patients with blood cancers.
Myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPN) are diagnosed in around 3,300 UK patients every year and cause an overproduction of blood cells creating a significant impact on quality-of-life, with symptoms ...
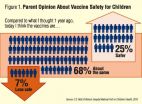
ANN ARBOR, Mich. -- Over the same time period that multiple outbreaks of measles and whooping cough made headlines around the country, parents' views on vaccines became more favorable, according to a new nationally-representative poll.
The University of Michigan C.S. Mott Children's Hospital National Poll on Children's Health asked parents in May how their views on vaccinations changed between 2014 and 2015 - during which two dozen measles outbreaks were reported in the U.S., including a multi-state outbreak traced to Disneyland.
One-third of parents who participated ...
A spider's web is one of the most intricate constructions in nature, but its precious silk has more than one use. Silk threads can be used as draglines, guidelines, anchors, pheromonal trails, nest lining, or even food. And each use requires a slightly different type of silk, optimized for its function.
"Each type of silk has similar proteins, but they are synthesized differently," said Sinan Keten, assistant professor of mechanical and civil engineering at Northwestern University's McCormick School of Engineering. "Then the spider knows how fast to reel the silk to get ...
An ambitious policy package is essential for the UK to transform its energy system to achieve the deep reductions in carbon emissions required to avoid dangerous climate change, according to research led by UCL scientists. To meet climate targets set for 2050, policies need to ensure strong action is taken now, while preparing for fundamental changes in how energy is provided and used in the long term.
The study is part of the Deep Decarbonization Pathway Project (DDPP) which is coordinated by the Institute for Sustainable Development and International Relations (IDDRI) ...
It may sound counter-intuitive, but crushing up bees into a 'DNA soup' could help conservationists understand and even reverse their decline - according to University of East Anglia scientists.
Research published today in the journal Methods in Ecology and Evolution shows that collecting wild bees, extracting their DNA, and directly reading the DNA of the resultant 'soup' could finally make large-scale bee monitoring programmes feasible.
This would allow conservationists to detect where and when bee species are being lost, and importantly, whether conservation interventions ...