(Press-News.org) ORLANDO, Fla. (July 21, 2015) - A new peer-reviewed study published in the Journal of Mammalogy by the Oxford University Press adds important insights to the debate over how long killer whales in human care live. The study found no difference in life expectancy between killer whales born at SeaWorld and a well-studied population of wild killer whales.
The study, "Comparisons of life-history parameters between free-ranging and captive killer whale (Orcinus orca) populations for application toward species management," compares current published data for survival and reproductive activity of known-age Pacific Northwest killer whales since 1975 with the life history of killer whales in SeaWorld's care. The average life expectancy for SeaWorld's killer whales is 41.6 years; average life expectancies for Southern and Northern Resident killer whales are 29.0 and 42.3 years respectively.
Additionally, the study shows that average calf survival rate from approximately 6 months of age (i.e., age at first sighting) to age 2 in the Southern Resident killer whale population (79.9 percent) is significantly less than SeaWorld's average calf survival rate from 40 days to age 2 (96.6 percent). The study may be accessed and read in full by following this link: http://jmammal.oxfordjournals.org/content/early/2015/07/09/jmammal.gyv113.article-info
"Although emotion will always be a part of the debate as to whether killer whales, or any other species, should be maintained in human care, it is absolutely necessary to have validated facts when an argument for or against is being made on scientific grounds," said study author Kevin Willis, Vice President for Biological Programs for the Minnesota Zoo. "Based on the available data, it is now clear that it cannot be truthfully argued that killer whales should not be maintained in captivity because they have a shortened life expectancy relative to their wild counterparts."
The objective of this study was to characterize and compare reproductive parameters and survivorship patterns of free-ranging killer whales in the Pacific Northwest and killer whales living at SeaWorld using methodologies previously published for zoological and free-ranging populations. The Northern and Southern Resident killer whale populations of the Pacific Northwest are the most studied and documented wild killer whales in the world. These new comparisons provide a novel metric from which comparisons with other populations can be made. They also shed new light on age estimates for the species as a whole.
"This article represents the first peer-reviewed publication that directly compares reproductive and survivorship patterns between captive and wild killer whales," said study author Todd Robeck, DVM, Ph.D., Vice President of Theriogenology for SeaWorld Parks & Entertainment.
"The results demonstrate unequivocally that killer whales in captivity have similar life expectancies to those in the wild and provide invaluable knowledge concerning normal reproductive patterns of this species. This information is imperative for developing management plans and directing future research efforts that are designed to protect wild killer whale populations."
The ability to study killer whales in controlled research settings in accredited zoological institutions like SeaWorld has provided most of the fundamental information known about the species' physiology including adaptations to diving; auditory detection, echolocation, and learning; reproductive physiology; growth and development; metabolic and energy requirements; and immune system function.
INFORMATION:
Media Inquiries:
Fred Jacobs
Vice President of Communications
Fred.Jacobs@SeaWorld.com
About SeaWorld Entertainment, Inc.
SeaWorld Entertainment, Inc. (NYSE: SEAS) is a leading theme park and entertainment company delivering personal, interactive and educational experiences that blend imagination with nature and enable its customers to celebrate, connect with and care for the natural world we share. The Company owns or licenses a portfolio of globally recognized brands including SeaWorld®, Shamu® and Busch Gardens®. Over its more than 50-year history, the Company has built a diversified portfolio of 11 destination and regional theme parks that are grouped in key markets across the United States, many of which showcase its one-of-a-kind zoological collection of approximately 89,000 marine and terrestrial animals. The Company's theme parks feature a diverse array of rides, shows and other attractions with broad demographic appeal which deliver memorable experiences and a strong value proposition for its guests.
SeaWorld Entertainment, Inc. is one of the world's foremost zoological organizations and a global leader in animal welfare, training, husbandry and veterinary care. The Company collectively cares for what it believes is one of the largest zoological collections in the world and has helped lead advances in the care of animals. The Company also rescues and rehabilitates marine and terrestrial animals that are ill, injured, orphaned or abandoned, with the goal of returning them to the wild. The SeaWorld rescue team has helped more than 26,000 animals in need over the last 50 years.
Copies of this and other news releases as well as additional information about SeaWorld Entertainment, Inc. can be obtained online at http://www.seaworldentertainment.com. Shareholders and prospective investors can also register to automatically receive the Company's press releases, SEC filings and other notices by e-mail by registering at that website.
You don't think you're hungry, then a friend mentions how hungry he is or you smell some freshly baked pizza and whoaaa, you suddenly feel really hungry. Or, you've had surgery and need a bit of morphine for pain. As soon as you hit that button you feel relief even though the medicine hasn't even hit your bloodstream.
These are two examples of the oft-studied placebo effect that demonstrate the amazing and still somewhat confounding powers of the human brain.
Now, CU-Boulder graduate student Scott Schafer, who works in Associate Professor Tor Wager's Cognitive and Affective ...
The health of Colorado's bighorn sheep population remains as precarious as the steep alpine terrain the animals inhabit, but a new study led by researchers at the University of Colorado Boulder has found that inbreeding--a common hypothesis for a recent decline--likely isn't to blame.
Bighorn herds tend to be small and isolated in their mountain ecosystems, putting the animals at high risk for a genetic "bottleneck," said Catherine Driscoll, a graduate student in the Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology at CU-Boulder and lead author of the study. Previous research ...
As well as the daily strain of their working lives, shift workers are probably also more likely than other people to develop cancer. While this has been well described for breast cancer, few studies had examined the correlation between shift work and prostate cancer. In a recent original article in Deutsches Ärzteblatt International (Dtsch Arztbl Int 112: 463-70), Gael P. Hammer et al. show that shift workers do not develop prostate cancer more frequently than their colleagues who work during the day.
Shift work is widespread: between approximately one in five and ...
CAMBRIDGE, Mass. -- John Leonard's group in the MIT Department of Mechanical Engineering specializes in SLAM, or simultaneous localization and mapping, the technique whereby mobile autonomous robots map their environments and determine their locations.
Last week, at the Robotics Science and Systems conference, members of Leonard's group presented a new paper demonstrating how SLAM can be used to improve object-recognition systems, which will be a vital component of future robots that have to manipulate the objects around them in arbitrary ways.
The system uses SLAM ...
This news release is available in Spanish.
Since 2006, the team of researchers has sequenced the mitochondrial DNA of all the known species of butterflies in the Iberian peninsula (228) and its main populations. The result is a report that compiles more than 3500 genetic sequences of all the species, which have been compared to the genetic sequences of other European populations. The paper has 277 pages of supplementary material, including pictures and 80 maps of the geographical distribution of the butterfly genetic lineages identified.
This is the first time ...
(Philadelphia, PA) - Patients who have lower extremity proximal deep vein thrombosis (LE-DVT), or a blood clot in their leg, are increasingly undergoing minimally invasive catheter-based blood clot removal - also referred to as catheter-directed thrombolysis (CDT) - rather than solely being treated with traditional blood-thinning medications (anticoagulation alone). This trend is due to recent literature showing reductions in lifestyle-limiting post-thrombotic complications of acute DVT in patients who undergo CDT compared to those that are treated with anticoagulation ...
This news release is available in German.
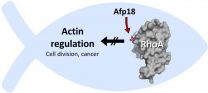
Pathogenic bacteria develop killer machines that work very specifically and highly efficiently. Scientists from the University of Freiburg have solved the molecular mechanism of a fish toxin that could be used in the future as a medication to treat cancer. The scientists have now published their research in the journal Nature Communications.
The Yersinia species of pathogens can cause the bubonic plague and serious gastrointestinal infections in humans. The pharmacologist Dr. Thomas Jank and his fellow researchers in the ...
La Jolla, Calif., July 23, 2015 - A new study by researchers at Sanford Burnham Prebys Medical Discovery Institute (SBP), the National Cancer Institute, and the Chulabhorn Research Institute has found that blocking the activity of a key immune receptor, the lymphotoxin-beta receptor (LTβR), reduces the progression of liver cancer. The results, published today in the online edition of Gut, could provide new treatment strategies for the disease, which is the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide.
"Our findings point to a new way to improve the treatment ...
After decades of overtreatment for low-risk prostate cancer and inadequate management of its more aggressive forms, patients are now more likely to receive medical care matched to level of risk, according to a study by researchers at UC San Francisco.
In the first study to document updated treatment trends, researchers found that from 2010 to 2013, 40 percent of men with low-risk prostate cancer opted for active surveillance, in which the disease is monitored closely with blood tests, imaging studies and biopsies. Treatment is deferred unless these tests show evidence ...
Today an international team of astronomers from NASA's Kepler mission have announced the discovery of a near-Earth-sized planet in the habitable zone of a Sun-like star.
Dr Daniel Huber from the University of Sydney's School of Physics is part of the team which made the discovery with NASA's Kepler Space Telescope.
The planet named Kepler-452b is 60 per cent larger than Earth and orbits a Sun-like star with an orbital period of 385 days.
The mere 20 day difference between the planet's orbital period and that of Earth's makes it the closest analogue to Earth ever ...