(Press-News.org) Researchers from North Carolina State University, Institut Langevin and Paris-Descartes University have conducted a proof-of-concept study that raises the possibility of using ultrasound techniques to detect cervical stiffness changes that indicate an increased risk of preterm labor in pregnant women. While additional work needs to be done, it may ultimately give doctors a new tool for determining when to provide treatment that can prevent preterm birth.
Premature births can mean low birthweights and other medical problems for newborns, but there are steps that doctors can take to reduce the chances of premature birth if early warning signs are detected. One of those early symptoms is a softening of the cervix. Traditionally, this stiffness is assessed by manually palpating the cervix.
"But that's a subjective measure, and we wanted to determine if ultrasound could be used to quantitatively assess how stiff the cervix is - and, by extension, whether a woman is at risk of going into labor prematurely," says Marie Muller, an assistant professor of mechanical engineering at NC State and lead author of a paper describing the work.
Muller and her colleagues decided to try a technique called shear wave elastography (SWE), which was developed to assess tissue stiffness for cancer diagnosis. They reasoned that if SWE worked for detecting changes in other body tissues, it may also work for detecting changes in the cervix.
Working with a maternity hospital in Paris, the researchers did SWE measurements of 157 pregnant women who were already scheduled for ultrasounds. The researchers then followed each patient's pregnancy.
The researchers found that patients between 24 and 35 weeks pregnant who had below average cervical stiffness were at higher risk of going into preterm labor.
In SWE, stiffness is measured based on how fast a mechanical shear wave propagates through the tissue. What the researchers found was that if the wave was more than one meter per second below the baseline for a woman's gestational age, or how far along she is in her pregnancy, the woman was more likely to have a preterm birth.
"This work is only a first step," Muller says. "We know the technique is reproducible. We know we can measure these changes in cervical stiffness. However, we need to do a longitudinal study that follows patients throughout pregnancy. That would give us a better understanding of how cervical stiffness changes over the course of pregnancy - and that would help us determine which changes are likely indicative of early onset labor."
Muller also notes that, while the SWE technique uses high-end ultrasound equipment, the equipment can be used for normal prenatal examinations as well as SWE assessments of cervical stiffness, which would hopefully mitigate any additional cost.
INFORMATION:
The paper, "Assessment of the Cervix in Pregnant Women Using Shear Wave Elastography: A Feasibility Study," is published in the journal Ultrasound in Medicine and Biology. The paper was co-authored by Dora Aït-Belkacem, Jean-Luc Gennisson, and Mickaël Tanter of Institut Langevin; Mahdieh Hessabi of Paris-Descartes University; Gilles Grangé, Edouard Lecarpentier, and Vassilis Tsatsaris of Paris-Descartes University and Premup Foundation; and François Goffinet of Paris-Descartes University, CIC Cochin-Necker and Premup Foundation. The work was supported by LABEX WIFI (France's Laboratory of Excellence program) under grant number ANR-10-LABX-24.
An international research team reports results of a three-year study of sediment samples collected offshore from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in a new paper published August 18, 2015, in the American Chemical Society's journal, Environmental Science and Technology.
The research aids in understanding what happens to Fukushima contaminants after they are buried on the seafloor off coastal Japan.
Led by Ken Buesseler, a senior scientist and marine chemist at the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI), the team found that a small fraction of contaminated ...
Only 1 in 10 heart failure patients is referred to a cardiac rehabilitation program after being hospitalized, despite strong evidence that such exercise programs improve quality of life and reduce the likelihood of future hospitalizations.
The findings, from a UCLA-led study, appear in the August 25 Journal of the American College of Cardiology. Researchers drew the data from a national database of more than 100,000 people with heart failure who were discharged from hospitals between 2005 and 2014 and were eligible for cardiac rehabilitation programs.
"Although we expected ...
A new class of fascinating technologies -- including optics in computing, telecommunications links and switches, and virtually any other optical component -- could be created simply by configuring a mesh of light-controlling devices known as interferometers. This is similar to the way electronic semiconductors can fashion the wide array of digital technologies we have at our disposal today.
Optical technologies have the potential to greatly reduce the power consumption of computers, speed telecommunications, and enhance the sensitivity of chemical and biological sensors. ...
A national survey of more than 750 emergency medical services providers conducted by researchers at Oregon Health & Science University identified airway management skills, personal anxiety and limited pediatric care proficiency among key factors that may contribute to pediatric safety events for children in out-of-hospital emergent care situations. The study, published online today in The Journal of Pediatrics, supports the American Academy of Pediatrics' recommendation for pediatric physician involvement in EMS training, medical oversight and policy development.
"Pediatric ...
Violent conflicts in Neolithic Europe were held more brutally than has been known so far. This emerges from a recent anthropological analysis of the roughly 7000-year-old mass grave of Schöneck-Kilianstädten by researcher of the Universities of Basel and Mainz. The findings, published in the journal PNAS, show that victims were murdered and deliberately mutilated.
It was during the time when Europeans first began to farm. To what degree conflicts and wars featured in the early Neolithic (5600 to 4900 B.C.), and especially in the so-called Linear Pottery culture ...
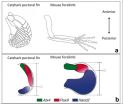
A study of catsharks reveals how alterations in the expression and function of certain genes in limb buds underlie the evolution of fish fins to limbs. The findings are reported by researchers from Tokyo Institute of Technology (Tokyo Tech), the Centre for Genomic Regulation (CRG, Barcelona) and their collaborators in the journal eLife and give new insight into how fish evolved to live on land in the form of early tetrapods.
The first four-legged, land-living creatures - known as early tetrapods - evolved from fish, following the transformation of fins into limbs. This ...
Patient satisfaction is a very poor proxy for quality of care comparisons in elective cranial neurosurgery. Because deaths are rare events in elective cranial neurosurgery, reporting of surgeon or even department-specific mortality figures cannot differentiate a high or low level of the quality of care.
The current focus on patient safety in health care has led to public quality-of-care comparisons between health care facilities and even between individual health care professionals. In the United States, a new reimbursement method based on patient satisfaction ratings ...
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - New research findings contradict a fundamental assumption about the functioning of "organic" solar cells made of low-cost plastics, suggesting a new strategy for creating inexpensive solar technology.
Commercialization of organic solar cells has been hindered by inefficiencies, but the findings point toward a potential path to create a new class of solar technology able to compete with standard silicon cells.
"These solar cells could provide a huge cost advantage over silicon," said Muhammad Ashraful Alam, Purdue University's Jai N. Gupta Professor ...
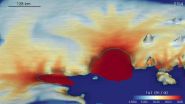
A new international study is the first to use a high-resolution, large-scale computer model to estimate how much ice the West Antarctic Ice Sheet could lose over the next couple of centuries, and how much that could add to sea-level rise. The results paint a clearer picture of West Antarctica's future than was previously possible. The study is published today (18 August) in The Cryosphere, an open access journal of the European Geosciences Union (EGU).
"The IPCC's [Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change] 4th and 5th Assessment Reports both note that the acceleration ...
A group of clinicians and geochemists are working to develop a test for the most common form of primary liver cancer, HCC (Hepatocellular Carcinoma). HCC kills over 600,000 people worldwide every year. It usually develops from chronic liver disease such as hepatitis or cirrhosis, but there is no good biochemical test to indicate when the cancer develops, meaning that even for patients most at risk, it is nearly impossible to know when a cancer may develop until symptoms appear. Now a multi-national group of scientists are developing a new test for HCC, based on methods ...