(Press-News.org) Computer graphics researchers have developed a way to efficiently render images of sand castles, gravel roads, snowmen, salt in a shaker or even ocean spray - any object consisting of randomly oriented, but discernible grains - that look realistic whether viewed from afar or up close.
The new method, developed by Disney Research in collaboration with researchers from Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, ETH Zurich, Cornell University and Dartmouth College, employs three different types of rendering techniques depending on the scale at which the object is viewed.
A sand castle scene created by the researchers, which contains about two billion grains, appears uniformly light brown and continuous when seen from a distance. But when the view zooms in, individual grains of three different colors are apparent.
Details of the method will be presented at ACM SIGGRAPH 2015, the International Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, in Los Angeles Aug. 9-13.
"Granular materials are common in our everyday environment, but rendering these materials accurately and efficiently at arbitrary scales remains an open problem in computer graphics," said Marios Papas, a Ph.D. student in computer graphics at Disney Research and ETH Zurich. The rendering framework he and his colleagues used to tackle this problem adapts to the structure of scattered light at different scales.
At the smallest scale, they consider the geometry, size and material properties of the individual grains and the density at which they are packed together. They capture the appearance of these individual grains with a rendering technique called path tracing. This traces many light paths from each pixel back to their sources, building a highly detailed and realistic model of the aggregate material. Using just a few paths per pixel typically results in very noisy images that are quick to compute, but high-quality images require simulating thousands of such light paths per pixel.
The intense computation required for this technique isn't feasible for the entire object, which might contain millions or billions of grains. So, as the scale increases and as it becomes harder to track which rays bounced off which grains, they use a different rendering technique, volumetric path tracing, which approximates the material as a continuous medium and requires less computation. While typically used to render more tenuous atmospheric effects like clouds or smoke, the researchers showed how this technique can also be used to accurately simulate the way light scatters within such granular materials at larger scales.
At even greater scales, particularly for materials that are highly reflective such as snow or spray, they use a third technique leveraging the diffusion approximation.
"It would be possible to use any one of these techniques to render the image, but path tracing the individual grains would require prohibitive amounts of computation time and the other techniques would fail to capture the appearance of individual grains at small scales," said the project lead Wojciech Jarosz, formerly a senior research scientist at Disney Research and now an assistant professor of computer science at Dartmouth College.
"One of our core contributions is showing how to systematically combine these disparate methods and representations to ensure visual consistency between grains visible at vastly different scales, both across the image or across time in an animation," Jarosz said.
Depending on the type of material, the hybrid approach can speed up computation by tens or hundreds of times in comparison to renderings done entirely with path tracing, according to the researchers' calculations.
INFORMATION:
In addition to Papas and Jarosz, the research team included Ralf Habel and Markus Gross of Disney Research, Johannes Meng and Carsten Dachsbacher of Karlsruhe and Steve Marschner of Cornell.
For more information, visit the project web site at http://www.disneyresearch.com/multi-scale-modeling-and-rendering-of-granular-materials/.
About Disney Research
Disney Research is a network of research laboratories supporting The Walt Disney Company. Its purpose is to pursue scientific and technological innovation to advance the company's broad media and entertainment efforts. Vice Presidents Jessica Hodgins and Markus Gross manage Disney Research facilities in Los Angeles, Pittsburgh, Zürich, and Boston and work closely with the Pixar and ILM research groups in the San Francisco Bay Area. Research topics include computer graphics, animation, video processing, computer vision, robotics, wireless & mobile computing, human-computer interaction, displays, behavioral economics, and machine learning.
Chicago, August 5, 2015--A new national survey conducted by The Associated Press-NORC Center for Public Affairs Research reveals a disparity among blacks' and whites' perception of violence against civilians by police. Nearly three-quarters of black respondents consider violence against civilians by police officers to be an extremely or very serious problem, compared to less than 20 percent of whites. However, the poll also finds agreement across racial groups on many of the causes of police violence, as well as further consensus that changes in policies and procedures ...
Disney Research has created LinkEdit, interactive software for predictably changing the shape or motion of planar linkages used in such objects as kinetic sculptures, folding furniture and mechanical toys.
The LinkEdit software enables users to make desired changes in a linkage, such as altering its size or shape, while preserving other features, such as the walking gait of a linkage for a mechanical leg. The researchers demonstrated this capability by making alterations to the Jansen linkage, the building block to the famous walking sculptures created by artist Theo ...
Forehead wrinkles that rapidly deepen and crow's feet that appear suddenly around the eyes might distress the average person, but the ability to quickly and realistically incorporate such details in a facial reconstruction is the key feature of a new performance capture method developed at Disney Research.
The method, which requires only a single video camera such as a webcam, is the first to both operate in real-time and to capture facial features in high resolution, including such details as wrinkles.
"This could open up a variety of new applications, from casual ...
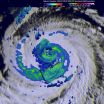
Heavy rain, towering thunderstorms, and a large area are things that NASA satellites observed as Typhoon Soudelor moves toward Taiwan on August 5, 2015.
NASA's Terra satellite passed over Soudelor on August 5, 2015 at 01:45 UTC and the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument captured a visible image of the large storm in the Philippine Sea. The eye appeared to be cloud-filled as bands of thunderstorms spiraled into the center of the storm.
The Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) mission core observatory, a satellite managed by both NASA and ...
A team of astronomers led by Caltech has discovered a giant swirling disk of gas 10 billion light-years away--a galaxy-in-the-making that is actively being fed cool primordial gas tracing back to the Big Bang. Using the Caltech-designed and -built Cosmic Web Imager (CWI) at Palomar Observatory, the researchers were able to image the protogalaxy and found that it is connected to a filament of the intergalactic medium, the cosmic web made of diffuse gas that crisscrosses between galaxies and extends throughout the universe.
The finding provides the strongest observational ...
Washington, DC, August 5, 2015 -- Potentially harmful bacteria can survive on endoscopes used to examine the interior of the digestive tract, despite a multi-step cleaning and disinfecting process, according to a study published in the August issue of the American Journal of Infection Control, the official publication of the Association for Professionals in Infection Control and Epidemiology (APIC).
Though endoscopes were cleaned in accordance with multi-society guidelines, viable microbes and residual contamination remained on surfaces after each stage of cleaning, ...
Dan's Wild Wild Science Journal
New paper shows global climate model errors are significantly less than thought
Scientists have matched the output of climate models to the way the Earth's temperature record is constructed in a new study in Geophysical Research Letters. Dan Satterfield explores how climate models are doing an even better job at predicting the Earth's temperature than was thought.
Eos.org
On the rebound: Modeling Earth's ever-changing shape
A new modeling tool easily computes the elastic response of changes in loading on Earth's surface to high resolution. ...
While undergoing laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy induced weight loss and improvements in obesity-related disorders, long-term followup shows significant weight regain and a decrease in remission rates of diabetes and, to a lesser extent, other obesity-related disorders over time, according to a study published online by JAMA Surgery.
Obesity was recognized as a global epidemic by the World Health Organization 15 years ago and rates of obesity have since been increasing. Obesity is currently considered a severe health hazard and a risk factor for diabetes mellitus, hypertension, ...
In a small study, women who had Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery reached certain blood alcohol concentrations in half the number of drinks compared to women who didn't have the surgery, and reported a greater feeling of drunkenness, according to a study published online by JAMA Surgery.
Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) is the most common bariatric surgical procedure performed in the world. Although RYGB surgery causes a marked reduction in food intake and induces remission of food addiction, it is associated with an increased risk of developing alcohol use disorders. It ...
Telephone-based cognitive behavioral therapy was better at reducing worry, generalized anxiety disorder symptoms and depressive symptoms in older adults who live in rural areas, where access to mental health treatment may be limited, according to an article published online by JAMA Psychiatry.
Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) is one of the most common anxiety disorders in older adults and is associated with poor quality of life, increased health care utilization and impaired memory. Medications and psychotherapy are the primary treatments. Many older adults prefer psychotherapy ...