Pitt team gets the beat, develops method of quantifying ciliary movement
2015-08-05
(Press-News.org) PITTSBURGH, Aug. 5, 2015 - Researchers at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine have figured out how to objectively quantify the beating action of cilia, the tiny, hair-like projections on cells that line nasal passages, the lungs and almost every other body tissue, according to a study published online today in Science Translational Medicine. Such digital signatures could help doctors more quickly and accurately diagnose ciliary motion (CM) defects, which can cause severe respiratory airway clearance defects and also developmental defects including congenital heart disease.
Currently, doctors try to identify CM defects using video-microscopy or indirectly via the examination of cilia ultrastructural defects using electron microscopy. This usually entails analysis of cilia movement in respiratory cells obtained from nasal passages, explained senior investigator Chakra Chennubhotla, Ph.D., assistant professor of computational and systems biology, Pitt School of Medicine.
"Visual reviews like these can be subjective, time-consuming and error-prone," he said. "In this project, our team used computational methods to objectively and reliably identify CM defects."
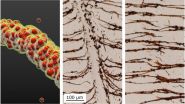
The researchers used two independent data sets - one from Children's Hospital of Pittsburgh of UPMC (CHP) and the other from Children's National Medical Center (CNMC) in Washington, D.C. - from healthy individuals as well as patients already diagnosed with either congenital heart disease or primary ciliary dyskinesia (PCD) to identify the digital signatures of normal and abnormal movement, accounting for factors such as how frequently the cilia beat back and forth, the breadth and rotation of their beat pattern, and their synchronicity.
The researchers then validated their technique by testing the patient samples in blind fashion, finding that the computational tool correctly identified more than 90 percent of PCD cases at CHP and all of the cases at CNMC. PCD is a rare condition in which the cilia are immotile or beat abnormally, leading to limitation of airway mucus clearance, compromised respiratory function and increased risk for lung infections and other bronchial problems.
"We hope to start a clinical trial in which doctors from around the country can upload a video of their patient's nasal lining to a website for assessment of ciliary motion with this technique," said co-investigator Cecilia Lo, Ph.D., Dr. F. Sargent Cheever Professor and chair of Developmental Biology, Pitt School of Medicine. "If successful, this approach may in the future serve as a rapid first-tier screen to identify at-risk patients."
INFORMATION:
Team members included Maliha Zahid, M.D., Ph.D., John Durkin, M.D., and Richard Francis, Ph.D., all of the University of Pittsburgh; and Shannon Quinn, Ph.D., now a faculty member at the University of Georgia.
The project was funded by National Institutes of Health grants HL-098180 and GM104412-01A1, and the Pennsylvania Department of Health.
About the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine
As one of the nation's leading academic centers for biomedical research, the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine integrates advanced technology with basic science across a broad range of disciplines in a continuous quest to harness the power of new knowledge and improve the human condition. Driven mainly by the School of Medicine and its affiliates, Pitt has ranked among the top 10 recipients of funding from the National Institutes of Health since 1998. In rankings recently released by the National Science Foundation, Pitt ranked fifth among all American universities in total federal science and engineering research and development support.
Likewise, the School of Medicine is equally committed to advancing the quality and strength of its medical and graduate education programs, for which it is recognized as an innovative leader, and to training highly skilled, compassionate clinicians and creative scientists well-equipped to engage in world-class research. The School of Medicine is the academic partner of UPMC, which has collaborated with the University to raise the standard of medical excellence in Pittsburgh and to position health care as a driving force behind the region's economy. For more information about the School of Medicine, see http://www.medschool.pitt.edu.
http://www.upmc.com/media
Contact: Anita Srikameswaran
Phone: 412-578-9193
E-mail: SrikamAV@upcm.edu
Contact: Amy Charley
Phone: 412-586-9778
E-mail: CharleyA@upcm.edu
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-08-05
ROSEMONT, Ill.-- Most patients younger than age 50 with a torn or severely damaged meniscus experienced reduced pain and improved knee function following transplant surgery, according to a study in the August 5 issue of the Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery (JBJS). However, many patients required additional surgery within 10 years.
The meniscus is a wedge-shaped piece of fibrocartilage in the knee that acts as a shock absorber between the thighbone and shinbone. A meniscus can be torn during sports or wear away over time as the body ages. For younger patients with knee ...
2015-08-05
Using photosynthetically active microorganisms, researchers at the Ruhr-Universität Bochum (RUB) have succeeded in manufacturing several biocatalysts suitable for industrial application: a crucial step towards sustainable chemical processes, according to Dr Marc Nowaczyk from the Chair for Plant Biochemistry and Jun.-Prof Dr Robert Kourist, Junior Research Group Microbial Biochemistry.
Sustainable manufacture of enzymes for the industry
Seeing as our planet's fossil resources are limited, researchers are looking for new methods for the production of certain substances, ...
2015-08-05
If you want to form very flexible chains of nanoparticles in liquid in order to build tiny robots with flexible joints or make magnetically self-healing gels, you need to revert to childhood and think about sandcastles.
In a paper published this week in Nature Materials, researchers from North Carolina State University and the University of North Carolina-Chapel Hill show that magnetic nanoparticles encased in oily liquid shells can bind together in water, much like sand particles mixed with the right amount of water can form sandcastles.
"Because oil and water don't ...
2015-08-05
Disney Research has developed a new method of rendering high-quality graphics for animated features that efficiently corrects for erroneous pixels while preserving the crisp detail in images, significantly increasing the efficiency of producing animated images.
The new approach enhances the performance of Monte Carlo ray tracing, a method for rendering 3-D scenes by randomly tracing the possible light paths for each pixel in an image. The images produced by ray tracing can be highly realistic, but can require large amounts of computer time to render.
The Disney researchers ...
2015-08-05
The elaborate costumes worn by Rapunzel, the heroine of Disney's "Tangled," are testament to the growing sophistication of cloth animation, but for art directors, who must tweak tens or hundreds of technical parameters, achieving a desired look for simulated clothing can be laborious.
To ease this process, Disney Research and Walt Disney Animation Studios have developed a tool that enables technical directors who must create garments that are soft, silky, wrinkly, heavy, or flowing, to use those same terms to control the computer programs that fashion simulated cloth.
The ...
2015-08-05
Little details, such as the wrinkling or twitching of an eyelid, can have a big impact on whether a digitally rendered face looks real in a film or videogame. Now scientists at Disney Research have devised the first method to capture these subtleties of the eyelids in detail.
Their method, to be presented at ACM SIGGRAPH 2015, the International Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, in Los Angeles Aug. 9-13, captures detailed, dynamic skin features and creates plausible folding and stretching in areas that aren't directly captured during data collection.
Artists ...
2015-08-05
Obtaining the aerodynamic properties necessary to simulate falling leaves or a tumbling box caught by the wind can be as simple as dropping the object off of a balcony and recording the fall, thanks to OmniAD, a data-driven technique developed at Disney Research.
You would not want to design an airplane with this method, but the results are good enough for simulating aerodynamic effects of light, 3-D objects in videogames and animations, said Nobuyuki Umetani of Disney Research and Tobias Martin of ETH Zurich. The system can even be used to design kites that actually ...
2015-08-05
The same sort of video processing effects that usually require video to be shot in controlled environments where 3-D positions of cameras and objects are precisely known can be achieved with real-world, handheld video shot from consumer-grade cameras using a new approach pioneered by Disney Research.
The technique, developed with Braunschweig University of Technology, compensates for the lack of exact 3-D information about a scene by taking advantage of the fact that most elements of a scene are visible many times in a video. The researchers found they could sample pixels ...
2015-08-05
A 3D-printed teddy bear can have a stiff head, a pliable tummy and bendable arms, even though all of it is made of the same relatively stiff material, using a new method developed by Disney Research.
By using the printer to alter the small-scale structure of the material, the Disney researchers showed they could vary its elasticity dramatically within the same object. They developed families of compatible microstructures with varying elastic properties, enabling designers to select the properties desired for each region of an object.
The team demonstrated their new ...
2015-08-05
Computer graphics researchers have developed a way to efficiently render images of sand castles, gravel roads, snowmen, salt in a shaker or even ocean spray - any object consisting of randomly oriented, but discernible grains - that look realistic whether viewed from afar or up close.
The new method, developed by Disney Research in collaboration with researchers from Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, ETH Zurich, Cornell University and Dartmouth College, employs three different types of rendering techniques depending on the scale at which the object is viewed.
A sand ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Pitt team gets the beat, develops method of quantifying ciliary movement