Toxin from salmonid fish has potential to treat cancer
Researchers from the University of Freiburg decode molecular mechanism of fish pathogen
2015-07-24
(Press-News.org) This news release is available in German.
Pathogenic bacteria develop killer machines that work very specifically and highly efficiently. Scientists from the University of Freiburg have solved the molecular mechanism of a fish toxin that could be used in the future as a medication to treat cancer. The scientists have now published their research in the journal Nature Communications.
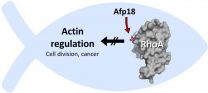
The Yersinia species of pathogens can cause the bubonic plague and serious gastrointestinal infections in humans. The pharmacologist Dr. Thomas Jank and his fellow researchers in the research group led by Prof. Dr. Dr. Klaus Aktories at the University of Freiburg studied a pathogen of the Yersinia family (Yersinia ruckeri). This pathogen causes redmouth disease in Salmonidae, which includes salmon and trout, resulting in large financial losses in the fish industry. The research group was able to identify a toxin injection machine in the Y. ruckeri genome. The structure of this machine resembles that of viruses that normally attack bacteria. The group demonstrated that the toxin Afp18 in this injection machine is an enzyme that deactivates the switch protein RhoA. RhoA is responsible for many vital processes in the cells of humans and fish. For example, it controls the building up and breaking down of actin filaments. These filaments are not only necessary for cell division, but also for the spreading of tumour metastases in the body.
In close collaboration with the developmental biologist Prof. Dr. Wolfgang Driever, also from the University of Freiburg, the research group injected the toxin Afp18 into zebra fish embryos. The result was that cell division was blocked, and the fish embryos did not develop. The toxin caused the actin filaments in the fish cells to collapse. This is because the Afp18 attaches a sugar molecule, an N-acetylglucosamine, onto the amino acid tyrosine in RhoA. According to the scientists, this is a very unusual reaction in nature. The team was able to shed light on this mechanism at the atomic level through the X-ray analysis of Afp18-modified RhoA crystals. For this, they collaborated with Prof. Dr. Daan von Aalten from the University of Dundee, Scotland. Rho-regulatory proteins are involved in the growth of cancer, especially metastasis. For this reason, the researchers from the University of Freiburg believe that this fish toxin has great therapeutic potential in cancer treatment.
INFORMATION:
Thomas Jank and Klaus Aktories are researchers at the Institute of Experimental and Clinical Pharmacology and Toxicology at the University of Freiburg. Wolfgang Driever is the head of the Department of Developmental Biology of the Institute of Biology I, also at the University of Freiburg. Both Aktories and Driever are members of the cluster of excellence BIOSS Centre for Biological Signalling Studies.
Original publication:
Thomas Jank*, Stephanie Eckerle*, Marcus Steinemann*, Christoph Trillhaase, Marianne Schimpl, Sebastian Wiese, Daan M.F. van Aalten, Wolfgang Driever & Klaus Aktories, "Tyrosine glycosylation of Rho by Yersinia toxin impairs blastomere cell behaviour in zebrafish embryos." Nature Communications 2015.
*Authors are equally involved.
Contact:
Dr. Thomas Jank
Institute of Experimental and Clinical Pharmacology and Toxicology
University of Freiburg
Phone: +49 (0)761-203-5308
Email: thomas.jank@pharmakol.uni-freiburg.de
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-07-24
La Jolla, Calif., July 23, 2015 - A new study by researchers at Sanford Burnham Prebys Medical Discovery Institute (SBP), the National Cancer Institute, and the Chulabhorn Research Institute has found that blocking the activity of a key immune receptor, the lymphotoxin-beta receptor (LTβR), reduces the progression of liver cancer. The results, published today in the online edition of Gut, could provide new treatment strategies for the disease, which is the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide.
"Our findings point to a new way to improve the treatment ...
2015-07-24
After decades of overtreatment for low-risk prostate cancer and inadequate management of its more aggressive forms, patients are now more likely to receive medical care matched to level of risk, according to a study by researchers at UC San Francisco.
In the first study to document updated treatment trends, researchers found that from 2010 to 2013, 40 percent of men with low-risk prostate cancer opted for active surveillance, in which the disease is monitored closely with blood tests, imaging studies and biopsies. Treatment is deferred unless these tests show evidence ...
2015-07-24
Today an international team of astronomers from NASA's Kepler mission have announced the discovery of a near-Earth-sized planet in the habitable zone of a Sun-like star.
Dr Daniel Huber from the University of Sydney's School of Physics is part of the team which made the discovery with NASA's Kepler Space Telescope.
The planet named Kepler-452b is 60 per cent larger than Earth and orbits a Sun-like star with an orbital period of 385 days.
The mere 20 day difference between the planet's orbital period and that of Earth's makes it the closest analogue to Earth ever ...
2015-07-24
EU's grid connected cumulative capacity in 2014 reached 129 GW, meeting 8% of European electricity demand, equivalent to the combined annual consumption of Belgium, the Netherlands, Greece and Ireland. According to a JRC report, the impressive growth of the industry will allow at least 12% electricity share by 2020, a significant contribution to the goal of the European energy and climate package of 20% share of energy from renewable sources.
The 2014 JRC wind status report presents the technology, market and economics of the wind energy sector with a focus on the EU. ...
2015-07-24
Scientists at the University of York believe they have identified how some tiny regulatory molecules in cells can make prostate cancers resistant to radiotherapy.
It is hoped that this new development could pave the way for more effective treatments - allowing a lower dose of radiotherapy to be used while prolonging the lives of thousands of men.
Prostate cancer is the most commonly diagnosed form of male cancer in the UK and kills more than 11,000 men every year.
In the latest studies, published in European Urology and the British Journal of Cancer, scientists in The ...
2015-07-24
July 24, 2015 - Patient satisfaction ratings after surgery for spinal degenerative disease--especially in terms of reduced pain and disability--are a good indicator of the procedure's effectiveness, reports a study in the August issue of Neurosurgery, official journal of the Congress of Neurological Surgeons. The journal is published by Wolters Kluwer.
"Patient satisfaction with outcome may accurately represent the effectiveness of surgical spine care in terms of one-year improvement in pain and disability," according to the new research by Dr. Clinton J. Devin of Vanderbilt ...
2015-07-24
It doesn't happen often that a young scientist makes a significant and unexpected discovery, but postdoctoral researcher Stephen Wu of the U.S. Department of Energy's Argonne National Laboratory just did exactly that. What he found--that you don't need a magnetic material to create spin current from insulators--has important implications for the field of spintronics and the development of high-speed, low-power electronics that use electron spin rather than charge to carry information.
Wu's work upends prevailing ideas of how to generate a current of spins. "This is a ...
2015-07-24
Needham, MA.-JBJS Case Connector, an online case report journal published by The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery, has issued a "Watch" regarding potential risks with anchor-based all-inside meniscal repairs. While all-inside techniques have many advantages, including shorter surgical time and reduced risk of damage to neurovascular tissues, potential drawbacks include risks of local soft-tissue irritation and implant migration or breakage.
In particular, the "Watch" offers important tips for successfully using FAST-FIX meniscal-repair devices produced by Smith & Nephew. ...
2015-07-24
Nailing the diagnosis of a psychiatric disorder may not be important in prescribing effective treatment, according to Mark Zimmerman, M.D., a clinical researcher at Rhode Island Hospital. His opinion editorial was published online today in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
"During the past 35 years, we have witnessed a revolution in the treatment of psychiatric disorders," said Zimmerman, director of outpatient psychiatry and the partial hospital program at Rhode Island Hospital and director of the Rhode Island Methods to Improve Diagnostic Assessment and Services ...
2015-07-24
A new Animal Conservation study shows that sports stadium lighting can alter patterns of bat species activity and feeding, which may in turn have cascading effects on other organisms and the ecosystem as a whole.
Using a novel field experiment, Dr. M. Corrie Schoeman demonstrates that urban exploiter bats are more likely to hunt insects attracted to bright light pollution sources such as stadiums than urban avoider bats. (Exploiter organisms can take advantage of food or resources supplied by humans, while avoider organisms have either a history of conflict with humans ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Toxin from salmonid fish has potential to treat cancer
Researchers from the University of Freiburg decode molecular mechanism of fish pathogen