Sandcastles inspire new nanoparticle binding technique
2015-08-05
(Press-News.org) If you want to form very flexible chains of nanoparticles in liquid in order to build tiny robots with flexible joints or make magnetically self-healing gels, you need to revert to childhood and think about sandcastles.
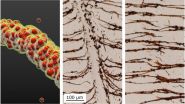
In a paper published this week in Nature Materials, researchers from North Carolina State University and the University of North Carolina-Chapel Hill show that magnetic nanoparticles encased in oily liquid shells can bind together in water, much like sand particles mixed with the right amount of water can form sandcastles.
"Because oil and water don't mix, the oil wets the particles and creates capillary bridges between them so that the particles stick together on contact," said Orlin Velev, INVISTA Professor of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at NC State and the corresponding author of the paper.
"We then add a magnetic field to arrange the nanoparticle chains and provide directionality," said Bhuvnesh Bharti, research assistant professor of chemical and biomolecular engineering at NC State and first author of the paper.
Chilling the oil is like drying the sandcastle. Reducing the temperature from 45 degrees Celsius to 15 degrees Celsius freezes the oil and makes the bridges fragile, leading to breaking and fragmentation of the nanoparticle chains. Yet the broken nanoparticles chains will re-form if the temperature is raised, the oil liquefies and an external magnetic field is applied to the particles.
"In other words, this material is temperature responsive, and these soft and flexible structures can be pulled apart and rearranged," Velev said. "And there are no other chemicals necessary."
"This research was the result of collaboration initiated by the NSF Materials Research Science and Engineering Center that facilitates interactions between Triangle universities." said Michael Rubinstein, John P. Barker Distinguished Professor of Chemistry at UNC and one of the co-authors of the paper.
INFORMATION:
The paper is also co-authored by Anne-Laure Fameau, a visiting researcher from INRA, France. The research is funded by the National Science Foundation through the Triangle MRSEC on Programmable Soft Matter and the U.S. Army Research Office.
Note to editors: An abstract of the paper follows.
"Nanocapillary-mediated magnetic assembly of nanoparticles into ultraflexible filaments and reconfigurable networks"
Authors: Bhuvensh Bharti and Orlin D. Velev, North Carolina State University; Anne-Laure Fameau, National Institute of French Agricultural Research; Michael Rubenstein, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill
Published: Aug. 3, 2015, online in Nature Materials
DOI: 10.1038/nmat4364
Abstract: The fabrication of multifunctional materials with tunable structure and properties requires programmed binding of their building blocks. For example, particles organized in long-ranged structures by external fields can be bound permanently into stiff chains through electrostatic or van der Waals attraction, or into flexible chains through soft molecular linkers such as surface-grafted DNA or polymers. Here, we show that capillarity-mediated binding between magnetic nanoparticles coated with a liquid lipid shell can be used for the assembly of ultraflexible microfilaments and network structures. These filaments can be magnetically regenerated on mechanical damage, owing to the fluidity of the capillary bridges between nanoparticles and their reversible binding on contact. Nanocapillary forces offer opportunities for assembling dynamically reconfigurable multifunctional materials that could find applications as micromanipulators, microbots with ultrasoft joints, or magnetically self-repairing gels.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-08-05
Disney Research has developed a new method of rendering high-quality graphics for animated features that efficiently corrects for erroneous pixels while preserving the crisp detail in images, significantly increasing the efficiency of producing animated images.
The new approach enhances the performance of Monte Carlo ray tracing, a method for rendering 3-D scenes by randomly tracing the possible light paths for each pixel in an image. The images produced by ray tracing can be highly realistic, but can require large amounts of computer time to render.
The Disney researchers ...
2015-08-05
The elaborate costumes worn by Rapunzel, the heroine of Disney's "Tangled," are testament to the growing sophistication of cloth animation, but for art directors, who must tweak tens or hundreds of technical parameters, achieving a desired look for simulated clothing can be laborious.
To ease this process, Disney Research and Walt Disney Animation Studios have developed a tool that enables technical directors who must create garments that are soft, silky, wrinkly, heavy, or flowing, to use those same terms to control the computer programs that fashion simulated cloth.
The ...
2015-08-05
Little details, such as the wrinkling or twitching of an eyelid, can have a big impact on whether a digitally rendered face looks real in a film or videogame. Now scientists at Disney Research have devised the first method to capture these subtleties of the eyelids in detail.
Their method, to be presented at ACM SIGGRAPH 2015, the International Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, in Los Angeles Aug. 9-13, captures detailed, dynamic skin features and creates plausible folding and stretching in areas that aren't directly captured during data collection.
Artists ...
2015-08-05
Obtaining the aerodynamic properties necessary to simulate falling leaves or a tumbling box caught by the wind can be as simple as dropping the object off of a balcony and recording the fall, thanks to OmniAD, a data-driven technique developed at Disney Research.
You would not want to design an airplane with this method, but the results are good enough for simulating aerodynamic effects of light, 3-D objects in videogames and animations, said Nobuyuki Umetani of Disney Research and Tobias Martin of ETH Zurich. The system can even be used to design kites that actually ...
2015-08-05
The same sort of video processing effects that usually require video to be shot in controlled environments where 3-D positions of cameras and objects are precisely known can be achieved with real-world, handheld video shot from consumer-grade cameras using a new approach pioneered by Disney Research.
The technique, developed with Braunschweig University of Technology, compensates for the lack of exact 3-D information about a scene by taking advantage of the fact that most elements of a scene are visible many times in a video. The researchers found they could sample pixels ...
2015-08-05
A 3D-printed teddy bear can have a stiff head, a pliable tummy and bendable arms, even though all of it is made of the same relatively stiff material, using a new method developed by Disney Research.
By using the printer to alter the small-scale structure of the material, the Disney researchers showed they could vary its elasticity dramatically within the same object. They developed families of compatible microstructures with varying elastic properties, enabling designers to select the properties desired for each region of an object.
The team demonstrated their new ...
2015-08-05
Computer graphics researchers have developed a way to efficiently render images of sand castles, gravel roads, snowmen, salt in a shaker or even ocean spray - any object consisting of randomly oriented, but discernible grains - that look realistic whether viewed from afar or up close.
The new method, developed by Disney Research in collaboration with researchers from Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, ETH Zurich, Cornell University and Dartmouth College, employs three different types of rendering techniques depending on the scale at which the object is viewed.
A sand ...
2015-08-05
Chicago, August 5, 2015--A new national survey conducted by The Associated Press-NORC Center for Public Affairs Research reveals a disparity among blacks' and whites' perception of violence against civilians by police. Nearly three-quarters of black respondents consider violence against civilians by police officers to be an extremely or very serious problem, compared to less than 20 percent of whites. However, the poll also finds agreement across racial groups on many of the causes of police violence, as well as further consensus that changes in policies and procedures ...
2015-08-05
Disney Research has created LinkEdit, interactive software for predictably changing the shape or motion of planar linkages used in such objects as kinetic sculptures, folding furniture and mechanical toys.
The LinkEdit software enables users to make desired changes in a linkage, such as altering its size or shape, while preserving other features, such as the walking gait of a linkage for a mechanical leg. The researchers demonstrated this capability by making alterations to the Jansen linkage, the building block to the famous walking sculptures created by artist Theo ...
2015-08-05
Forehead wrinkles that rapidly deepen and crow's feet that appear suddenly around the eyes might distress the average person, but the ability to quickly and realistically incorporate such details in a facial reconstruction is the key feature of a new performance capture method developed at Disney Research.
The method, which requires only a single video camera such as a webcam, is the first to both operate in real-time and to capture facial features in high resolution, including such details as wrinkles.
"This could open up a variety of new applications, from casual ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Sandcastles inspire new nanoparticle binding technique
