Muscle fibers grown in the lab offer new model for studying muscular dystrophy
New technique for deriving muscle cells offers model for studying muscle diseases and potential treatments
2015-08-03
(Press-News.org) Skeletal muscle is one of the most abundant tissue types in the human body, but has proven difficult to produce in large quantities in the lab. Unlike other cell types, such as heart cells, neurons and cells found in the gut, previous attempts to efficiently and accurately derive muscle cells from pre-cursor cells or culture have not been fruitful. In a new study published this week in Nature Biotechnology, investigators from Brigham and Women's Hospital (BWH) report that by identifying and mimicking important developmental cues, they have been able to drive cells to grow into muscle fibers, producing millimeter-long muscle fibers capable of contracting in a dish and multiplying in large numbers. This new method of producing muscle cells could offer a better model for studying muscle diseases, such as muscular dystrophy, and for testing out potential treatment options.
Previous studies have used genetic modification to create small numbers of muscle cells in the lab, but the research team, led by investigators from BWH and the Harvard Stem Cell Institute, wanted a technique that would allow them to grow large numbers of muscle cells efficiently for use in clinical applications.
"We took the hard route: we wanted to recapitulate all of the early stages of muscle cell development that happen in the body and recreate that in a dish in the lab," said corresponding author Olivier Pourquie, PhD, of BWH's Department of Pathology and the Department of Genetics at Harvard Medical School. "We analyzed each stage of early development, and generated cell lines that glowed green when they reached each stage. Going step by step, we managed to mimic each stage of development and coax cells toward muscle cell fate."
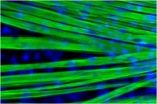
The team found that a combination of secreted factors that are important at early embryonic stages are also essential for stimulating differentiation - or the specialization of stem cells into particular cell types - in the lab. Using just the right recipe for differentiation, the team was able to produce long, mature fibers in a dish, derived from mouse or human pluripotent stem cells. They also cultured stem cells from the mouse model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy, observing the striking branched pattern that dystrophin-deficient muscle fibers show in the body.
The research team was also able to produce more immature cells known as satellite cells which, when grafted into a mouse model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy, produced muscle fibers. Further studies will be needed to determine if the new strategy could be optimized to develop cell therapies for treating degenerative diseases in humans.
In addition to developing a better model for Duchenne muscular dystrophy, the new protocol may also be useful for studying other muscle diseases such as sarcopenia (degenerative muscle loss), cachexia (wasting away of muscle associated with severe illness) and other muscular dystrophies.
"This has been the missing piece: the ability to produce muscle cells in the lab could give us the ability to test out new treatments and tackle a spectrum of muscle diseases," said Pourquie.
INFORMATION:
This work was supported by the European Research Council, the Stowers Institute for Medical Research, the Howard Hughes Medical Institute, the FP7 EU grant Plurimes (agreement no. 602423) and by a strategic grant from the French Muscular Dystrophy Association (AFM).
Brigham and Women's Hospital (BWH) is a 793-bed nonprofit teaching affiliate of Harvard Medical School and a founding member of Partners HealthCare. BWH has more than 4.2 million annual patient visits, nearly 46,000 inpatient stays and employs nearly 16,000 people. The Brigham's medical preeminence dates back to 1832, and today that rich history in clinical care is coupled with its national leadership in patient care, quality improvement and patient safety initiatives, and its dedication to research, innovation, community engagement and educating and training the next generation of health care professionals. Through investigation and discovery conducted at its Brigham Research Institute (BRI), BWH is an international leader in basic, clinical and translational research on human diseases, more than 1,000 physician-investigators and renowned biomedical scientists and faculty supported by nearly $600 million in funding. For the last 25 years, BWH ranked second in research funding from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) among independent hospitals. BWH continually pushes the boundaries of medicine, including building on its legacy in transplantation by performing a partial face transplant in 2009 and the nation's first full face transplant in 2011. BWH is also home to major landmark epidemiologic population studies, including the Nurses' and Physicians' Health Studies and the Women's Health Initiative as well as the TIMI Study Group, one of the premier cardiovascular clinical trials groups. For more information, resources and to follow us on social media, please visit BWH's online newsroom.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-08-03
LA JOLLA--T cells are the guardians of our bodies: they constantly search for harmful invaders and diseased cells, ready to swarm and kill off any threats. A better understanding of these watchful sentries could allow scientists to boost the immune response against evasive dangers (e.g., cancer or infections), or to silence it when it mistakenly attacks the body itself (e.g., autoimmune disorders or allergies).
Now, scientists at the Salk Institute have discovered that T cell triggering relies on a dynamic protein network at the cell surface, as reported in August 3, ...
2015-08-03
New brain research has mapped a key trouble spot likely to contribute to intellectual disability in Down syndrome. In a paper published in Nature Neuroscience [3 Aug], scientists from the University of Bristol and UCL suggest the findings could be used to inform future therapies which normalise the function of disrupted brain networks in the condition.
Down syndrome is the most common genetic cause of intellectual disability, and is triggered by an extra copy of chromosome 21. These findings shed new light on precisely which part of the brain's vast neural network contribute ...
2015-08-03
Greenhouse-gas emissions from human activities do not only cause rapid warming of the seas, but also ocean acidification at an unprecedented rate. Artificial carbon dioxide removal (CDR) from the atmosphere has been proposed to reduce both risks to marine life. A new study based on computer calculations now shows that this strategy would not work if applied too late. CDR cannot compensate for soaring business-as-usual emissions throughout the century and beyond, even if the atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) concentration would be restored to pre-industrial levels at some ...
2015-08-03
NEW YORK, NY (August 3, 2015) - Scientists at The New York Stem Cell Foundation (NYSCF) Research Institute successfully designed a revolutionary, high-throughput, robotic platform that automates and standardizes the process of transforming patient samples into stem cells. This unique platform, the NYSCF Global Stem Cell ArrayTM, for the first time gives researchers the scale to look at diverse populations to better understand the underlying causes of disease and create new individually tailored treatments, enabling precision medicine in patient care.
A paper published ...
2015-08-03
When it comes to making decisions involving others, the impression we have of their character weighs more heavily than do our assessments of how they can benefit us, a team of New York University researchers has found.
"When we learn and make decisions about people, we don't simply look at the positive or negative outcomes they bring to us--such as whether they gave us a loan or helped us move," explains Leor Hackel, a doctoral candidate in NYU's Department of Psychology and the study's lead author. "Instead, we often look beyond concrete outcomes to form trait impressions, ...
2015-08-03
Our brains are constantly barraged with sensory information, but have an amazing ability to filter out just what they need to understand what's going on around us. For instance, if you stand perfectly still in a room, and that room rotates around you, it's terrifying. But stand still in a room and turn your eyes, and the same visual input feels perfectly normal. That's thanks to a complex process in our brain that tell us when and how to pay attention to sensory input. Specifically, we ignore visual input caused by our own eye movements.
Now, researchers at The Rockefeller ...
2015-08-03
Skygazers at northern latitudes are familiar with the W-shaped star pattern of Cassiopeia the Queen. This circumpolar constellation is visible year-round near the North Star. Tucked next to one leg of the W lies a modest 5th-magnitude star named HD 219134 that has been hiding a secret.
Astronomers have now teased out that secret: a planet in a 3-day orbit that transits, or crosses in front of its star. At a distance of just 21 light-years, it is by far the closest transiting planet to Earth, which makes it ideal for follow-up studies. Moreover, it is the nearest rocky ...
2015-08-03
WASHINGTON, D.C. - Shifts in trade winds and ocean currents powered a resurgence of endangered Galápagos penguins over the past 30 years, according to a new study. These changes enlarged a cold pool of water the penguins rely on for food and breeding - an expansion that could continue as the climate changes over the coming decades, the study's authors said.
The Galápagos Islands, a chain of islands 1,000 kilometers (600 miles) west of mainland Ecuador, are home to the only penguins in the Northern Hemisphere. The 48-centimeter (19-inch) tall black and white ...
2015-08-03
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] -- Even after centuries of earnest oaths and laws, the debate about whether money compromises medicine remains unresolved, observes Dr. Eli Adashi in a new paper in the AMA Journal of Ethics. The problem might not be truly intractable, he said, but recent reforms will likely make little progress or difference.
"This is one of those things we have to appreciate as being with us for a long time," said Adashi, former dean of medicine and biological sciences at Brown University. "It will probably be with us forever. It's probably not entirely ...
2015-08-03
Soldiers who served in the glaring desert sunlight of Iraq and Afghanistan returned home with an increased risk of skin cancer, due not only to the desert climate, but also a lack of sun protection, Vanderbilt dermatologist Jennifer Powers, M.D., reports in a study published recently in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology.
"The past decade of United States combat missions, including operations in Iraq and Afghanistan, have occurred at a more equatorial latitude than the mean center of the United States population, increasing the potential for ultraviolet irradiance ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Muscle fibers grown in the lab offer new model for studying muscular dystrophy
New technique for deriving muscle cells offers model for studying muscle diseases and potential treatments



