INFORMATION:
This research was supported by the National Science Foundation.
About Carnegie Mellon University: Carnegie Mellon is a private, internationally ranked research university with programs in areas ranging from science, technology and business, to public policy, the humanities and the arts. More than 13,000 students in the university's seven schools and colleges benefit from a small student-to-faculty ratio and an education characterized by its focus on creating and implementing solutions for real problems, interdisciplinary collaboration and innovation.
Fewer women than men are shown online ads related to high-paying jobs
Carnegie Mellon uses simulated user profiles to probe online ad ecosystem
2015-07-07
(Press-News.org) Experiments by Carnegie Mellon University showed that significantly fewer women than men were shown online ads promising them help getting jobs paying more than $200,000, raising questions about the fairness of targeting ads online.
The study of Google ads, using a CMU-developed tool called AdFisher that runs experiments with simulated user profiles, established that the gender discrimination was real, said Anupam Datta, associate professor of computer science and of electrical and computer engineering. Still unknown, he emphasized, is who or what is responsible. Was it the preference of advertisers? Or was it the unintended consequence of machine learning algorithms that drive online recommendation engines?
"This just came out of the blue," Datta said of the gender discrimination finding, which was part of a larger study of the operation of Google's Ad Settings Web page, formerly known as Ad Preferences. The finding underscores the importance of using tools such as AdFisher to monitor the online ad ecosystem.
"Many important decisions about the ads we see are being made by online systems," Datta said. "Oversight of these 'black boxes' is necessary to make sure they don't compromise our values."
The study, published in the Proceedings on Privacy Enhancing Technologies and presented this month, used the automated AdFisher tool to run 21 experiments evaluating Ad Settings, a Web page Google created to give users some control over the ads delivered to them. The work is part of a growing body of research that has established Carnegie Mellon as a leader in the study of cybersecurity and online privacy.
AdFisher creates hundreds of simulated users, enabling researchers to run browser-based experiments in which they can identify various effects from changes in preferences or online behavior. AdFisher uses machine learning tools to analyze the results and perform rigorous statistical analyses.
"We can't look inside the black box that makes the decisions, but AdFisher can find changes in preferences and changes in the behavior of its virtual users that cause changes in the ads users receive," said Michael Carl Tschantz, a Ph.D. alumnus of Carnegie Mellon who is now a researcher at the International Computer Science Institute in Berkeley, Calif. Previous researchers have been able to show only a correlation, not causation, between changes in Ad Settings and ads displayed to users.
To study the impact of gender, researchers used AdFisher to create 1,000 simulated users - half designated male, half female - and had them visit 100 top employment sites. When AdFisher then reviewed the ads that were shown to the simulated users, the site most strongly associated with the male profiles was a career coaching service for executive positions paying more than $200,000.
"The male users were shown the high-paying job ads about 1,800 times, compared to female users who saw those ads about 300 times," said Amit Datta, a Ph.D. student in electrical and computer engineering. By comparison, the ads most associated with female profiles were for a generic job posting service and an auto dealer.
The researchers have no evidence that Google is doing anything illegal or that it violates its own policies, Anupam Datta said. Though AdFisher can identify discrepancies, it can't explain why they occur without a look inside the black box, he added. Such discrepancies could come from the advertiser or Google's system selecting to target males.
Anupam Datta is currently working with Microsoft Research to get an inside look at Microsoft's ad ecosystem. He said he hopes other organizations will use tools such as AdFisher to monitor the behavior of their ad targeting software and that regulatory agencies such as the Federal Trade Commission will use the tool to help spot abuses.
In addition to the findings regarding gender discrimination, another experiment showed that some changes in ads presented to users based on their browsing activity are not transparently explained via the Ad Settings page. When the simulated users visited Web pages associated with substance abuse, Google subsequently began sending them more ads for a drug rehabilitation center.
Even so, this change was not reflected in Ad Settings, making it impossible for the user to change preferences and halt the substance abuse-related ads. Anupam Datta said that is likely because the change in ads was the consequence of remarketing. In remarketing, Google enables advertisers to reach users who have already visited their page. This finding demonstrates that the Ad Settings page doesn't provide a complete picture of the inferences Google has made about a user. The authors noticed Google started highlighting this limitation on the Ad Settings page a few weeks ago.
In another experiment, the researchers found that adjusting Ad Settings can enable users to avoid some classes of ads they may dislike. They found that simulated users visiting online dating websites could remove that interest on Ad Settings to receive fewer ads related to online dating, giving users some choice over the ads that Google shows to them.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Taking the pain out of office work
2015-07-07
Office work will become much less of a pain in the neck if Julie Côté has her way. That`s because this kinesiology researcher who teaches at McGill University is interested in finding ways to reduce or even prevent the kinds of muscular and skeletal stresses and pains that will affect one in ten office workers at some point in their careers. "Even though office workers may not naturally see it that way, their body is basically their work instrument, just as it is for an athlete," says Côté. "It can get injured in similar ways and for similar reasons: ...
Discovery could improve in vitro fertilization success rates for women around the world
2015-07-07
PORTLAND, Ore. - Scientists at Oregon Health & Science University, Stanford University, University of Valencia and IGENOMIX have discovered that chromosomal abnormalities in human embryos created for in vitro fertilization, or IVF, can be predicted within the first 30 hours of development at the cell-1 stage which results from the union of a female egg and male sperm.
This discovery, published online today in the journal Nature Communications, could improve IVF success rates, which has hovered around 30 to 35 percent for numerous years worldwide. It is estimated that ...
Scientists study ways to integrate biofuels and food crops on farms
2015-07-07
We ask a lot of the land: feed the world with crops, power the world with bioenergy, retain nutrients so they don't pollute our water and air. To help landscapes answer these high demands, scientists from the U.S. Department of Energy's Argonne National Laboratory are designing ways to improve--and hopefully optimize--land use.
In collaboration with the farming community of the Indian Creek Watershed in central Illinois, these researchers are finding ways to simultaneously meet three objectives: maximize a farmer's production, grow feedstock for bioenergy and protect ...
Pupil response predicts depression risk in kids
2015-07-07
How much a child's pupil dilates in response to seeing an emotional image can predict his or her risk of depression over the next two years, according to new research from Binghamton University.
VIDEO: https://youtu.be/Wxn6WevWJdk
According to Brandon Gibb, professor of psychology at Binghamton University and director of the Mood Disorders Institute and Center for Affective Science, the new findings suggest that physiological reactivity to sad stimuli, assessed using pupillometry, serves as one potential biomarker of depression risk among children of depressed mothers. ...
Extended-field IMRT does not increase duodenal toxicity risk
2015-07-07
Fairfax, Va., July 7, 2015--A study of women with cervical or endometrial cancer who require treatment to the para-aortic (PA) lymph nodes can safely receive extended-field intensity modulated radiation therapy (EF-IMRT) without increased risk of duodenal toxicity, according to a study published in the July-August 2015 issue of Practical Radiation Oncology (PRO), the American Society for Radiation Oncology's (ASTRO's) journal focused on the clinical practice of radiation oncology.
IMRT is one of the radiation therapy (RT) treatment options for cervical and endometrial ...
Molecule linked to muscle fatigue in humans; enhances exercise tolerance when fed to mice
2015-07-07
Everyone's muscles have different limits. While professional athletes can train for hours before feeling fatigued, others struggle to mow the lawn or climb stairs. No panacea exists to create an equal playing field, nor will one likely be discovered, but a new study from Duke University questions whether this limit can be nutritionally extended. The research appears July 7 in Cell Metabolism as part of a special issue on "Physical Activity and Metabolic Health."
The researchers began by identifying an enzyme in skeletal muscle that helps to enhance how much moderate or ...
Nutritional supplement boosts muscle stamina in animal studies
2015-07-07
DURHAM, N.C. - The benefits of exercise are well known, but physical fitness becomes increasingly difficult as people age or develop ailments, creating a downward spiral into poor health.
Now researchers at Duke Medicine report there may be a way to improve exercise tolerance and, by extension, its positive effects.
Reporting in the July 7 issue of the journal Cell Metabolism, the research team describes a small molecule and its metabolic pathway that work together to optimize energy use in exercising muscles. In mouse studies, animals that received a nutrient supplement ...
Investigators develop activated T cell therapy for advanced melanoma
2015-07-07
CLEVELAND - T cells from patients with melanoma can trigger a protective immune response against the disease according to a new study out of University Hospitals Case Medical Center Seidman Cancer Center and Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine.
Published in the July/August issue of Journal of Immunotherapy, these new findings demonstrate that T cells derived from lymph nodes of patients with melanoma can be expanded in number and activated in the laboratory for intravenous administration in the treatment of patients. Led by Julian Kim, MD, Chief Medical ...
Goat meat consumption on the rise as immigrants keep ties to home culture
2015-07-07
If you're seeing more goat meat in grocery stores and on restaurant menus these days, you can probably chalk it up to a particular expression of ethnic identity--an expression that has important implications for immigrants, marketers, and policymakers, according to a recent study in the Journal of Public Policy & Marketing.
"Goat meat is becoming more popular in America, and in large part it's been due to the desire of immigrants to retain the tastes and preferences of their country of origin," write the authors of the study, Denver D'Rozario and Guang Yang (both at Howard ...
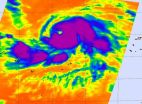
NASA sees Typhoon Nangka strengthen
2015-07-07
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Typhoon Nangka on July 6 and took an infrared look at the large storm as it strengthened from a tropical storm into a typhoon.
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument aboard NASA's Aqua satellite gathered infrared temperature data on Nangka on July 6 at 15:11 UTC (1:11 p.m. EDT). The infrared data showed a large storm with the bulk of thunderstorms east of the low-level center. The 20 nautical-mile-wide (23 miles/37 km) eye of the storm is also visible on the image.
Fragmented bands of powerful thunderstorms surrounded ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
$3.4 million grant to improve weight-management programs
Higher burnout rates among physicians who treat sickle cell disease
Wetlands in Brazil’s Cerrado are carbon-storage powerhouses
Brain diseases: certain neurons are especially susceptible to ALS and FTD
Father’s tobacco use may raise children’s diabetes risk
Structured exercise programs may help combat “chemo brain” according to new study in JNCCN
The ‘croak’ conundrum: Parasites complicate love signals in frogs
Global trends in the integration of traditional and modern medicine: challenges and opportunities
Medicinal plants with anti-entamoeba histolytica activity: phytochemistry, efficacy, and clinical potential
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
[Press-News.org] Fewer women than men are shown online ads related to high-paying jobsCarnegie Mellon uses simulated user profiles to probe online ad ecosystem