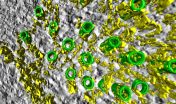
(Press-News.org) University of Warwick researchers have discovered a cell structure which could help scientists understand why some cancers develop.
For the first time a structure called 'the mesh' has been identified which helps to hold together cells. This discovery, which has been published in the online journal eLife, changes our understanding of the cell's internal scaffolding.
This also has implications for researchers' understanding of cancer cells as the mesh is partly made of a protein which is found to change in certain cancers, such as those of the breast and bladder.
The finding was made by a team led by Dr Stephen Royle, associate professor and senior Cancer Research UK Fellow at the division of biomedical cell biology at Warwick Medical School. Dr Royle said: "As a cell biologist you dream of finding a new structure in cells but it's so unlikely. Scientists have been looking at cells since the 17th Century and so to find something that no-one has seen before is amazing."
Researchers at the University's Warwick Medical School made the discovery by accident while looking at gaps between microtubules which are part of the cells' 'internal skeleton'. In dividing cells, these gaps are incredibly small at just 25 nanometres wide - 3,000 times thinner than a human hair.
One of Dr Royle's PhD students was examining structures called mitotic spindles in dividing cells using a technique called tomography which is like a hospital CAT scan but on a much smaller scale. This meant that they could see the structure which they later named the mesh.
Mitotic spindles are the cell's way of making sure that when they divide each new cell has a complete genome. Mitotic spindles are made of microtubules and the mesh holds the microtubules together, providing support. While "inter-microtubule bridges" in the mitotic spindle had been seen before, the researchers were the first to view the mesh.
The study received funding and support from Cancer Research UK and North West Cancer Research.
Dr Royle said: "We had been looking in 2D and this gave the impression that 'bridges' linked microtubules together. This had been known since the 1970s. All of a sudden, tilting the fibre in 3D showed us that the bridges were not single struts at all but a web-like structure linking all the microtubules together."
The discovery impacts on the research into cancerous cells. A cell needs to share chromosomes accurately when it divides otherwise the two new cells can end up with the wrong number of chromosomes. This is called aneuploidy and this has been linked to a range of tumours in different body organs.
The mitotic spindle is responsible for sharing the chromosomes and the researchers at the University believe that the mesh is needed to give structural support. Too little support from the mesh and the spindle will be too weak to work properly, however too much support will result in it being unable to correct mistakes. It was found that one of the proteins that make up the mesh, TACC3, is over-produced in certain cancers. When this situation was mimicked in the lab, the mesh and microtubules were altered and cells had trouble sharing chromosomes during division.
Dr Emma Smith, senior science communications officer at Cancer Research UK, said: "Problems in cell division are common in cancer - cells frequently end up with the wrong number of chromosomes. This early research provides the first glimpse of a structure that helps share out a cell's chromosomes correctly when it divides, and it might be a crucial insight into why this process becomes faulty in cancer and whether drugs could be developed to stop it from happening."
North West Cancer Research (NWCR) has funded the research as part of a collaborative project between the University of Warwick and the University of Liverpool, where part of the research is being carried out.
Anne Jackson, CEO at NWCR, said: "Dr Royle and Professor Ian Prior at the University of Liverpool have made significant inroads into our understanding of the way in which cancer cells behave, which could potentially better inform future cancer therapies.
"As a charity we fund only the highest standard of research, as evidenced by Dr Royle's work.
"All our funded projects undergo a thorough peer review process, before they are considered by our scientific committee. Our specially selected scientific committee includes some of the UK's leading professors, award-winning scientists and pioneering professionals."
INFORMATION:
Warwick Medical School's division of biomedical cell biology carries out fundamental molecular and cellular research into biomedical problems. Major human diseases such as cancer, inflammation, neuro-degeneration and bacterial/viral infection are primarily diseases of cells. Without a molecular understanding of the underlying cell biology, intelligent directed therapeutic intervention is impossible. The division's research focuses on fundamental cell biology processes such as cell division and intracellular communication.
Treating obese pregnant women with a diabetes drug does not stop their babies from being born overweight, a study has found.
Doctors had hoped that the treatment would help to reduce obesity rates and lower the number of difficult births.
Heavier babies are more likely to grow into overweight adults. They also have a higher risk of illnesses later in life, such as diabetes and heart disease.
It is thought that the additional weight gain in the womb is caused by exposure to excess blood sugar.
Researchers tested whether treating overweight mothers-to-be with the ...
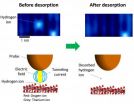
A research team comprising scientists from Tohoku University, RIKEN, the University of Tokyo, Chiba University and University College London have discovered a new chemical reaction pathway on titanium dioxide (TiO2), an important photocatalytic material.
The reaction mechanism, reported in ACS Nano, involves the application of an electric field that narrows the width of the reaction barrier, thereby allowing hydrogen atoms to tunnel away from the surface. This opens the way for the manipulation of the atomic-scale transport channels of hydrogen, which could be important ...
(BOSTON) - Traditional robots are made of components and rigid materials like you might see on an automotive assembly line - metal and hydraulic parts, harshly rigid, and extremely strong. But away from the assembly line, for robots to harmoniously assist humans in close-range tasks scientists are designing new classes of soft-bodied robots. Yet one of the challenges is integrating soft materials with requisite rigid components that power and control the robot's body. At the interface of these materials, stresses concentrate and structural integrity can be compromised, ...
The middle classes from developing countries are more susceptible than western Caucasians to obesity, type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease in today's changing environment. New research published today in Cell Metabolism from the University of Sydney in Australia, the National Centre for Cell Science and the DYP Medical College in Pune, India reveals this may be a result of the nutrition endured by their ancestors.
The findings in the paper titled Multigenerational Undernutrition and Diabetes could explain projections that more than 70 per cent of the global burden ...
ORLANDO, FL - While multidirectional instability of the shoulder (MDI) has been traditionally treated without surgery, research presented today at the American Orthopaedic Society for Sports Medicine's (AOSSM) Annual Meeting in Orlando, FL, shows surgery is also effective for this type of dislocation.
"We examined 41 athletes who received arthroscopic surgery for MDI, and noted 73% returned to play at equal or only slightly lower level than before the injury," commented M. Brett Raynor, MD, lead author from Steadman Philippon Research Institute Program. "Our study group ...
ORLANDO, FL - Athletes who suffer a shoulder instability injury may return to play more successfully after being treated arthroscopically compared to nonoperative treatment, say researchers presenting their work today at the American Orthopaedic Society for Sports Medicine's (AOSSM) Annual Meeting.
"Our research highlights that collegiate collision athletes with in-season shoulder instability injuries are more likely to return to sport successfully the following season, if they undergo arthroscopic stabilization compared to nonoperative treatment," said lead author Jon ...
ORLANDO, FL - While athletes undergoing anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) surgery often have an additional meniscus injury, treating these tears at the same time may not be necessary. Research presented today by the MOON Knee Group at the American Orthopaedic Society for Sports Medicine's (AOSSM) Annual Meeting in Orlando shows positive results for meniscal tears that were deemed stable and left alone at the time of ACL reconstruction.
"We examined 194 patients with meniscus tears who did not receive treatment at the time of ACL surgery," noted lead author Kyle R. Duchman, ...
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is one of most common causes of death in the world today - active smoking accounting for approx. 85% of all cases. Yet ground-breaking research from the University of Copenhagen indicates that accelerated decline of lung function is not a prerequisite for COPD.
It has been generally assumed that all people suffering COPD experience an accelerated decline of lung function, which is why so many large studies have focused on reducing this decline. However, this new study reveals that this is the case for only approx. 50% of patients ...
CANCER RESEARCH UK scientists have found that 'jumping genes' may add to the genetic chaos behind more than three-quarters of oesophageal cancer cases, according to research* published in BMC Genomics today (Friday).
The scientists, from the University of Cambridge, used cutting-edge technology that can read DNA to study the genes of 43 oesophageal tumour and blood samples to discover how much these mobile genetic sequences travel.
'Jumping genes', called L1 elements, can uproot themselves and move to new areas in the DNA, sometimes accidentally moving into genes that ...
CHILDREN with a rare type of cancer called Wilms' tumour who are at low risk of relapsing can now be given less intensive treatment, avoiding a type of chemotherapy that can cause irreversible heart problems in later life.
The move follows the results of a Cancer Research UK trial, published in the Lancet* today (Thursday), showing that the drug doxorubicin can be safely omitted from treatment without affecting patients' chances of survival.
Wilms' tumour is a type of kidney cancer that affects around 80 children a year in the UK, most under the age of seven. Until now, ...