Findings identify receptors modulating macrophage responses to spinal cord injury
2015-07-10
(Press-News.org) LEXINGTON, Ky. (Jul. 10, 2015) -- Macrophages are cellular sentinels in the body, assigned to identify "attacks" from viruses, bacteria, or fungi and sound the alarm when they are present. However, these cells are a "double edged sword" in spinal cord injury, providing both neural repair-promoting properties and pathological functions that destroy neuronal tissue
"We know from previous research that macrophages are versatile, and signals at the injury site can stimulate repair or destruction--or confusingly, both," said John Gensel Ph.D., Assistant Professor of Physiology in the Spinal Cord and Brain Injury Research Center at the University of Kentucky. "But the mechanisms through which these signals stimulate the good and/or bad functions in macrophages are not known. So the next big question to answer in the efforts to understand and treat SCI was, 'Why?'"
Gensel teamed up with Phillip Popovich, Ph.D, Professor in the Department of Neuroscience and Director of the Center for Brain and Spinal Cord Repair (CBSCR) at The Ohio State University to explore the mechanisms governing the positive and negative processes that occur in macrophages following spinal cord injury.
"On the cellular level, the body's response to spinal cord injury is similar to the immune response to attacks by bacteria or viruses," Gensel said. "The functions that macrophages adopt in response to these stimuli were the focus of our study."
Gensel and Popovich looked at more than 50 animals with spinal cord injury to try to identify which macrophage receptors promoted neuronal repair and which directed the destructive process.
"We found that activating bacterial receptors boosted the macrophage response and limited damage to the spinal cord following injury, while activating fungal receptors actually contributed to pathology," Gensel said.
While this study oversimplifies the complex process by which macrophages promote repair and destruction of neuronal tissues, it nonetheless sheds light on opportunities to modulate macrophage responses after spinal cord injury, potentially reducing - or even reversing - damage and the resulting side-effects.
"The implications are exciting: we now can look for treatments targeted to the receptors that jump-start the macrophage's restorative effects without activating the receptors that modulate the destructive processes in that same cell."
The study has been published as a Featured Article in the most recent issue of the Journal of Neuroscience.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-07-10
This news release is available in Spanish.
Scientists at the Centre for Genomic Regulation (CRG), the research company Starlab and the group BR::AC (Barcelona Research Art & Creation) of the University of Barcelona developed a device that produces sounds from brain signals. This highly interdisciplinary team is led by Mara Dierssen, head of the Cellular & Systems Neurobiology group at CRG. Its ultimate goal is to develop an alternative communication system for people with cerebral palsy to allow them to communicate--and more specifically in this pilot phase, ...
2015-07-10
The great white shark (Carcharodon carcharias) has a terrifying reputation. Shark attacks, though very rare, loom large in our imaginations, drawing intense media attention when they occur. Recent injuries in North Carolina are putting sharks in the limelight again. But going after sharks à la Jaws is not the best way to protect people in the water, said shark researchers.
California scientists found that the risk of white shark attack for individual ocean users in California has fallen strikingly, by over 91 percent, since 1950, in a study to be published online ...
2015-07-10
Many areas of fundamental research are interested in graphene owing to its exceptional characteristics. It is made of one layer of carbon atoms, which makes it light and sturdy, and it is an excellent thermal and electrical conductor. Its unique features make it potentially suitable for applications in a number of areas . Scientists at EPFL's Bionanophotonic Systems Laboratory (BIOS) together with researchers from ICFO- The Institute of Photonic Sciences in Barcelona, have now harnessed graphene's unique optical and electronic properties to develop a reconfigurable highly ...
2015-07-10
Men may feel threatened by female supervisors and act more assertively toward them than male bosses, which could disrupt the workplace with struggles over power dynamics, according to new research published by the Society for Personality and Social Psychology.
"The concept of masculinity is becoming more elusive in society as gender roles blur, with more women taking management positions and becoming the major breadwinners for their families," said lead researcher Ekaterina Netchaeva, an assistant professor of management and technology at Bocconi University in Milan, ...
2015-07-10
Heidelberg, 10 July 2015 - Researchers at EMBL Heidelberg have produced detailed images of the intricate protein-coats that surround trafficking vesicles - the "transport pods" that move material around within biological cells. The study, published today in Science, provides a new understanding of the complex machines that make up the cells' logistics network.
Vesicles are responsible for transporting molecules between the different compartments within a cell and also for bringing material into cells from outside. There are several types of vesicle: each has a specific ...
2015-07-10
University of Warwick researchers have discovered a cell structure which could help scientists understand why some cancers develop.
For the first time a structure called 'the mesh' has been identified which helps to hold together cells. This discovery, which has been published in the online journal eLife, changes our understanding of the cell's internal scaffolding.
This also has implications for researchers' understanding of cancer cells as the mesh is partly made of a protein which is found to change in certain cancers, such as those of the breast and bladder.
The ...
2015-07-10
Treating obese pregnant women with a diabetes drug does not stop their babies from being born overweight, a study has found.
Doctors had hoped that the treatment would help to reduce obesity rates and lower the number of difficult births.
Heavier babies are more likely to grow into overweight adults. They also have a higher risk of illnesses later in life, such as diabetes and heart disease.
It is thought that the additional weight gain in the womb is caused by exposure to excess blood sugar.
Researchers tested whether treating overweight mothers-to-be with the ...
2015-07-10
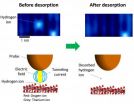
A research team comprising scientists from Tohoku University, RIKEN, the University of Tokyo, Chiba University and University College London have discovered a new chemical reaction pathway on titanium dioxide (TiO2), an important photocatalytic material.
The reaction mechanism, reported in ACS Nano, involves the application of an electric field that narrows the width of the reaction barrier, thereby allowing hydrogen atoms to tunnel away from the surface. This opens the way for the manipulation of the atomic-scale transport channels of hydrogen, which could be important ...
2015-07-10
(BOSTON) - Traditional robots are made of components and rigid materials like you might see on an automotive assembly line - metal and hydraulic parts, harshly rigid, and extremely strong. But away from the assembly line, for robots to harmoniously assist humans in close-range tasks scientists are designing new classes of soft-bodied robots. Yet one of the challenges is integrating soft materials with requisite rigid components that power and control the robot's body. At the interface of these materials, stresses concentrate and structural integrity can be compromised, ...
2015-07-10
The middle classes from developing countries are more susceptible than western Caucasians to obesity, type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease in today's changing environment. New research published today in Cell Metabolism from the University of Sydney in Australia, the National Centre for Cell Science and the DYP Medical College in Pune, India reveals this may be a result of the nutrition endured by their ancestors.
The findings in the paper titled Multigenerational Undernutrition and Diabetes could explain projections that more than 70 per cent of the global burden ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Findings identify receptors modulating macrophage responses to spinal cord injury