NASA looks at Typhoon Chan-Hom's strongest winds on approach to China
2015-07-10
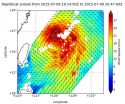
(Press-News.org) RapidScat is an instrument that sits on the International Space Station and reads surface winds over the ocean. It has been invaluable to tropical cyclone forecasters, showing where the strongest winds are located in storms. RapidScat spotted Chan-Hom's strongest winds away from Taiwan as it approached mainland China for landfall.
On July 9, the RapidScat instrument that flies aboard the International Space Station, observed Chan-Hom's strongest winds stretched from the northwestern to southeastern side of the storm, reaching speeds of more than 30 meters per second (108 kph/67 mph). RapidScat scanned the storm's surface winds for about 90 minutes from 3:14 p.m. to 4:47 p.m. EDT.
When NASA's Terra satellite passed over Typhoon Chan-Hom early on July 10 (EDT) the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument captured a visible-light image of the storm that showed the eye had "re-opened." In earlier imagery, the eye had become cloud-filled.
The China National Meteorological Center (CNMC) issued a typhoon red warning. The CNMC also issued a yellow warning for heavy rain. From 2:00 p.m. on July 10 (local time, China) to July 11, heavy rain is expected in Zhejiang, Shanghai, southeastern Jiangsu, southeastern Anhui, northeastern Fujian and Taiwan. Eastern Zhejiang and Taiwan will see extreme rains on July 10.
On July 9 at 1500 UTC (11 a.m. EDT), Typhoon Chan-Hom had maximum sustained winds 100 knots (115.5 mph/185.2 kph) It was centered 27.3 North latitude and 124.0 East longitude, about 630 nautical miles (725 miles/1,167 km) south-southwest of Yongsan, South Korea. It was moving to the northwest at 8 knots (10.3 mph/16.6 kph) and is generating rough seas with waves to 35 feet (10.6 meters).
The Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) noted that Chan-Hom is weakening as it approaches the Chinese mainland, south of Shanghai. After landfall, Chan-Hom is expected to turn north and northeast moving into the Yellow Sea. Thereafter it is expected to dissipate after moving over the Korean peninsula.
For updated warnings and watches from China's National Meteorological Centre, visit: http://www.cma.gov.cn/en/WeatherWarnings/.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-07-10
DETROIT - A Wayne State University School of Medicine professor, in collaboration with researchers at CReAte Fertility Center, University of Toronto, Harvard University and Georgia Reagents University, has developed the first diagnostic test for sperm RNA based on next-generation sequencing. For couples with unexplained infertility, the test may help determine the best infertility treatment for couples having difficulty conceiving.
Published this week in Science Translational Medicine, "Absence of sperm RNA elements correlates with idiopathic male infertility," by the ...
2015-07-10
This news release is available in German.
Are wind farms harmful to humans? Some believe so, others refute this; this controversial topic makes emotions run high. To give the debate more objectivity, an international team of experts dealt with the fundamentals of hearing in the lower limit range of the audible frequency range (i.e. infrasound), but also in the upper limit range (i.e. ultrasound). The project, which is part of the European Metrology Research Programme (EMRP), was coordinated by the Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt (PTB). At PTB, not only acoustics ...
2015-07-10
July 10, 2015 - For children with cleft lip and palate, the chances of undergoing secondary surgery vary depending on the center where they're treated, reports a study in Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery--Global Open®, the official open-access medical journal of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS).
When secondary surgeries are performed, they don't necessarily improve the child's final facial appearance, according to the new research by ASPS Member Surgeon Dr. Thomas J. Sitzman of Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center and colleagues.
Secondary ...
2015-07-10
Random-access memory, or RAM, is where computers like to store the data they're working on. A processor can retrieve data from RAM tens of thousands of times more rapidly than it can from the computer's disk drive.
But in the age of big data, data sets are often much too large to fit in a single computer's RAM. The data describing a single human genome would take up the RAM of somewhere between 40 and 100 typical computers.
Flash memory -- the type of memory used by most portable devices -- could provide an alternative to conventional RAM for big-data applications. It's ...
2015-07-10
LEXINGTON, Ky. (Jul. 10, 2015) -- Macrophages are cellular sentinels in the body, assigned to identify "attacks" from viruses, bacteria, or fungi and sound the alarm when they are present. However, these cells are a "double edged sword" in spinal cord injury, providing both neural repair-promoting properties and pathological functions that destroy neuronal tissue
"We know from previous research that macrophages are versatile, and signals at the injury site can stimulate repair or destruction--or confusingly, both," said John Gensel Ph.D., Assistant Professor of Physiology ...
2015-07-10
This news release is available in Spanish.
Scientists at the Centre for Genomic Regulation (CRG), the research company Starlab and the group BR::AC (Barcelona Research Art & Creation) of the University of Barcelona developed a device that produces sounds from brain signals. This highly interdisciplinary team is led by Mara Dierssen, head of the Cellular & Systems Neurobiology group at CRG. Its ultimate goal is to develop an alternative communication system for people with cerebral palsy to allow them to communicate--and more specifically in this pilot phase, ...
2015-07-10
The great white shark (Carcharodon carcharias) has a terrifying reputation. Shark attacks, though very rare, loom large in our imaginations, drawing intense media attention when they occur. Recent injuries in North Carolina are putting sharks in the limelight again. But going after sharks à la Jaws is not the best way to protect people in the water, said shark researchers.
California scientists found that the risk of white shark attack for individual ocean users in California has fallen strikingly, by over 91 percent, since 1950, in a study to be published online ...
2015-07-10
Many areas of fundamental research are interested in graphene owing to its exceptional characteristics. It is made of one layer of carbon atoms, which makes it light and sturdy, and it is an excellent thermal and electrical conductor. Its unique features make it potentially suitable for applications in a number of areas . Scientists at EPFL's Bionanophotonic Systems Laboratory (BIOS) together with researchers from ICFO- The Institute of Photonic Sciences in Barcelona, have now harnessed graphene's unique optical and electronic properties to develop a reconfigurable highly ...
2015-07-10
Men may feel threatened by female supervisors and act more assertively toward them than male bosses, which could disrupt the workplace with struggles over power dynamics, according to new research published by the Society for Personality and Social Psychology.
"The concept of masculinity is becoming more elusive in society as gender roles blur, with more women taking management positions and becoming the major breadwinners for their families," said lead researcher Ekaterina Netchaeva, an assistant professor of management and technology at Bocconi University in Milan, ...
2015-07-10
Heidelberg, 10 July 2015 - Researchers at EMBL Heidelberg have produced detailed images of the intricate protein-coats that surround trafficking vesicles - the "transport pods" that move material around within biological cells. The study, published today in Science, provides a new understanding of the complex machines that make up the cells' logistics network.
Vesicles are responsible for transporting molecules between the different compartments within a cell and also for bringing material into cells from outside. There are several types of vesicle: each has a specific ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] NASA looks at Typhoon Chan-Hom's strongest winds on approach to China