(Press-News.org) When Greek mythology and cell biology meet, you get the protein Callipygian, recently discovered and named by researchers at The Johns Hopkins University for its role in determining which area of a cell becomes the back as it begins to move.
The findings, made in the amoeba Dictyostelium discoideum, shed light on how symmetrical, round cells become "polarized," or asymmetrical and directional. A summary of the findings was published online June 30 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
"Cells have to have a front and a back to migrate," says Peter Devreotes, Ph.D., professor and director of the Department of Cell Biology at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine. "Callipygian shuts off proteins that work at the front edge of cells. By doing so, it helps create the back of a cell, so we named it after the statue Venus Callipyge."
During cell migration, the front and back of the cell have to coordinate with each other, almost like dance partners. When a chemical "move-this-way" signal reaches a cell, a single protrusion, or pseudopod, begins to form in that direction due to rodlike actin filaments that grow and push the cell's membrane out. The back of the cell is then pulled forward, and the process repeats itself. Both extension of the front and retraction of the back require specific sets of proteins that must localize to the correct sites within the cell for proper migration.
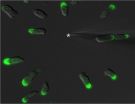
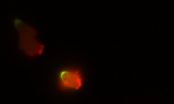
To find more proteins involved in cell movement, Kristen Swaney, Ph.D., then a graduate student in Devreotes' laboratory, decided to mark proteins by genetically attaching a fluorescent tag to them. Based on their sequences, two dozen of these were predicted to interact with the well-known front molecule PIP3, suggesting that they too would move to the front of the cell after a migration signal was received. Most of them did, but Callipygian went to the back, says Swaney. It didn't bind to PIP3, either.
"We already knew a lot about front proteins and how pseudopods are generated, but the formation of the back of the cell is more of a mystery, so we decided to follow Callipygian's lead," says Devreotes.
One challenge migrating cells face is preventing pseudopods from forming anywhere other than the front of the cell. The researchers found that Callipygian assists in this by accumulating at the back of the cell and preventing actin rods from growing to form a pseudopod. "Callipygian essentially turns off the back of the cell," says Swaney.
The team found that Callipygian uses a positive feedback mechanism to help polarize the cell. "It responds to cell polarity by moving to the back of the cell where it makes changes that create more polarity, which causes more Callipygian to move to the back of the cell," says Devreotes.
The team then studied its structure and figured out which part of the protein makes it move to the back of the cell. They found that adding a key segment from Callipygian to any other protein will make it move to the back of the cell too. According to Swaney, this ability to steer proteins to the "wrong" place in the cell will be a useful tool for studying many other proteins involved in cell polarity.
The researchers are continuing to work on understanding the dynamics of "front-and-back proteins" and how they contribute to cell polarity and migration, hoping to shed light on processes such as wound healing and cancer cell metastasis.
INFORMATION:
Other authors of the report include Jane Borleis and Pablo Iglesias of The Johns Hopkins University.
This work was supported by grants from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences (GM28007, GM34933) and the American Heart Association (09PRE2300057).
Scientists have discovered new ways in which the malaria parasite survives in the blood stream of its victims, a discovery that could pave the way to new treatments for the disease.
The researchers at the Medical Research Council's (MRC) Toxicology Unit based at the University of Leicester and the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine identified a key protein, called a protein kinase, that if targeted stops the disease. The study is published today (Tuesday) in Nature Communications.
Malaria is caused by a parasite that lives inside an infected mosquito and ...
Testing thousands of approved drugs, EPFL scientists have identified an unlikely anti-tuberculosis drug: the over-the-counter antacid lansoprazole (Prevacid®).
Tuberculosis continues to be a global pandemic, second only to AIDS as the greatest single-agent killer in the world. In 2013 alone, the TB bug Mycobacterium tuberculosis caused 1.5 million deaths and almost nine million new infections. Resistance to TB drugs is widespread, creating an urgent need for new medicines. EPFL scientists have now identified lansoprazole, a widely used, over-the-counter antacid, as ...
New research from the University of Copenhagen and Herlev and Gentofte Hospital shows that high vitamin C concentrations in the blood from the intake of fruit and vegetables are associated with a reduced risk of cardiovascular disease and early death.
Fruit and vegetables are healthy. We all know that. And now there is yet another good reason for eating lots of it. New research from the University of Copenhagen shows that the risk of cardiovascular disease and early death falls with a high intake of fruit and vegetables, and that this may be dued to vitamin C.
The ...
CHARLOTTESVILLE, VA (JULY 7, 2015). Researchers at Brown University examined three magnetically programmable shunt valves to see if the magnetic field emissions of headphones can cause unintentional changes in shunt valve settings. Based on their findings, the researchers state that it is highly unlikely that commercially available headphones will interfere with programmable shunt valve settings. Full details of this study can be found in "Programmable shunts and headphones: Are they safe together?" by Heather S. Spader, MD, and colleagues, published today online, ahead ...
CHARLOTTESVILLE, VA (JULY 7, 2015). Researchers conducted a prospective observational study in elderly patients and adult patients receiving antiplatelet therapy who presented with mild head injury at two trauma hospitals in Vienna: the Trauma Hospital Meidling and the Donauspital. The focus of the study was to see if blood serum levels of S100B protein in these patients could help identify whether their injuries included intracranial bleeding. If there was no indication of intracranial hemorrhage, these patients would not need additional testing or hospitalization. The ...
Policymakers and developers planning high-density housing near public transit with the goal of reducing automobile use and greenhouse gas emissions that contribute to global warming need a clearer understanding of the health risks from air pollution that may be created if that housing is also built near busy roads and freeways, according to new research by Keck School of Medicine of the University of Southern California (USC) scientists.
The study is one of the first to focus on the burden of heart disease that can result from residential exposures near major roadways ...
Weather is frequently portrayed in popular music, with a new scientific study finding over 750 popular music songs referring to weather, the most common being sun and rain, and blizzards being the least common. The study also found many song writers were inspired by weather events.
The study, led by the University of Southampton, together with the Universities of Oxford, Manchester, Newcastle (all part of the Tyndall Centre for Climate Change Research) and the University of Reading analysed the weather through lyrics, musical genre, keys and links to specific weather ...
Faith-based organisations [1] are crucial in achieving the promise of universal health coverage--an adequate standard of health care for all people--especially for poor and marginalised groups, according to a new three-part Series on faith-based health care, published in The Lancet. The Series argues that building on the extensive experience, strengths, and capacities of faith-based organisations (eg, geographical coverage, influence, and infrastructure) offers a unique opportunity to improve health outcomes.
Because of their broad reach and influence, faith-based groups ...
Drinking alcohol while pregnant is common, ranging from 20% to 80% among those questioned in the UK, Ireland, Australia and New Zealand, reveals a study of almost 18,000 women published in the online journal BMJ Open.
Women across all social strata drank during pregnancy, the findings showed. But expectant mums were significantly more likely to be drinkers if they were also smokers.
The researchers base their findings on an analysis of data from three studies: The Growing up in Ireland (GUI) study; the Screening for Pregnancy Endpoints (SCOPE) study; and the Pregnancy ...
The heightened risk of death after admission to hospital at the weekend--the so-called 'weekend effect'--is a feature of several developed countries' healthcare systems, and not just a problem for hospitals in England, reveals research published online in BMJ Quality & Safety.
The international nature of the findings suggests that this is a systematic phenomenon that not only crosses time, but also space, say the researchers.
In a bid to look in more detail at the evidence for the link between higher rates of death for patients admitted to hospital at weekends compared ...