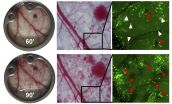
(Press-News.org) Children consume more low-nutrition, high-calorie food such as cookies and candy after observing seemingly overweight cartoon characters, according to a first-of-its-kind study led by the University of Colorado Boulder.
The results of the new study, involving Colorado State University and published online in the Journal of Consumer Psychology, show that kids are responsive to the apparent bodyweight of cartoon characters like the aptly named Grimace, a rotund, milkshake-loving creature created by McDonald's restaurant in the 1970s.
Children tend to perceive ovoid, or egg-shaped, characters as overweight even though the creatures are imaginary, found the study.
"Because research like this is new -- looking at kids and stereotyping particularly of cartoon characters -- we weren't sure whether kids would be aware of bodyweight norms," said Margaret C. Campbell, marketing professor at CU-Boulder's Leeds School of Business and lead author of the study. "But surprisingly, they apply typically human standards to cartoon creatures -- creatures for which there isn't a real baseline."
In addition, seeing ovoid cartoon characters can influence children to eat more unhealthy food, according to the study.
"They have a tendency to eat almost twice as much indulgent food as kids who are exposed to perceived healthier looking cartoon characters or no characters at all," said Campbell.
The inclination to eat more junk food was curtailed, however, when kids in the study first had the opportunity to summon their previously learned health knowledge. That is, before looking at the ovoid cartoon character and then taking a cookie taste-test, the children's health knowledge was activated when they were asked to choose the healthiest option represented in six pairs of pictures and words -- such as getting your sleep versus watching TV, soda versus milk and playing inside versus playing outside -- which led to lighter cookie consumption.
"This is key information we should continue to explore," said Campbell. "Kids don't necessarily draw upon previous knowledge when they're making decisions. But perhaps if we're able to help trigger their health knowledge with a quiz just as they're about to select lunch at school, for instance, they'll choose the more nutritious foods."
Kenneth Manning, professor of marketing at Colorado State University; Bridget Leonard, CU-Boulder graduate student at the time of the study and now assistant professor of marketing at Indiana University-Purdue University Fort Wayne; and Hannah Manning, CSU student, co-authored the paper.
The findings -- gathered from just over 300 participants in three age groups averaging 8, 12 and 13 years old -- have implications for marketers as well as parents navigating a world where children encounter cartoon characters in a variety of media, from books to graphic novels, TV shows, video games, movies and more.
"What I would like to see is companies being a lot more responsible with their own marketing choices," said Campbell. "I think it is important for parents to know they should think about the way they might be associating food with fun for kids -- in the form of exposure to cartoon characters, for instance -- as opposed to associating food with nutrition and the family structure."
The Kellogg's brand is an example of a company that changed the image of one of its cartoon characters in a responsible way, according to Campbell. Several years ago, it revamped Tony the Tiger to be slimmer and more athletic, which may link the character with healthier eating ideas rather than linking to ideas of eating lots of sugary cereal, she said.
INFORMATION:
Immune cells that creep across blood vessels trigger potentially fatal bleeding in platelet-deficient mice, according to a report published in The Journal of Experimental Medicine. If the same is true in humans, blocking the passage of these cells could prevent dangerous complications in patients undergoing transplants or chemotherapy.
Bone marrow transplantation and chemotherapy are known to deplete blood-clotting cells called platelets, resulting in potentially fatal bleeding (hemorrhage) in some patients. Previous studies showed that inflammation was required for bleeding ...
BOSTON (July 13, 2015)--Physicians in their medical residency training programs often focus on scientific reasoning and research evidence in their efforts to provide medical care. While appropriate, this focus may overshadow subtle and indirect communication that reveals important information about the patient's experience with their illness that will help the physician provide better care. A new study by researchers at Tufts University School of Medicine and Boston College presents the results of a strategy to train medical residents to reflect on interactions with patients ...
James Cook University scientists have helped invent a clever technique to tell black leopards apart - a trick that may end up saving their skins.
Scientists from JCU in Australia and others have been studying the leopards on the Malay Peninsula - where almost all of the big cats are jet black.
Experts have no idea why the leopards are black and, until recently, could not tell them apart, hindering research and conservation efforts.
But researchers have now devised a simple method to solve the problem by manipulating the mechanism of automatic cameras.
"Most automatic ...
Scientists have found that strains of the wheat pathogen causing severe yellow rust epidemics in Europe have their origin in the centre of diversity in the Himalayan region. This disease can have a great impact on wheat production in Europe, including organic crop production in Denmark.
Wheat is the most widely cultivated food crop in the world. However, the global production of wheat is under constant threat from devastating fungal diseases. The ever more frequent and severe large-scale epidemics caused by these fungi pose a severe threat to global food security.
Scientists ...
A new study has found that cancer survivors' options for adoption may be limited by adoption agencies' policies. Published early online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society, the study also indicates that a training program for oncology healthcare providers can help them provide valuable information to patients who are making decisions about fertility and adoption.
Because cancer and the therapies used to treat it can leave some patients infertile, many young cancer survivors may turn to adoption when hoping to start--or add to--a family. Adoption ...
ANN ARBOR, Mich. -- Few people today would dare call President Richard Nixon a radical liberal. But 44 years ago, he proposed a health plan that went far beyond what today's Affordable Care Act includes. After the first plan failed, he did it again three years later.
And just like today's heated rhetoric from opponents of the ACA, also called "Obamacare" after the president who introduced it, Nixon's plans were met with inflamed opposition from the other party.
In a new article in the journal Pediatrics, a team from the Child Health Evaluation and Research Unit at ...
This news release is available in German.
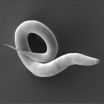
Slugs and other invertebrates provide essential public transport for small worms in the search for food, according to research published in the open access journal BMC Ecology.
Nematode worms (including Caenorhabditis elegans) are around a millimeter long and commonly found in short-lived environments, such as decomposing fruit or other rotting plant material. The worms face a high level of unpredictability in these environments as temperature and food availability fluctuate, and frequently need to move to new locations. ...
Treatment could save the NHS £3.1 billion every year
More than 200,000 patients in the UK suffer with chronic wounds
Healing time can be reduced by a third
Healing times for skin ulcers and bedsores can be reduced by a third with the use of low-intensity ultrasound, scientists from the University of Sheffield and University of Bristol have found.
Researchers from the University of Sheffield's Department of Biomedical Science discovered the ultrasound transmits a vibration through the skin and wakes up cells in wounds helping to stimulate and accelerate the healing ...
When two different sized galaxies smash together, the larger galaxy stops the smaller one making new stars, according to a study of more than 20,000 merging galaxies.
The research, published today, also found that when two galaxies of the same size collide, both galaxies produce stars at a much faster rate.
Astrophysicist Luke Davies, from The University of Western Australia node of the International Centre for Radio Astronomy Research (ICRAR), says our nearest major galactic neighbour, Andromeda, is hurtling on a collision course with the Milky Way at about 400,000 ...
As the world's leaders gather in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, for the Financing for Development Conference [1], a study published in The Lancet demonstrates that a new approach is needed for classifying funding that reflects the function the funding serves, rather than the specific disease or country. The study is the first in-depth assessment of how donor funding is spent on global versus country-specific functions of health [2].
The paper also presents an expanded definition of official development assistance (ODA) for health, which is used to identify important underfunded ...